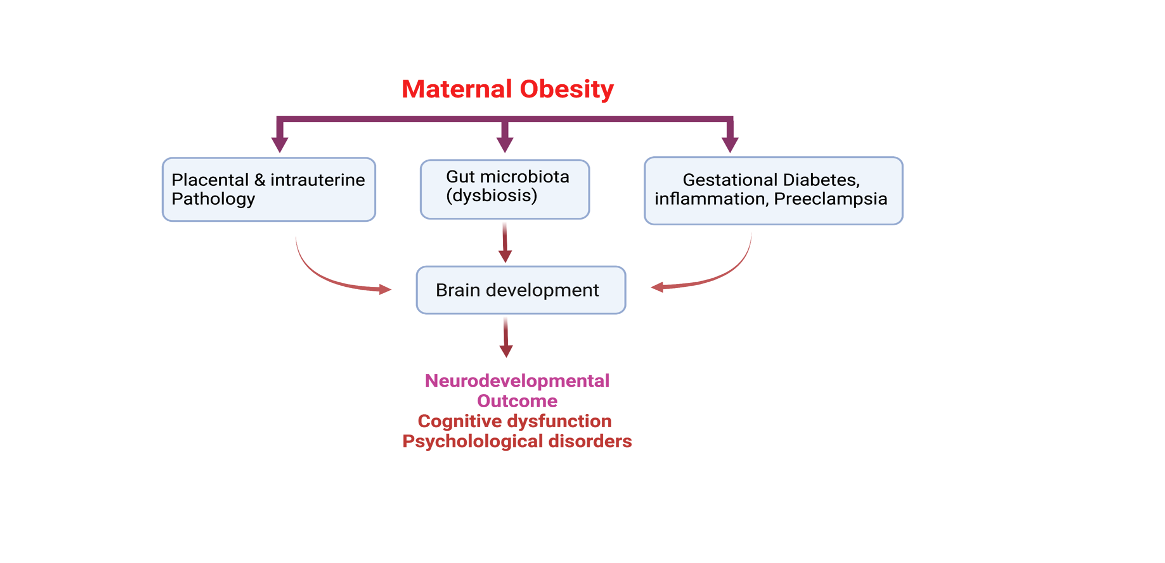
Obesity in pregnancy induces metabolic syndrome, low-grade inflammation, altered endocrine factors, placental function, and the maternal gut microbiome. All these factors impact fetal growth and development, including brain development. The lipid metabolic transporters of the maternal-fetal-placental unit are dysregulated in obesity. Consequently, the transport of essential long-chain PUFAs for fetal brain development is disturbed. The mother’s gut microbiota is vital in maintaining postnatal energy homeostasis and maternal-fetal immune competence. Obesity during pregnancy changes the gut microbiota, affecting fetal brain development. Obesity and a high-fat diet in pregnancy can induce placental and intrauterine inflammation and thus influence the neurodevelopmental outcomes of the offspring. Several epidemiological studies observed an association between maternal obesity and adverse neurodevelopment. This review discusses the effects of maternal obesity and gut microbiota on fetal neurodevelopment outcomes. In addition, the possible mechanisms of the impacts of obesity and gut microbiota on fetal brain development are discussed.