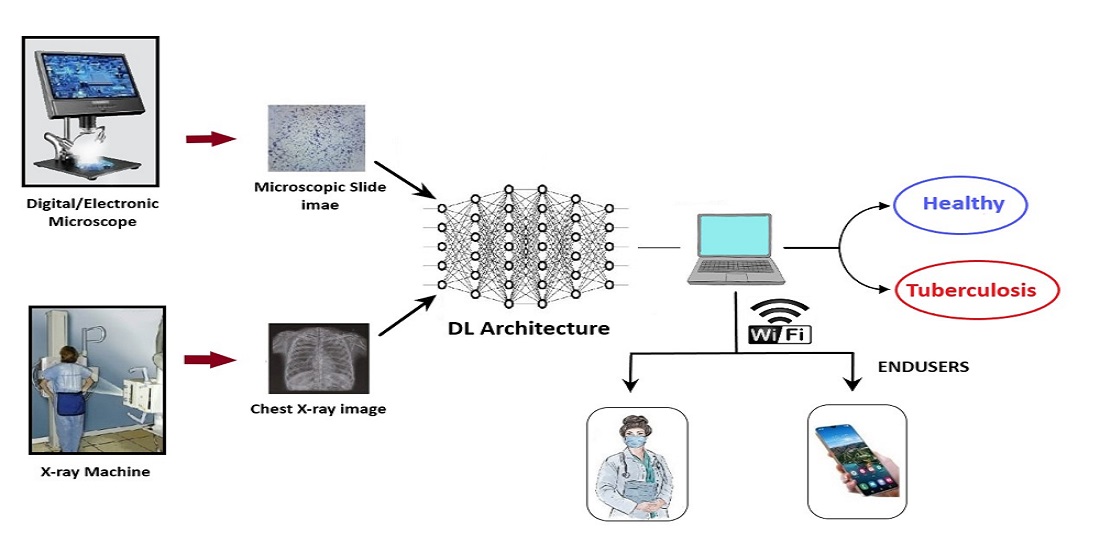
Tuberculosis (TB) disease still remain a major global threat due to the growing number of drug-resistant species and global warming. Despite the fact that there are new molecular diagnostic approaches, however, majority of developing countries and remote clinics depends on conventional approaches such as Tuberculin test, microscopic examinations and radiographic imaging (Chest X-ray). These techniques are hindered by several challenges which can lead to miss-diagnosis especially when interpreting large number of sample cases. Thus, in order to reduce workload and prevent miss-diagnosis, scientists incorporated computer-aided technology for detection of medical images known as Computer aided Detection (CADe) or Diagnosis (CADx). The use of AI-powered techniques has shown to improve accuracy, sensitivity, specificity. In this review, we discussed about the epidemiology, pathology, diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. The review also provides background information on Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Transfer Learning (TL) and their applications in detection of tuberculosis from both microscopic slide images and X-ray images. The review also proposed an IoT/AI powered system which allows transfer of results obtained from DL models with end users through internet networks. The concept of futuristic diagnosis, limitations of current techniques and open research issues are also discussed.