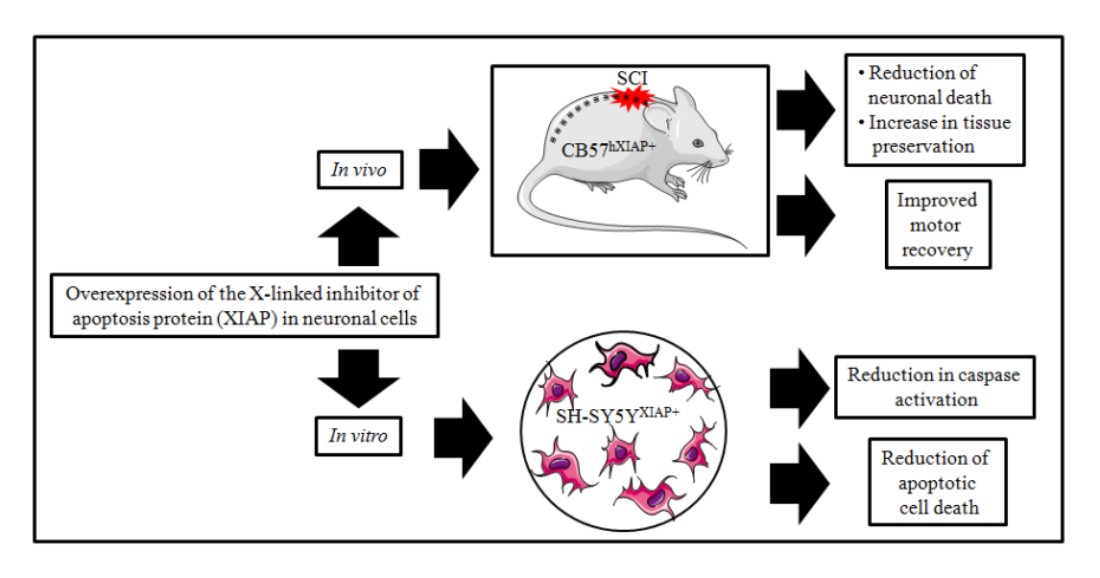
Trauma to the spinal cord causes extensive neuronal death contributing to the loss of sensory-motor and autonomic functions below the injury level. Apoptosis affects neurons after spinal cord injury (SCI) and is associated with increased caspase activity. Cleavage of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) after SCI may contribute to this rise of caspase activity. Accordingly, we have shown that the elevation of XIAP resulted in increased neuronal survival after SCI and improved functional recovery. Therefore, we hypothesize that neuronal overexpression of XIAP can be neuroprotective after SCI with improved functional recovery. In line with this, studies of a transgenic mouse with overexpression of XIAP in neurons revealed that higher levels of XIAP after spinal cord trauma favours neuronal survival, tissue preservation, and motor recovery after the spinal cord trauma. Using the human SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing XIAP we show further that XIAP reduced caspase activity and apoptotic cell death after pro-apoptotic stimuli. In conclusion, this study shows that the levels of XIAP expression are an important factor for the outcome after spinal cord trauma and identifies XIAP as an important therapeutic target for alleviating the deleterious effects of SCI.