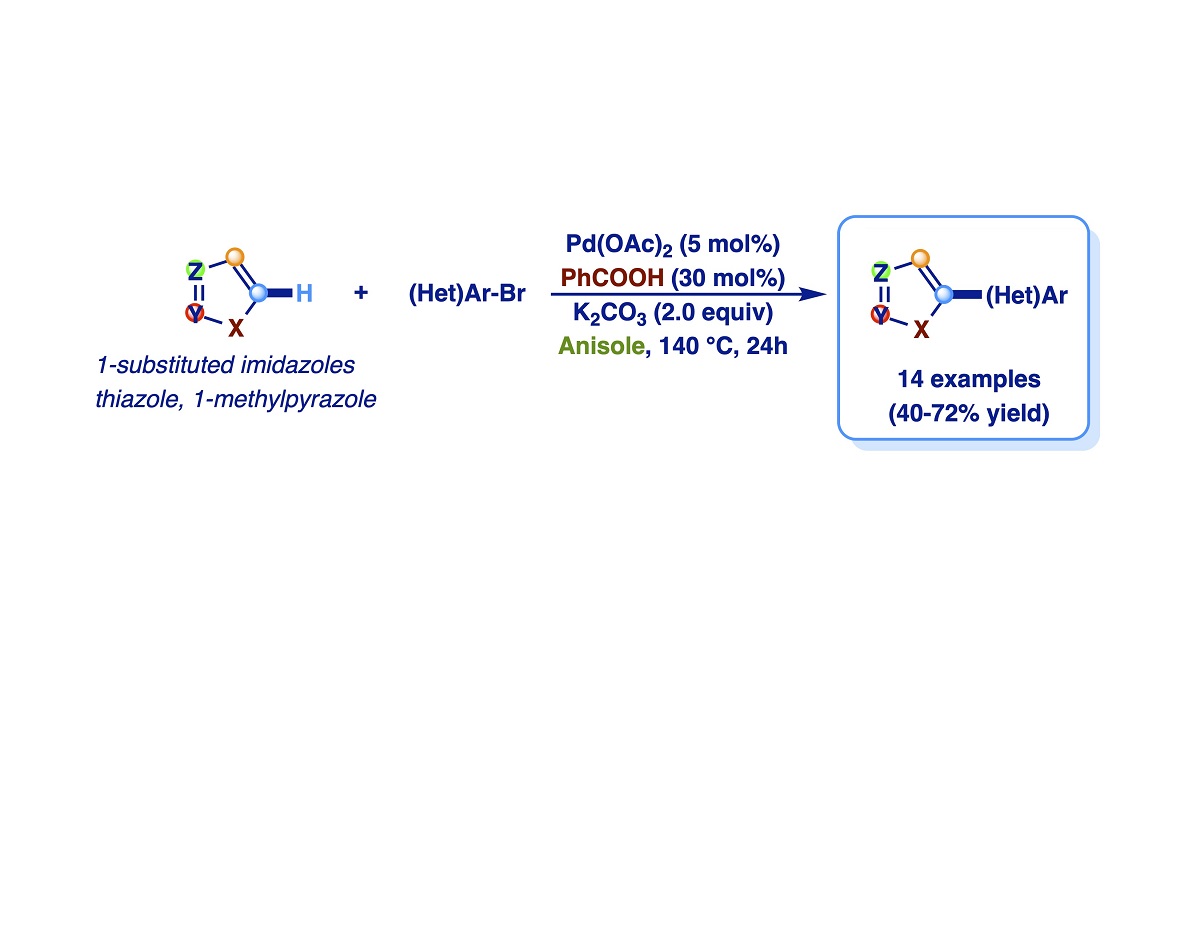
Due to the widespread application of (hetero)arylazoles, the development of straightforward functional group-tolerant synthetic methods that enable selective heteroaromatic elaboration under mild conditions aroused considerable attention. Over the last years we were interested in studies aimed to broaden the substrate scope of the direct functionalization of azoles and, in particular, to develop efficient synthetic protocols for the carbon-carbon bond forming reaction by selective palladium-catalyzed Csp2-H bond activation of imidazole derivatives. During these studies, we discovered that the outcome of the Pd-catalyzed arylation of imidazoles with aryl bromides is deeply influenced by the nature of the reaction solvent. Specifically, it is well known that the Pd-catalyzed direct arylation of imidazoles with aromatic halides selectively leads to C-5 monoarylation products when polar aprotic solvents such as DMF (or DMA) are used as a reaction medium, but these solvents are coded as dangerous according to EHS (Environmental, Health, Safety) parameters. Instead, the use of aromatic solvents as the reaction medium for direct arylations, although some of them show good EHS values, is poorly reported, probably due to their low solvent power against reagents and their potential involvement in undesired side reactions. So, with the intention of filling this gap, in this paper, we have developed a selective C-5 arylation procedure in anisole as the solvent, discovering also the unprecedented role of benzoic acid as a promoter of the coupling.