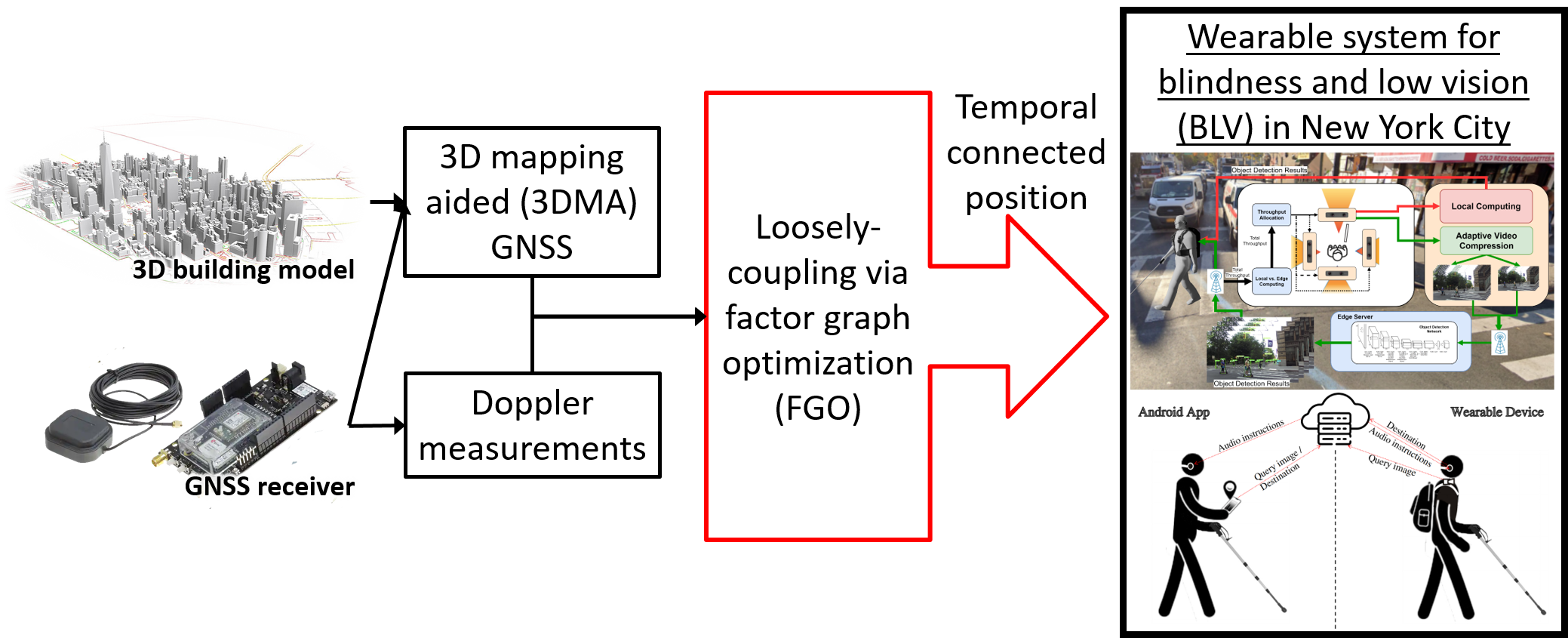
Smart health applications have received significant attention in recent years. Novel applications hold significant promise to overcome many of the inconveniences faced by persons with disabilities throughout daily living. For people with blindness and low vision (BLV), environmental perception is compromised, creating myriad difficulties. Precise localization is still a gap in the field and is critical to safe navigation. Conventional GNSS positioning cannot provide satisfactory performance in urban canyons. 3D mapping-aided (3DMA) GNSS may serve as an urban GNSS solution, since the availability of 3D city models has widely increased. As a result, this study developed a real-time 3DMA GNSS-positioning system based on state-of-the-art 3DMA GNSS algorithms. Shadow matching was integrated with likelihood-based ranging 3DMA GNSS, generating positioning hypothesis candidates. To increase robustness, the 3DMA GNSS solution was then optimized with Doppler measurements using factor graph optimization (FGO) in a loosely-coupled fashion. This study also evaluated positioning performance using an advanced wearable system’s recorded data in New York City. The real-time forward processed FGO can provide a root-mean-square error (RMSE) with about 21 m. The RMSE drops to 16 m when the data is post-processed with FGO in a combined direction. Overall results show that the proposed loosely-coupled 3DMA FGO algorithm can provide a better and more robust positioning performance for the multi-sensor integration approach used by this wearable for persons with BLV.