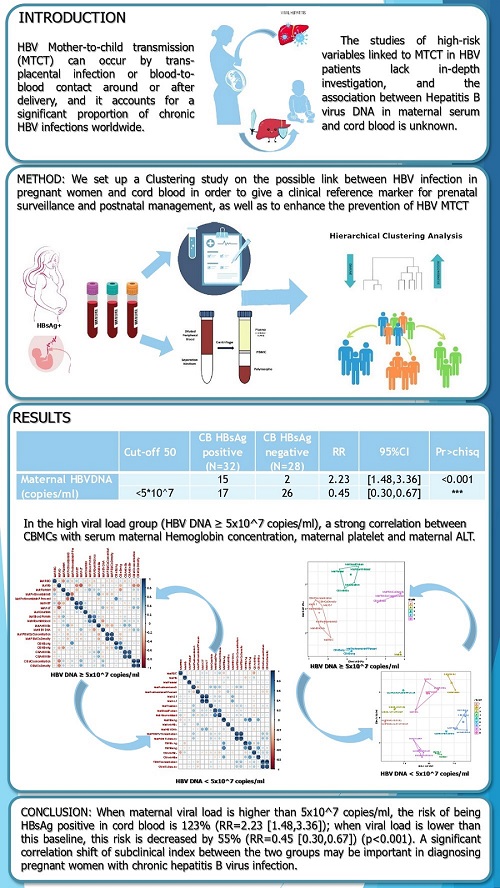
BACKGROUND&AIMS: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a major public health problem. The interaction between HBV and the host inflammatory response is an important factor contributing to liver damage and disease development. We compared the correlation between the subclinical index and PBMCs concentration in two groups of pregnant women (HBsAg positive), which are different in HBV DNA concentration in Vietnam. METHODS: The Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) was run with 20 different clustering methods on data collected from 80 Vietnamese pregnant women and their babies (60/80 cord blood). RESULTS: In the high viral load group (HBV DNA ≥ 5x10^7 copies/ml), a strong correlation between CBMCs with serum maternal Haemoglobin concentration and maternal platelet and maternal ALT. Their R values are: -0.88, 0.82, and 0.84 with p=8.97E-03, 2.41E-02 and 1.75E-01, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: We found a significant correlation shift of subclinical index between the two groups, which may be important in diagnosing pregnant women with chronic hepatitis B virus infection.