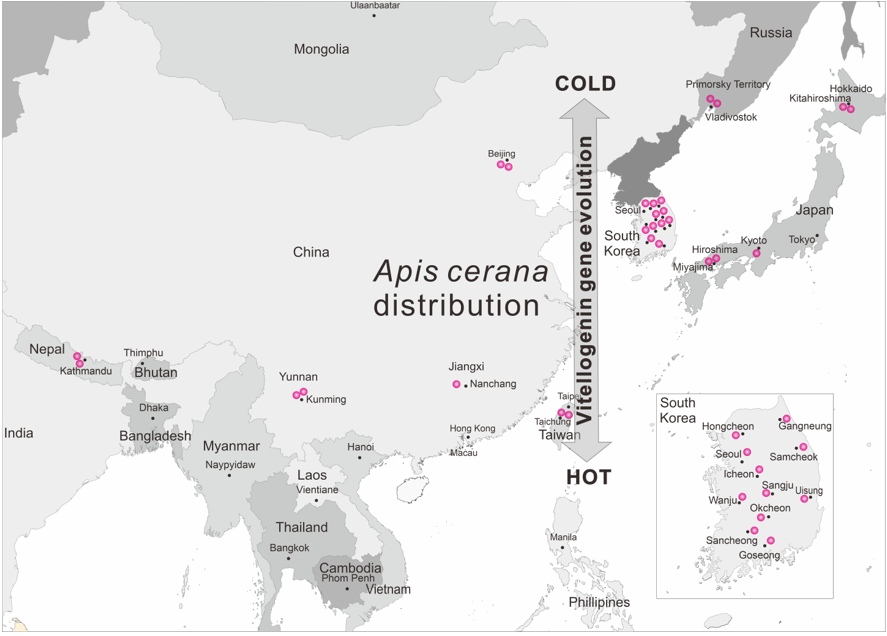
Apis cerana and Apis mellifera, are very important honey species for agriculture in Asian countries. In recent decades, A. cerana populations have sharply declined in all Asian countries as a result of Sacbrood Virus infection and have now recovered to their original size. It can change the genetic structure of local populations of A. cerana. We used the nuclear gene Vitellogenin VG to assess the genetic structure of local populations of A. cerana and the signature of adaptive selection. We performed a population genetic analysis of the honey bees A. cerana from South Korea in comparison with A. cerana samples from Russia, Japan, Nepal, and China. The sequences of the gene VG of a closely related honey bee species, A. mellifera, from India and Poland were used as outgroup samples. A comparative analysis of northern and southern A. cerana populations was performed. The signatures of positive adaptive selection were found in the local population of A. cerana. We performed the Tajima's neutrality D test for A. cerana populations from different local populations based on the gene VG exon sequences. All A. cerana populations showed signs of population size expansion following the possible recent decline in population sizes. The local populations of A. c. koreana were subdivided according to their geographical distribution into southern, northern, and central Korean clusters. The gene VG exon sequences can be used as informative markers for monitoring the changes in genetic structure and adaptation to the environment processes in A. cerana populations.