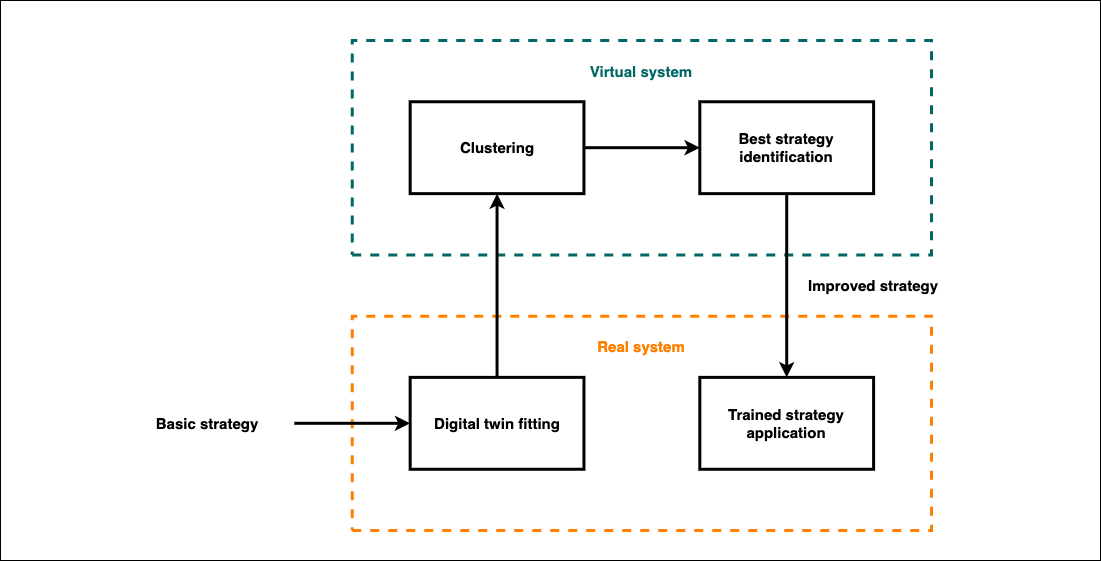
With increasing constraints on energy and resource markets and the non-decreasing trend in energy demand, the need for relevant clean energy generation and storage solutions is growing and is gradually reaching the individual home. But small-scale energy storage is still an expensive investment in 2022 and the risk/reward ratio is not yet attractive enough for individual homeowners. One solution is for homeowners not to store excess clean energy individually but to produce hydrogen for mutual use. In this paper a collective production of hydrogen for a daily filling of a bus is considered. Following our previous work on the subject, the investigation consists of finding an optimal buy/sell rule to the grid, and the use of the energy with an additional objective: mobility. The dominant technique in the energy community is reinforcement learning, which is however difficult to use when the learning data is limited as in our study. We chose a less data-intensive and yet technically well-documented approach. Our results show that rulebooks, different but more interesting than the usual robust rule, exist and can be cost-effective. But they require fine-tuning as to not deteriorate system performance. In some cases, it is worth missing the H2 production requirement in exchange for higher economic performance.