1. Introduction
Pro-inflammatory cytokines, the microbiota and the gut barrier function, and phagocytosis are some important mediators involved in the interplay of innate-adaptive immune responses [
1,
2,
3,
4] for the elimination and clearance of infectious agents, including viruses and the newly appeared SARS-CoV-2 [
5,
6,
7]. Chemokines, such as interferon (IFN)ɣ-inducible protein 10 (IP-10) are involved in acute exacerbations of asthma [
8] and an increase of inflammation and keratinocyte apoptosis in atopic dermatitis [
9]. The monocyte chemoattractant peptide-1 (MCP-1) participates in allergen sensitization [
10] and it has been shown that MCP-1 produced by keratinocytes plays a role in the process of mononuclear cell infiltration in occupational allergic contact dermatitis [
11]. On the other hand, dysregulation of the intestinal barrier has been associated with chronic immune diseases (e.g. food allergy, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease), but bacterial pathogens and components of innate and adaptive immunity have been identified in the underlying regulation pathways of the gut barrier function [
12].
In the current era of the pandemic and of growing antibiotic resistances, a focus of interest has been the use of nutritional supplements with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activity relevant to maintain a strong healthy immune system [
13,
14]. The search for new natural ingredients easily and widely available without the unwanted side effects of pharmaceutical drugs has raised significantly in recent years Ideal candidates will be agents which could not trigger microbial resistance, and which could be safely administered to all ages and types of populations both immunocompromised or poly-medicated.
In this line, recent research conducted with crude natural extracts such as plants, sea organisms and mushrooms has shown their effects as anti-inflammatory and antiviral agents through several mechanisms [
15,
16]. Edible mushrooms or yeasts have many nutritional and medicinal values to human health. As an example,
Hericium erinaceus extract showed promising antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antiviral activity [
17]. Yeasts such as
Saccharomyces cerevisiae and
Saccharomyces boulardii have proven
in vivo their protective effects against bacterial translocation, preservation of the gut barrier function and the regulation of immunity. In many cases though, the beneficial immune modulation effects were seen when the administration was given prior to the challenge [
18,
19]
A nutritional supplement composed of a synergistic combination of yeast-based ingredients (ABB C1
®) showed the capacity to stimulate trained immunity in a randomized controlled trial in volunteers vaccinated against influenza or COVID-19 after a short supplementation period which started at the same time of the vaccination [
20]. ABB C1
® is a unique combination of a β-1,3/1,6-glucan complex extracted from the cell wall of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae through a gentle process that preserves its structure
, and a consortium of postbiotic
Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermented in the presence of selenium and zinc. ABB C1
® represents a unique source of yeast β -glucan and highly bioavailable selenium and zinc.
Selenium is a potent antioxidant, enhances the function of cytotoxic effector cells, and is important for maintaining T cell maturation, functions, and T-cell dependent antibody production [
21]. Recent review articles of selenium deficiency and viral infection show that lower serum selenium levels are associated with worse prognosis of the infectious disease [
22]. Nutritional intervention securing an adequate supply of selenium has been recommended for rising antiviral resistance [
23]. In a similar way, zinc is a critical trace mineral for antiviral immunity. Results of five studies with 1506 participants included in a meta-analysis showed that zinc supplementation led to a significant lower risk of mortality in COVID-19 patients when it was compared with non-supplemented controls [
24]. On the other hand, β-glucan is a polysaccharide that is abundantly found in the cell wall of
S. cerevisiae and primes the immune system to respond better to any viral infection [
25]. Also, the use of oral β-glucan has been hypothesized to boost immune responses and abrogate symptoms in viral infection [
26,
27]. Therefore, it was considered of interest to assess the anti-inflammatory effect of ABB C1
® on intestinal cells, preservation of the gut barrier integrity, and activity in stimulating phagocytosis of peripheral cells. Confirmation of favourable effects of ABB C1
® in these experimental studies may explain some of the mechanisms of action by which ABB C1® exerts its clinical benefits and would further support its use as a dietary supplement for improving the immune response to infectious diseases, as well as to prevent allergic processes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigational product
The investigation product (ABB C1®, AB Biotek Human Nutrition & Health, Peterborough, UK) was composed of a synergistic combination of yeast-based ingredients: a β-1,3/1,6-glucan complex from S. cerevisiae (68.89%) and a consortium of heat-treated postbiotic S. cerevisiae rich in selenium and zinc (31.11%).
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of ABB C1® on Intestinal Cells/Epithelial Signalling Assay
The anti-inflammatory effect of ABB C1
® on intestinal cells was studied by chemokine production by Caco-2 cells in the presence and absence of a pro-inflammatory stimulus (adapted from [
28]). Caco-2 were cultured to confluence in 96-well plates in culture medium (modified Eagle’s medium MEM]), supplemented with 20% (v/v) foetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% non-essential amino acids (NEAA), 1% Glutamax™, 1% sodium pyruvate, with or without 1% penicillin-streptomycin and gentamicin (50 μg/mL) (all obtained from Invitrogen, Breda, The Netherlands). At the start of the experiment, cells were washed once with antibiotic-free culture medium. The monolayers were incubated with test components in triplicate for 1 hour at 37°C in antibiotic-free medium. Then, cells were further incubated for 24 hours in the presence of the test components and 50 μg/mL gentamicin with and without a mixture of recombinant tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (10 ng/mL) and recombinant interferon (IFN-ɣ) (5 ng/mL) as pro-inflammatory stimulus. Supernatants were collected 24 hours after stimulation and stored at -20°C. A Bio-Plex Multiplex Immunoassay System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was used to measure IFN-ɣ induced protein-10 (IP-10), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) levels according to the manufacturer’s instructions. IP-10 and MCP-1 levels were expressed as pg/mL. Both experiments were performed once in triplicate.
Metabolic activity of the cells for testing cytotoxicity of the test compounds was analysed by WST-1 assay (Roche), according to the manufacturers protocol, after collecting the culture supernatant of the epithelial signalling assay.
2.3. Gut Barrier Integrity Assay
Protection of epithelium disruption after a challenge: The effect of ABB C1
® on gut barrier function upon a challenge was studied by transepithelial electric resistance (TEER) over a gut cell layer [
29]. Caco-2 cells were cultured in MEM medium in the same conditions than in the previous experiment. Then, the cells were seeded (2 x 10
4 cells/cm
2) on Transwell polycarbonate cell culture inserts with a mean pore size of 0.4 µm and a diameter of 0.33 cm
2 until full differentiation (± 1000 ohms [Ω]) (Greiner Bio-one, Alphen aan de Rijn, The Netherlands). As indicative measure for barrier integrity, TEER was measured with an EVOM2 Epithelial Volt/Ohm Meter (World Precision Instruments). On the day of the experiment, the cells were washed and incubated for 1 hour at 37°C with antibiotic- and serum-free medium containing the test components. Subsequently, the wells were exposed to
Escherichia coli (ETEC H10407) infected at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 200 in the presence of the test components. TEER was measured before the start of the experiment (t = -1), 1 hour after exposure to the test components before addition of the pathogens (t = 0), and after 1 (t = 1), 2 (t = 2), 4 (t = 4), and 6 (t = 6) hours after exposure to the pathogen. The TEER values of the individual conditions after exposure to the pathogens were compared to their own TEER value at t = 0 and expressed as ∆TEER (Ω/cm
2). A negative control (ETEC H10407 only) was included.
Spontaneous build-up of the epithelium: on the day of the experiment, the cells were washed and incubated for 1 hour at 37°C with antibiotic- and serum-free medium containing the test components. TEER was measured before the start of the experiment (t = -1) every 2 days for 22 days. The TEER values of the individual conditions were compared to their own TEER value at t = 0 and expressed as ∆TEER (Ω/cm2). A negative control without the study product was included. Both experiments were performed once in triplicate.
2.4. Stimulation of Phagocytosis of Peripheral Blood Monocytes and Leukocytes and Peritoneal Macrophages in Mice
In this experiment of phagocytosis of peripheral blood monocytes and leukocytes and peritoneal macrophages in mice, 10 BALB/c nude mice of both sexes and 8-weeks-old were included in each study group. The products (control yeast β-1,3/1,6-glucan, control algae β-1,3-glucan, and ABB C1®) were given for 10 days by forced feeding. Eight samples of peripheral blood per mice were extracted (0.1 mL) from the mice fed with various doses of the products or PBS (negative control). Samples were incubated in vitro with 0.05 mL of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate particles (HEMA) (5 x 108 mL). The tubes were incubated at 37°C for 60 min with intermittent shaking. Smears were stained with Wright’s stain (Sigma-Aldrich, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). The cells with three of more HEMA particles were considered positive. At least 300 cells were examined in each experiment. Results were standardized to reflect the β-glucan dosage received by the mice: 100% for the positive controls β-1-3/1,6 glucan from yeast and β-1,6-glucan from algae, and 68.89% for ABB C1®.
Handling of mice and all experimental procedures were conducted under regular conditions in accordance with the European Convention for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals as approved by the Czech Animal Care and Use Committee. Last approval June 2021.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Quantitative data are expressed as mean and standard deviation (± SD). The Student’s t test (two-sided) or the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s procedure was used for the comparison of data according to conditions of application. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Anti-inflammatory effect on intestinal cells
ABB C1
® cytotoxicity was discarded by an WST-1 assay before starting the anti-inflammatory effect on intestinal cells (data not shown). The anti-inflammatory effect evaluated in the presence and absence of a pro-inflammatory challenge (tumour necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]/interferon gamma [IFN-ɣ]) showed statistically significant reductions of IP-10 and MCP-1 levels (
Table 1).
3.2. Gut Barrier Integrity Assay
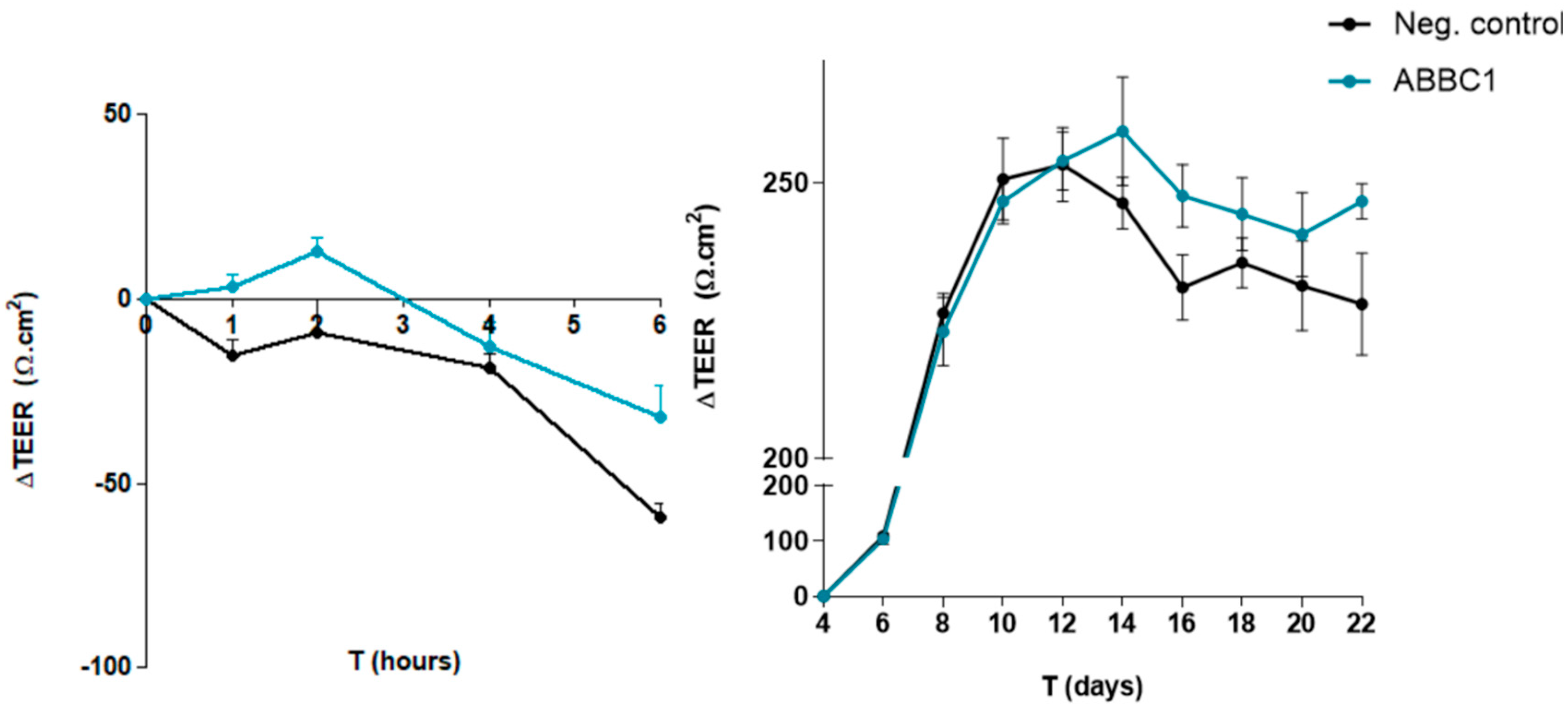
The capacity of ABB C1® to protect the gut epithelium disruption caused an infectious agent
Escherichia coli (ETEC H10407) was evaluated. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) values were significantly higher for ABB C1
® after 1 and 6 hours of testing, with
p < 0.05 and
p < 0.1 respectively (
Figure 1, left panel). The total area under the curve (AUC) showed a statistical trend towards a significant increase in the ABB C1
® condition (
p < 0.1). In addition, spontaneous build-up of the gut epithelium monolayer over 22 days was also greater in the ABB C1
® condition as compared with a negative control (
Figure 1, right panel). Numerical values are shown in
Table 2 and
Table 3.
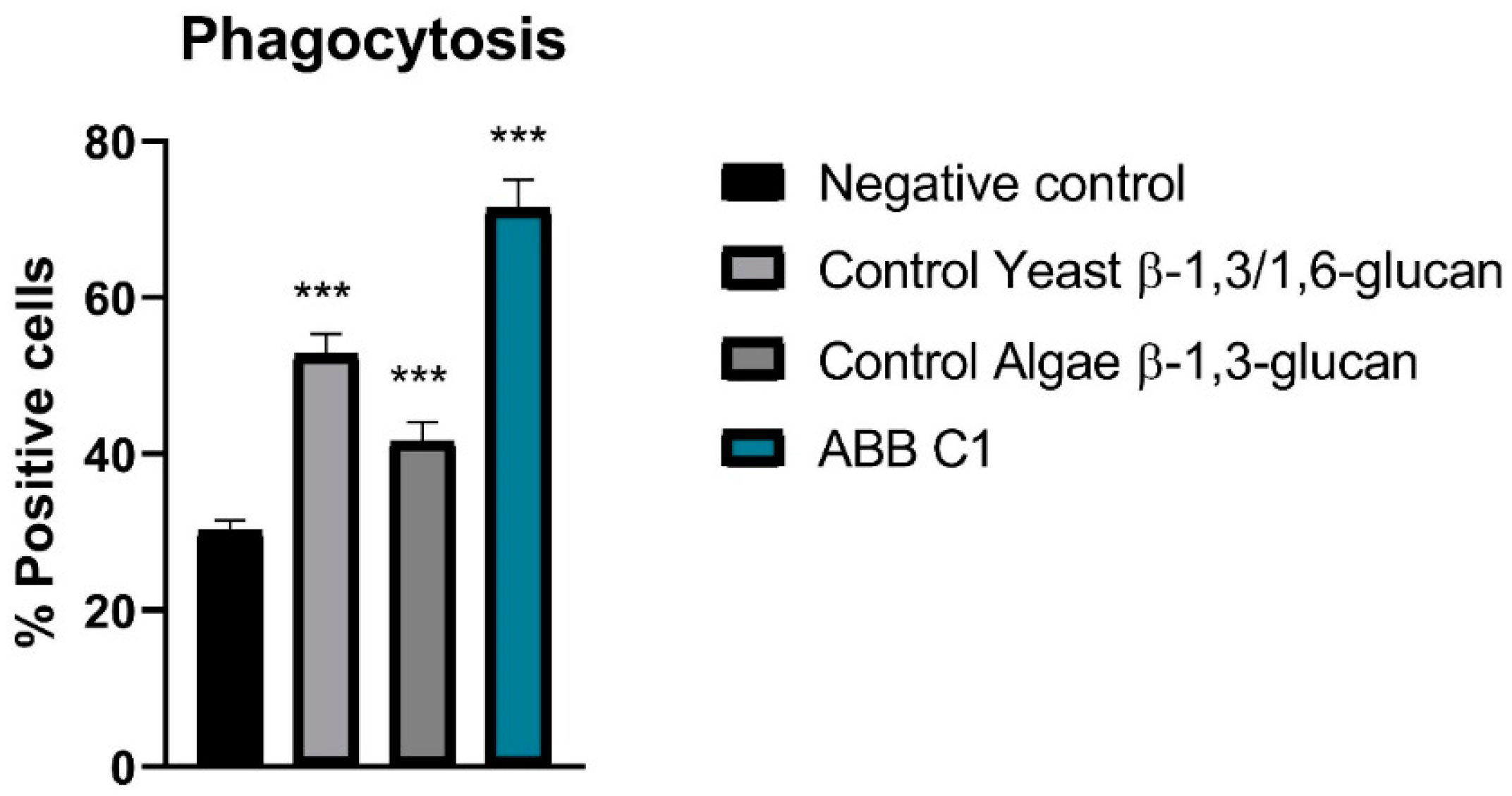
3.3. Stimulation of Phagocytosis of Peripheral Cells
In relation to stimulation of phagocytosis of peripheral blood monocytes and leukocytes and peritoneal macrophages cells in vivo, all samples showed activity, although the highest activity was observed in the ABB C1
® condition as compared with controls of algae β-1,3-glucan and yeast β-1,3/1,6 glucan (
Figure 2 and
Table 4).
4. Discussion
In the two in vitro studies and in the experimental study in mice, the product based on a synergistic combination of β-glucans and selenium- and zinc-enriched S. cerevisiae (ABB C1®) showed significantly more favourable effects as compared with the control conditions regarding an anti-inflammatory effect, a protection of the gut barrier disruption, and as a stimulation of phagocytosis in peripheral blood monocytes and leukocytes and peritoneal macrophages.
The anti-inflammatory effect was shown by significantly lower levels of IP-10 and MCP-1 as compared to controls in both testing conditions, with and without TNF-α/INF-ɣ challenge mimicking inflammatory conditions
Elevated IP-10 and MCP-1 levels in patients with infectious disease and their possible usefulness as biomarkers of disease severity and therapeutic response have been reported in different studies [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37].
IP-10, also known as C–X–C motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10) or small-inducible cytokine B10 is a cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. IP-10 binds CXCR3 receptor inducing chemotaxis, apoptosis, cell growth and angiostasis. Alterations in its expression levels have been associated with inflammatory diseases including infectious diseases, immune dysregulation, and tumour development [
36]. IP-10 is also recognized as a biomarker that predicts severity of various infectious diseases. A study assessing 51 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis explored their evolution after 2 months of anti-tuberculosis therapy, showing that serum levels of IP-10 after treatment were associated with poor prognosis and long-term mortality [
31].
MCP-1, also known as Chemokine (CC-motif) ligand 2 (CCL2), has a vital role in the process of inflammation, where it attracts or enhances the expression of other inflammatory factors/cells. By this mechanism of migration and infiltration of inflammatory cells and other cytokines at the site of inflammation, it is involved in the pathogenesis of numerous disease conditions either directly or indirectly [
33,
38]. Furthermore, high levels of MCP-1 have been reported to be useful to identify poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients on hospital admission [
30,
35,
37].
For these reasons, the ability of ABB C1® to counteract these pro-inflammatory cytokines could be clinically relevant in the recovery and prognosis of infection.
Gut microbiome dysbiosis and gut barrier dysfunction in viral infection represent a source of bacteraemia, which may contribute to worsening outcomes [
39]. Patients presenting poor outcomes are also those in which the immune system’s hyperresponsiveness and a severe inflammatory condition (cytokine storm) are particularly evident and have been associated with impaired microbiota phenotype [
40]. Alteration of gut microbiota increases the risk for microbial translocation and reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune response in infection [
41]. Results of our
in vitro study of the protective effect of ABB C1
® against disruption of the gut barrier and enhancement of spontaneous build-up of the gut epithelium monolayer support a plausible beneficial effect of dietary supplementation with ABB C1
® in infectious diseases. Furthermore, several studies reviewed by Wesemann and Nagler explain the potential role of microbiome and barrier function in allergy, including but not limited to food allergy [
42]. Based on the combined anti-inflammatory effect and preservation of gut barrier function, nutritional supplementation with ABB C1
® may play a role contributing to improve symptoms and reduce severity of infections and allergy.
In the experimental study of stimulation of phagocytosis of peripheral cells in mice, two positive controls previously tested in the laboratory were included in the experiment: a β-1,3/1,6 glucan from yeast and a β-1,3-glucan from algae. The algae glucan had the lower effect, which is consistent with its chemical structure, comprising a linear carbohydrate chain with β-1,3 bonds [
43]. Phagocytosis is known to play a crucial role in initiating the innate immune response against infection. Although phagocytic functions are performed by binding of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMP) with their cell surface receptors on the phagocytes, leading to signal transduction and the release of inflammatory mediators, β-glucan-induced phagocytosis is mediated by various phagocytic receptors, mainly dectin-1 and complement receptors (CR3), and contributes to initiation of immune responses [
44,
45].
Future research to explore potential direct antiviral and antimicrobial effects could be of help to further support the benefits of supplementation with ABB C1® as an immune modulator in infectious disease.
5. Conclusions
Taken together, the findings of these three experimental studies show that ABB C1
®, which is a combination of yeast-based ingredients with a unique 1,3/1,6-glucan complex, and a consortium of heat-treated probiotic
S. cerevisiae rich in selenium and zinc, exhibited anti-inflammatory properties, protection of the gut barrier, and stimulated phagocytosis. Given the safety and tolerability of the product shown in a previous randomized controlled trial in healthy volunteers after getting vaccinated against influenza or Covid-19 [
20] and considering the present findings, the use of dietary supplementation with ABB C1
® in immunological challenges such infectious disease or allergic episodes may be useful to ameliorate symptoms and improve prognosis in clinical practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M. T., J.C. and C.d.L.; methodology, M.T, J.C. and V.V.; software, M.T.; validation, M. T., J.C. and C.d.L; formal analysis, M.T.; investigation, M. T., J.C., V.V. and C.d.L; resources, C.d.L.; data curation, M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T.; writing—review and editing, M. T., J.C., V.V. and C.d.L; visualization, C.d.L. supervision, C.d.L..; project administration, M.T.; funding acquisition, C.d.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Czech Animal Care and Use Committee.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Study data are available from the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marta Pulido, MD, PhD, for editing the manuscript and editorial assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
M.T., J.C. and C.d.L. are full time employees of AB Biotek Human Nutrition & Health.
References
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front Immunol 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stow, J.L.; Murray, R.Z. Intracellular trafficking and secretion of inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2013, 24, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuking, M.B.; Köller, Y.; Rupp, S.; McCoy, K.D. The interplay between the gut microbiota and the immune system. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 411-418.
- Hosseini, A.; Hashemi, V.; Shomali, N.; Asghari, F.; Gharibi, T.; Akbari, M.; Gholizadeh, S.; Jafari, A. Innate and adaptive immune responses against coronavirus. Biomed Pharmacother 2020, 132, 110859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, R.; Kalmarzi, R.N.; Roghani, S.A. A review on the immune responses against novel emerging coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Immunol Res 2021, 69, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Channappanavar, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. Coronaviruses: Innate immunity, inflammasome activation, inflammatory cell death, and cytokines. Trends Immunol 2020, 41, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, F.; Fallahi, P. IP-10 in occupational asthma: review of the literature and case-control study. Clin Ter 2017, 168, e151–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bari, F. Atopic dermatitis and alpha-chemokines. Clin Ter 2015, 166, e182–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holla, L.I.; Mrazek, F.; Petrek, M. MCP-1 and CCR2 gene polymorphisms in Czech patients with allergic disorders. Int J Immunogenet 2009, 36, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, W.; Lu, D.; Liu, X.; Chen, L. MCP-1 produced by keratinocytes is associated with leucocyte recruitment during elicitation of nickel-induced occupational allergic contact dermatitis. Toxicol Ind Health 2018, 34, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Hogan, S-P. Intestinal barrier function: molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009, 124, 3-20.
- Hamulka, J.; Jeruszka-Bielak, M.; Górnicka, M.; Drywień, M.E.; Zielinska-Pukos, M.A. Dietary supplements during COVID-19 outbreak. Results of Google Trends Analysis Supported by PLifeCOVID-19 Online Studies. Nutrients 2020, 13, 5413. [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, G.; Spada, E.; Comberiati, P.; Peroni, D.G. Could nutritional supplements act as therapeutic adjuvants in COVID-19? Ital J Pediatr 2021, 47, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, W., Helal, E. Chemical constituents and potential pleiotropic activities of Foeniculum vulgare (Fennel) ethanolic extract; in vitro approach. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry, 2022; 65(7), 617-626. [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, H.A.; Bashar, M.A.E.; Rady, I.; El-Wetidy, M.S.; Suleiman, W.B.; Al-Otibi, F.O.; Al-Rashed, S.A.; Abd El-Maoula, L.M.; Salem, E.-S.S.; Attia, E.M.H.; Bakry, S. Two Red Sea Sponge Extracts (Negombata magnifica and Callyspongia siphonella) Induced Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, W.B., Shehata, R.M. & Younis, A.M. In vitro assessment of multipotential therapeutic importance of Hericium erinaceus mushroom extracts using different solvents. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022 9, 99. [CrossRef]
- Generoso, S.V., Viana, M., Santos, R., Martins, F.S., Machado, J.A., Arantes, R.M., Nicoli, J.R., Correia, M.I., Cardoso, V.N.. Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain UFMG 905 protects against bacterial translocation, preserves gut barrier integrity and stimulates the immune system in a murine intestinal obstruction model. Arch Microbiol. 2010, 192(6), 477-84. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Generoso, S.V., Viana, M., Santos, R., Martins, F.S., Machado, J.A., Arantes, R.M., Nicoli, J.R., Correia, M.I., Cardoso, V.N.. Protection against increased intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation induced by intestinal obstruction in mice treated with viable and heat-killed Saccharomyces boulardii. Eur J Nutr. 2011, 50(4), 261-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.A.M.; Bifano, M.; Roca Goma, E.; Plasencia, C.M.; Torralba, A.O.; Font, M.S.; Millán, P.R. 2021. Effect and tolerability of a nutritional supplement based on a synergistic combination of β-glucans and selenium- and zinc-enriched Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ABB C1®) in volunteers receiving the influenza or the COVID-19 vaccine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4347. [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.; Kim, H. Mini-Review on the roles of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in the immune system against COVID-19. Molecules 2020, 25, 5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhrolmobasheri, M.; Mazaheri-Tehrani, S.; Kieliszek, M.; Zeinalian, M.; Abbasi, M.; Karimi, F.; Mozafari, A.M. COVID-19 and selenium deficiency: A systematic review. Biol Trace Elem Res 2022, 200, 3945–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales Martinez, S.; Huang, Y.; Acuna, L.; Laverde, E.; Trujillo, D.; Barbieri, M.A.; Tamargo, J.; Campa, A.; Baum, M. Role of Selenium in Viral Infections with a Major Focus on SARS-CoV-2 Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(1), 280. [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaeizadeh, S.A. Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis. Eur J Med Res 2022, 27, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawhara, S. How to boost the immune defence prior to respiratory virus infections with the special focus on coronavirus infections. Gut Pathog 2020, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, A.; Yan, J. Could the induction of trained immunity by β-glucan serve as a defense against COVID-19? Front Immunol 2020, 11, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir KMI, Choi JS. Clinical and Physiological Perspectives of β-Glucans: The Past, Present, and Future. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 5;18(9):1906. [CrossRef]
- Van De Walle, J., Hendrickx, A., Romier, B., Larondelle, Y., & Schneider, Y.-J. Inflammatory parameters in Caco-2 cells: Effect of stimuli nature, concentration, combination and cell differentiation. Toxicology in Vitro, 2010, 24(5), 1441–1449. [CrossRef]
- Chen S, Einspanier R, Schoen J. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER): a functional parameter to monitor the quality of oviduct epithelial cells cultured on filter supports. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015, 144(5), 509-15. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Su, L.; Zhang, D.; Fan, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Xie, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. IP-10 and MCP-1 as biomarkers associated with disease severity of COVID-19. Mol Med 2020, 26, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y-C.; Chin, C-h.; Liu, S-F.; Wu, C-C.; Tsen, C-C.; Wang, Y-H.; Chao, T-Y.; Lie, C-H.; Chen, C-j.; Wang, C-C.; Lin, M-C. Prognostic values of serum IP-10 and IL-17 in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Dis Markers. 2011, 31, 101–10. [CrossRef]
- Pons, M.J.; Ymaña, B.; Mayanga-Herrera, A.; Sáenz, Y.; Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Tapia-Rojas, S.; Gamarra, R.; Blanco, A.B.; Moncunill, G.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F. Cytokine profiles associated with worse prognosis in a hospitalized Peruvian COVID-19 cohort. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 700921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Anshita, D.; Ravichandiran, V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 101, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Manetti, A.C.; Franceschi, F.; La Russa, R.; Bertozzi, G.; Maiese, A.; Savioli, G.; Volonnino, G.; Longhitano, Y. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and therapy. Medicina (Kaunas) 2022, 58, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumboyono, K.; Chomsy, I.N.; Iskandar, A.; Aryati, A.; Parwati, I.; Wihastuti, T.A. The potential predictive role of tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 for COVID-19 patients survival. Infect Drug Resist 2022, 15, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu M, Guo S, Hibbert JM, Jain V, Singh N, Wilson NO, Stiles JK. CXCL10/IP-10 in infectious diseases pathogenesis and potential therapeutic implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 121–30. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Tan, C.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Shen, G.; Zhu, P.; Yang, G.; Xie, X. Changes of serum IL-10, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α, IP-10 and IL-4 in COVID-19 patients. Int J Clin Pract 2021, 75, e14462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- anjiv Singh, D. Anshita, V. Ravichandiran, MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. International Immunopharmacology, 2021, 101, Part B, 107598. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Patton, M.J.; Floyd, J.L.; Vieira, C.P.; Fortmann, S.; DuPont, M.; Harbour, A.; Jeremy, C.S.; Wright, J.; Lamendella, R.; Stevens, B.R.; Grant, M.B. Plasma microbiome in COVID-19 subjects: an indicator of gut barrier defects and dysbiosis. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021, 2021.04.06.438634. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Viana, S.D.; Reis, F. Gut microbiota dysbiosis-immune hyperresponse-inflammation triad in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): impact of pharmacological and nutraceutical approaches. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Zuo, T.; Lui, G.C.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, A.Y.; Chung, A.C.; Cheung, C.P.; Tso, E.Y.; Fung, K.S.; Chan, V.; Ling, L.; Joynt, G.; Hui, D.S.; Chow, K.M.; Ng, S.S.S.; Li, T.C.; Ng, R.W.; Yip, T.C.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, F.K.; Wong, C.K.; Chan, P.K.; Ng, S.C. Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesemann, D.R.; Nagler, C. R. The Microbiome, Timing, and Barrier Function in the Context of Allergic Disease. Immunity 2016, 44, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raa, J. Immune modulation by non-digestible and non-absorbable beta-1,3/1,6-glucan, Microb Ecl Health Dis 2015, 26, 1. [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, H.S.; Wolf, A.J.; Underhill, D.M. Beta-glucan recognition by the innate immune system. Immunol Rev 2009, 230, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Song, Q.; Zhao, C. The phagocytic receptors of β-glucan. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 205, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).