Submitted:
17 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
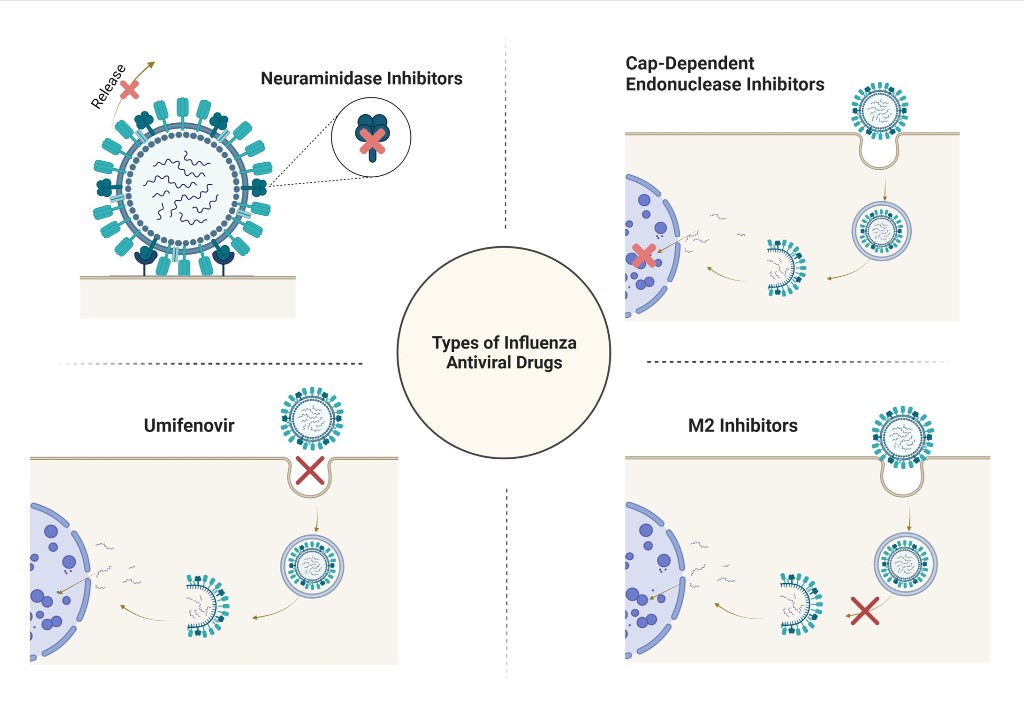
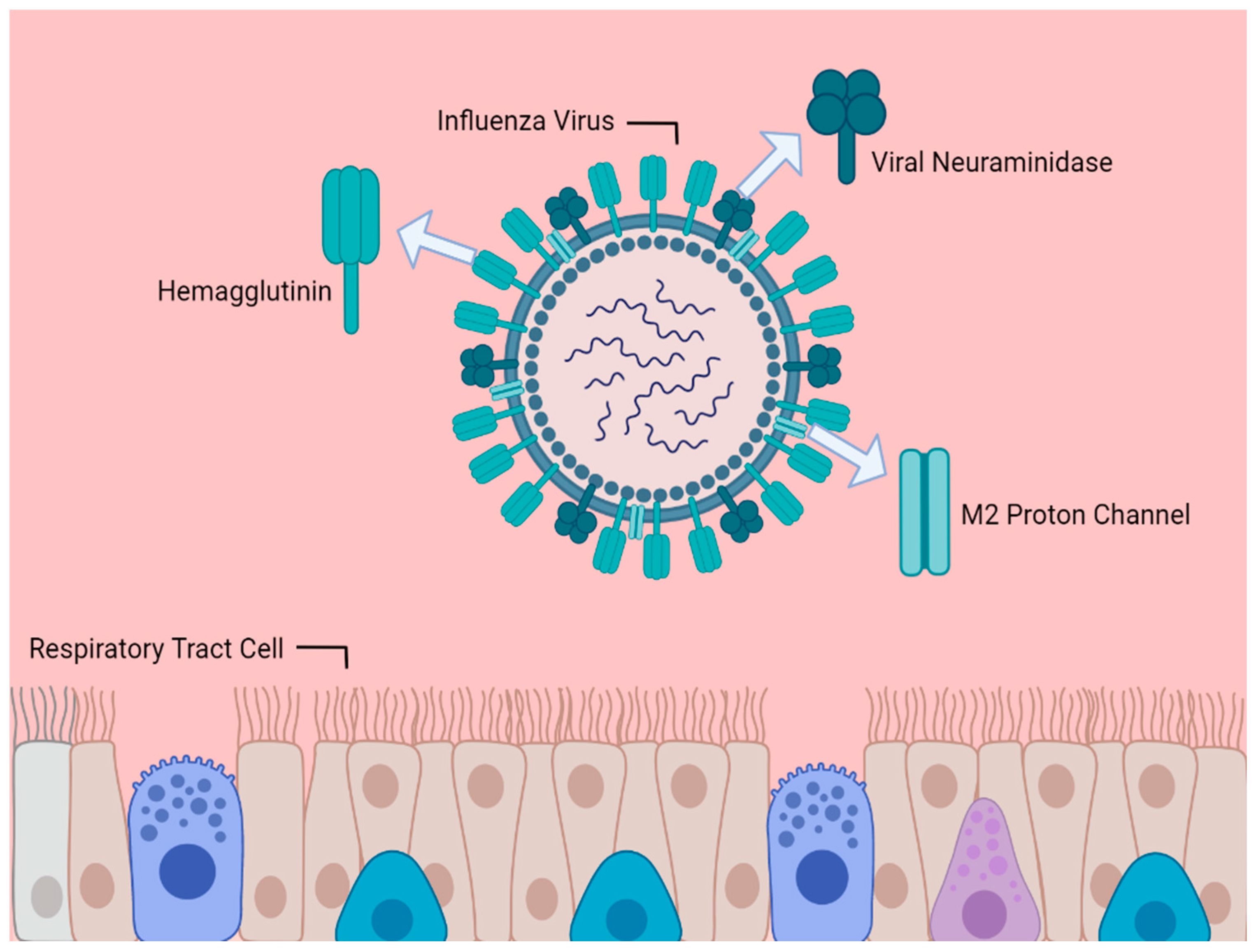
1. Introduction
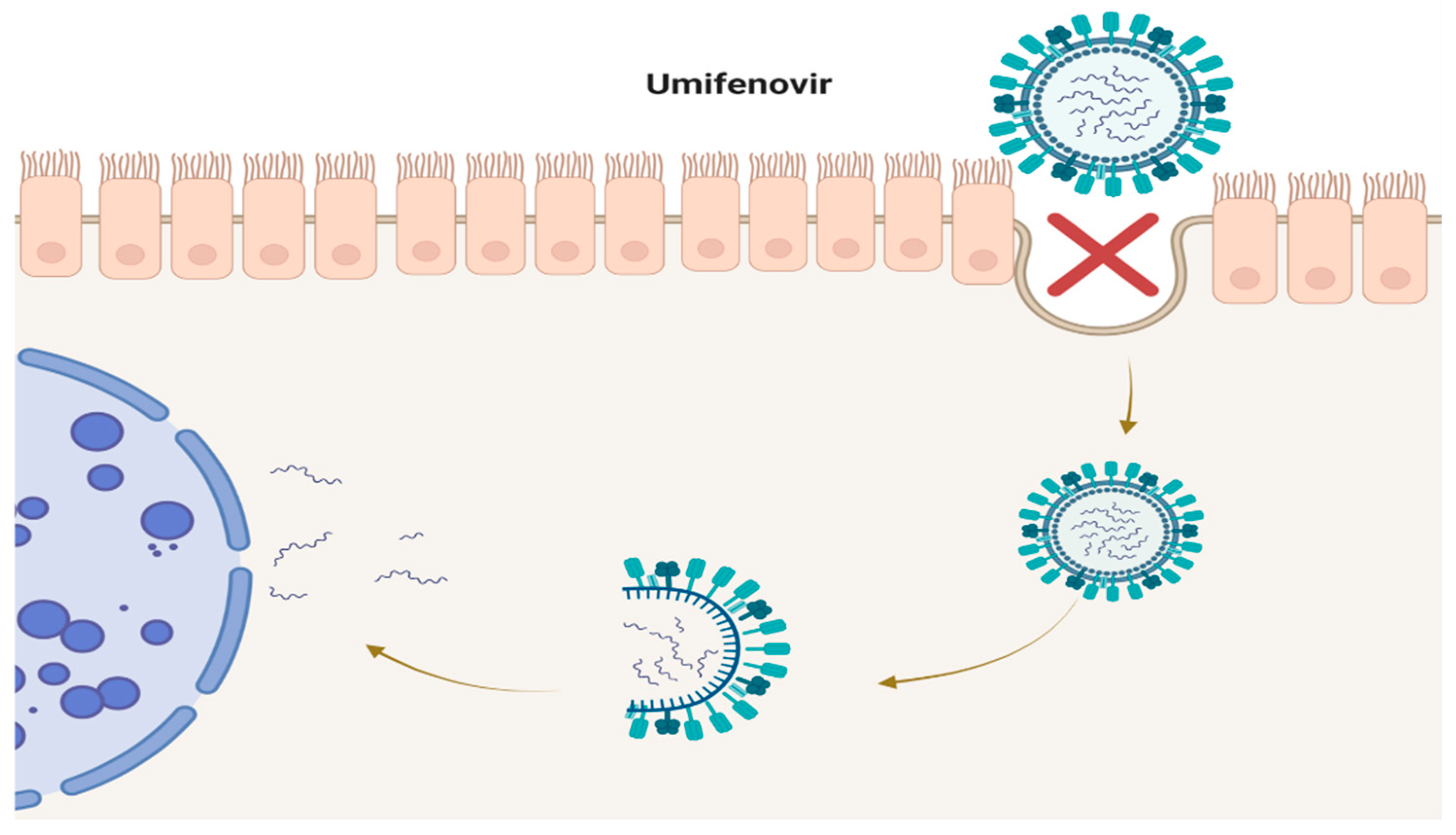
2. Umifenovir
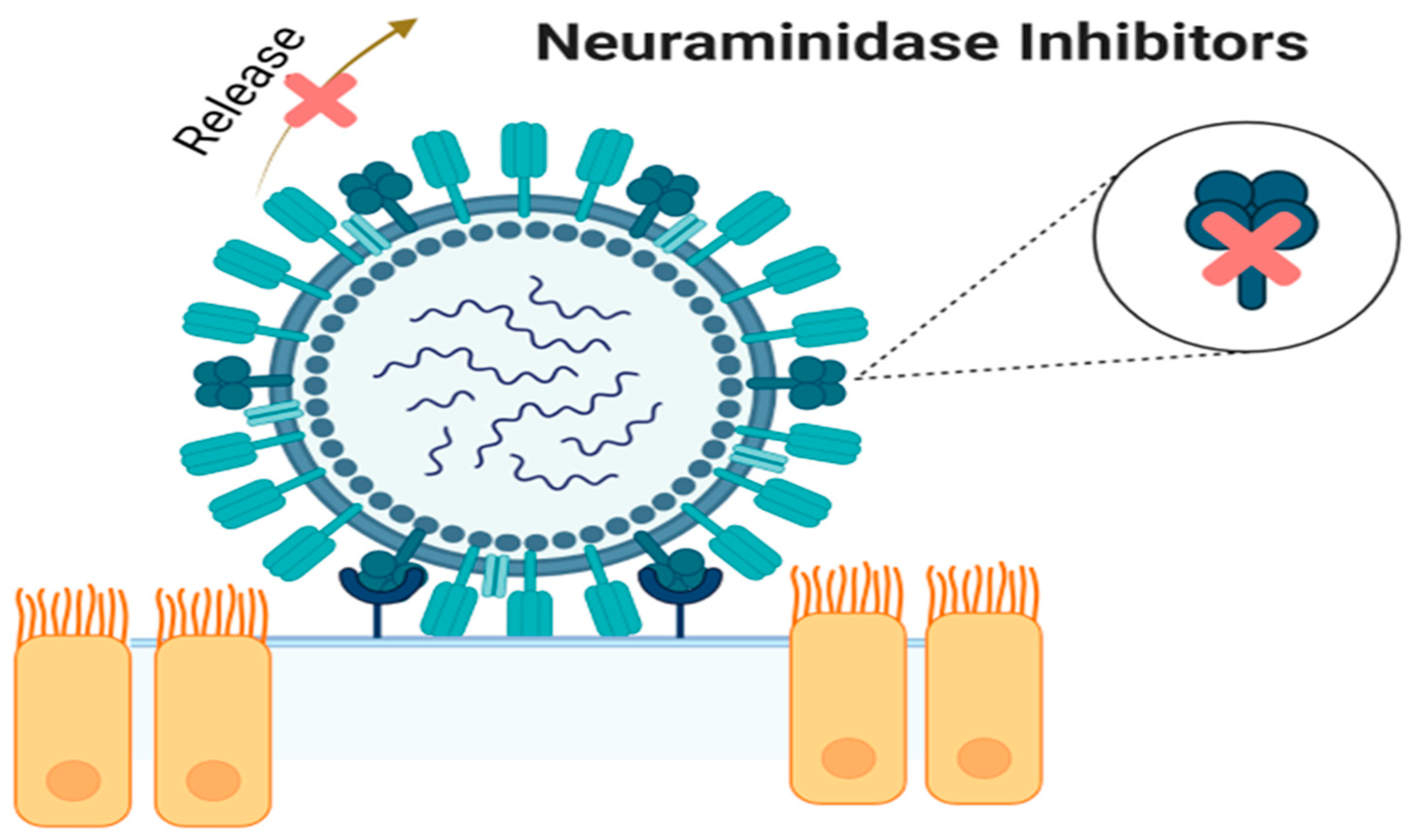
3. Neuraminidase Inhibitors
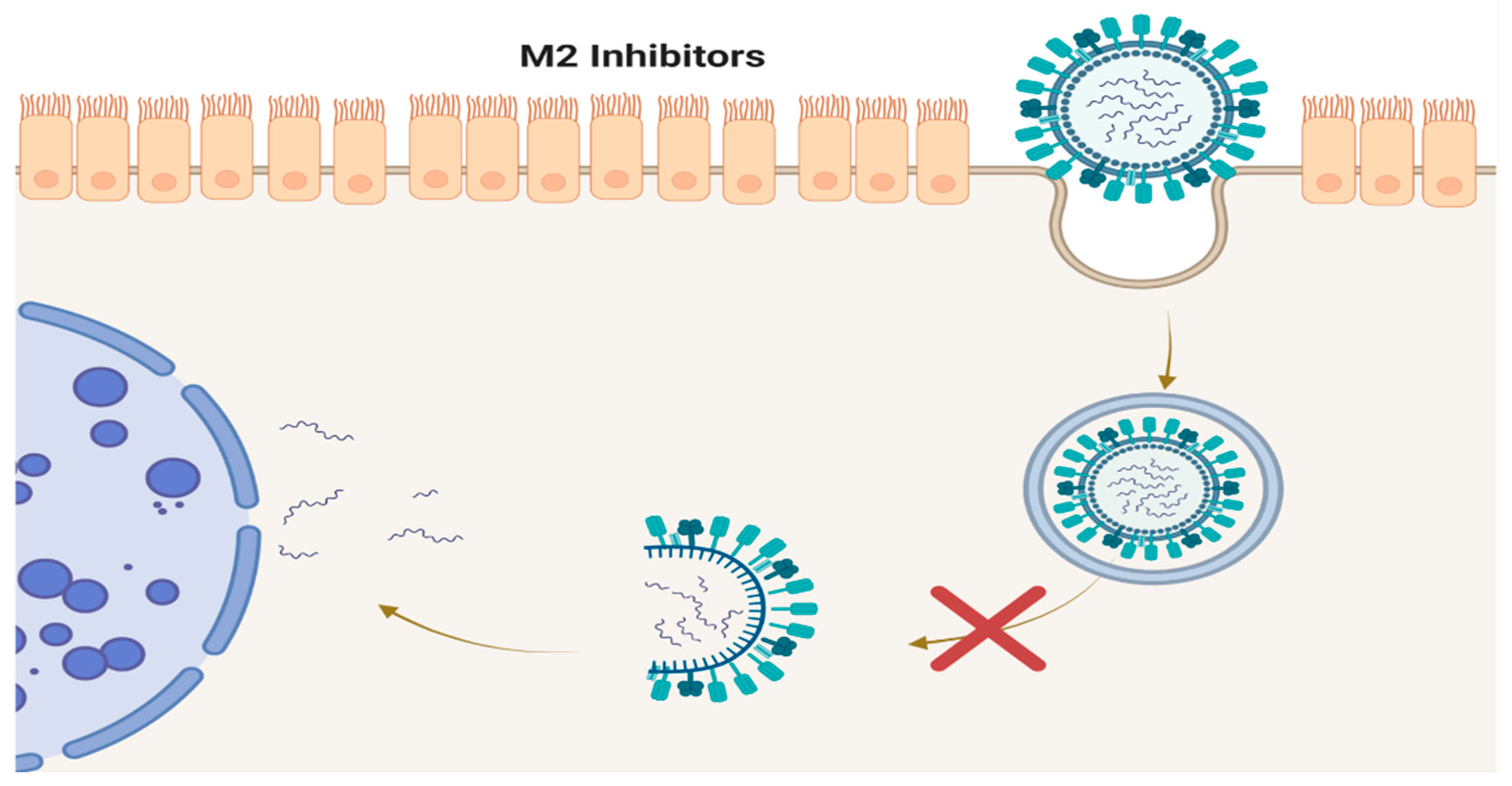
4. M2 Inhibitors (Adamantanes)
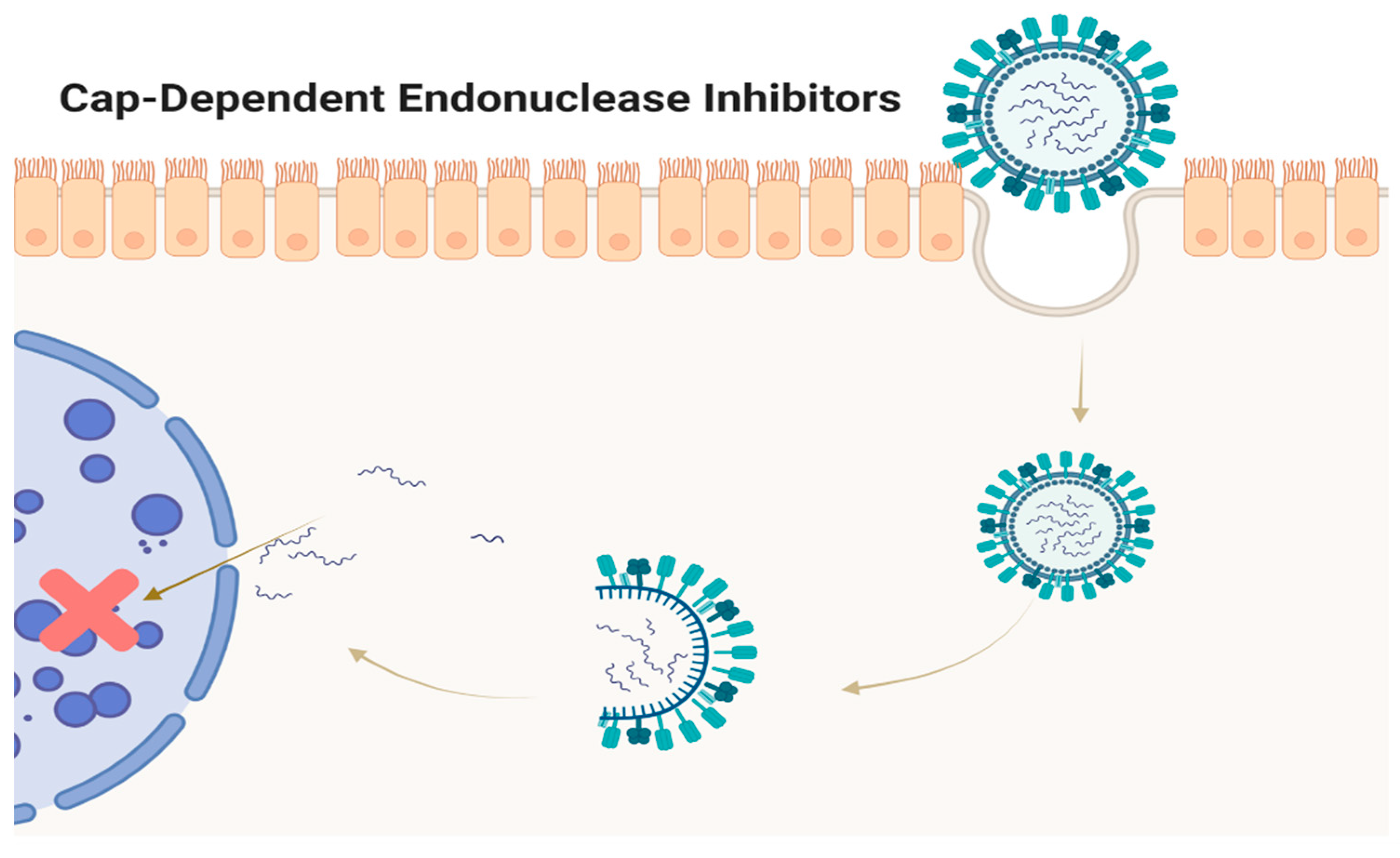
5. CAP-Dependent Endonuclease Inhibitors
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Gaitonde, D.Y.; Moore, F.C.; Morgan, M.K. Influenza: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2019, 100, 751–758. [Google Scholar]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Morens, D.M. Influenza: the once and future pandemic. Public Health Rep 2010, 125, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.S.; Fukuda, K. Lessons from influenza pandemics of the last 100 years. Clin Infect Dis. 2020, 70, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberis, I.; Myles, P.; Ault, S.K.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Martini, M. History and evolution of influenza control through vaccination: from the first monovalent vaccine to universal vaccines. J Prev Med Hyg. 2016, 57, E115–E120. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T. Baloxavir Marboxil: The first cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor for the treatment of influenza. Ann Pharmacother. 2019, 53, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koel, B.F.; Mögling, R.; Chutinimitkul, S.; et al. Identification of amino acid substitutions supporting antigenic change of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses. J Virol. 2015, 89, 3763–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscona, A. Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza. N Engl J Med. 2005, 353, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, S.; Watanabe, A.; Ikematsu, H.; et al. Laninamivir octanoate for post-exposure prophylaxis of influenza in household contacts: a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial. J Infect Chemother. 2013, 19, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Furuta, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; et al. In vitro and in vivo activities of T-705 and oseltamivir against influenza virus. Antivir. Chem Chemther. 2003, 14, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriskin, Y.S.; Leneva, I.A.; Pécheur, E.I.; Polyak, S.J. Arbidol: a broad-spectrum antiviral compound that blocks viral fusion. Curr.Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haviernik, J.; Štefánik, M.; Fojtíková, M.; et al. Arbidol (Umifenovir): A Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Drug That Inhibits Medically Important Arthropod-Borne Flaviviruses. Viruses 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryabin, P.G.; Garaev, T.M.; Finogenova, M.P.; Odnovorov, A.I. Assessment of the antiviral activity of 2HCl*H-His-Rim compound compared to the anti-influenza drug Arbidol for influenza caused by A/duck/Novosibirsk/56/05 (H5N1) (Influenza A virus, Alphainfluenzavirus, Orthomyxoviridae). Vopr Virusol. 2019, 64, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaising, J.; Polyak, S.J.; Pécheur, E.-I. Arbidol as a broad-spectrum antiviral: An update. Antivir Res. 2014, 107, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.J.; Burtseva, E.I.; Ellery, P.J.; et al. Antiviral activity of arbidol, a broad-spectrum drug for use against respiratory viruses, varies according to test conditions. J Med Virol. 2012, 84, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fediakina, I.; Leneva, I.; Iamnikova, S.; Livov, D.; Glushkov, R.; Shuster, A. Sensitivity of influenza A/H5 viruses isolated from wild birds on the territory of Russia to arbidol in the cultured MDCK cells. Vopr Virusol. 2005, 50, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fediakina, I.; MIu, S.; Deriabin, P.; et al. Susceptibility of pandemic influenza virus A 2009 H1N1 and highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A H5N1 to antiinfluenza agents in cell culture. Antibiot Khimioter 2011, 56, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leneva, I.; Shuster, A. Antiviral etiotropic chemicals: efficacy against influenza A viruses A subtype H5N1. Vopr Virusol. 2006, 51, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Xiong, H.; He, J.; et al. Antiviral activity of arbidol against influenza A virus, respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, coxsackie virus and adenovirus in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Abouzid, M. Arbidol targeting influenza virus A Hemagglutinin; a comparative study. Biophy. Chem. 2021, 277, e106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, R.U.; Wilson, I.A. Structural basis of influenza virus fusion inhibition by the antiviral drug Arbidol. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017, 114, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leneva, I.A.; Russell, R.J.; Boriskin, Y.S.; Hay, A.J. Characteristics of arbidol-resistant mutants of influenza virus: implications for the mechanism of anti-influenza action of arbidol. Antivir Res. 2009, 81, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proskurnina, E.V.; Izmailov, D.Y.; Sozarukova, M.M.; Zhuravleva, T.A.; Leneva, I.A.; Poromov, A.A. Antioxidant Potential of Antiviral Drug Umifenovir. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2020, 25, e1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtseva, E.; Shevchenko, E.; Leneva, I.; et al. Rimantadine and arbidol sensitivity of influenza viruses that caused epidemic morbidity rise in Russia in the 2004-2005 season. Vopr Virusol. 2007, 52, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romanovskaia, A.; Durymanov, A.; Sharshov, K.; et al. Investigation of susceptibility of influenza viruses A (H1N1), the cause of infection in humans in April-May 2009, to antivirals in MDCK cell culture. Antibiot Khimioter. 2009, 54, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leneva, I.; Fediakina, I.; MIu, E.; et al. Study of the antiviral activity of Russian anti-influenza agents in cell culture and animal models. Vopr Virusol. 2010, 55, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Leneva, I.A.; Falynskova, I.N.; Leonova, E.I.; et al. [Umifenovir (Arbidol) efficacy in experimental mixed viral and bacterial pneumonia of mice. Antibiot Khimioter 2014, 59, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Leneva, I.A.; Falynskova, I.N.; Makhmudova, N.R.; Poromov, A.A.; Yatsyshina, S.B.; Maleev, V.V. Umifenovir susceptibility monitoring and characterization of influenza viruses isolated during ARBITR clinical study. J Med Virol. 2019, 91, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leneva, I.A.; Burtseva, E.; Kirillova, E.S.; Kolobukhina, L.V.; Prilipov, A.; Zaplatnikov, A.L. Assessment of a risk for development of umifenovir resistance in epidemic strains of influenza A and B viruses in clinical settings. Infektsionnye Bolezni. 2019, 17, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leneva, I.; Fediakina, I.; Gus' kova, T.; Glushkov, R. Sensitivity of various influenza virus strains to arbidol. Influence of arbidol combination with different antiviral drugs on reproduction of influenza virus A. Terapevticheskii Arkhiv. 2005, 77, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Pshenichnaya, N.Y.; Bulgakova, V.A.; Lvov, N.I.; et al. Clinical efficacy of umifenovir in influenza and ARVI (study ARBITR). Terapevticheskii Arkhiv. 2019, 91, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pshenichnaya, N.; Bulgakova, V.; Selkova, E.; et al. Umifenovir in treatment of influenza and acute respiratory viral infections in outpatient care. Int J Infect Dis 2019, 79, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xiong, H.R.; Lu, L.; et al. Antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity of arbidol hydrochloride in influenza A (H1N1) virus infection. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013, 34, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, C.; et al. Inhibition of the infectivity and inflammatory response of influenza virus by Arbidol hydrochloride in vitro and in vivo (mice and ferret). Biomed Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Z.; Cai, B.Q.; Li, L.Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of arbidol in treatment of naturally acquired influenza. Acta Acad Med Sin. 2004, 26, 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Vavricka, C.J.; Kiyota, H.; Suzuki, Y. Influenza a virus neuraminidase inhibitors. Methods in molecular biology. In: Suzuki, Y.; ed. Glycovirology 2022, 321–353. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.C.; Feng, I.J.; Tang, H.J.; Shih, M.F.; Hua, Y.M. Comparative effectiveness of neuraminidase inhibitors in patients with influenza: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Infect Chemother. 2022, 28, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClellan, K.; Perry, C.M. Oseltamivir. Drugs. 2001, 61, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.E. Pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir: an oral antiviral for the treatment and prophylaxis of influenza in diverse populations. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010, 65 Suppl. S2, ii5–ii10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annex, I. Summary of product characteristics. Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products. The European Public Assessment Report (EPAR). Stocrin. London: The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products; 1999. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/annual-report/annual-report-european-agency-evaluation-medicinal-products-1999_en.pdf.
- Elliott, M. Zanamivir: from drug design to the clinic. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B. 2001, 356, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Peramivir: A review in uncomplicated influenza. Drugs. 2018, 78, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, Y.; Ishibashi, T.; Fukuyama, H.; Fukase, H.; Shimada, J. Pharmacokinetics and safety of intravenous peramivir, neuraminidase inhibitor of influenza virus, in healthy Japanese subjects. Antivir Ther. 2017, 22, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, T.; Jones, M.A.; Doshi, P.; et al. Neuraminidase inhibitors for preventing and treating influenza in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014, 2014, eCd008965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemken, T.L.; Furmanek, S.P.; Carrico, R.M.; et al. Effectiveness of oseltamivir treatment on clinical failure in hospitalized patients with lower respiratory tract infection. BMC Infect Dis 2021, 21, e1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebell, M.H.; Call, M.; Shinholser, J. Effectiveness of oseltamivir in adults: a meta-analysis of published and unpublished clinical trials. Fam Pract. 2013, 30, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneghan, C.J.; Onakpoya, I.; Thompson, M.; Spencer, E.A.; Jones, M.; Jefferson, T. Zanamivir for influenza in adults and children: systematic review of clinical study reports and summary of regulatory comments. BMJ 2014, 348, e2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.; Akashi-Ueda, R.; Takamatsu, K.; Matsumura, T. Safety and efficacy of peramivir for influenza treatment. Drug Des Devel Ther 2014, 8, 2017–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.M.; Skoglund, E.W.; Ison, M.G. Peramivir: an intravenous neuraminidase inhibitor. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Lin, S.H.; Wang, L.C.; Chiu, H.Y.; Lee, J.A. Comparison of Antiviral Agents for Seasonal Influenza Outcomes in Healthy Adults and Children: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2021, 4, e2119151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Fry, A.M.; Gubareva, L.V. Neuraminidase inhibitor resistance in influenza viruses and laboratory testing methods. Antivir Ther. 2012, 17, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Chotpitayasunondh, T.; Cox, N.J.; et al. Antiviral resistance during the 2009 influenza A H1N1 pandemic: public health, laboratory, and clinical perspectives. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012, 12, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, L.T.; Holder, B.P.; Abed, Y.; Boivin, G.; Beauchemin, C.A. The H275Y neuraminidase mutation of the pandemic A/H1N1 influenza virus lengthens the eclipse phase and reduces viral output of infected cells, potentially compromising fitness in ferrets. J Virol. 2012, 86, 10651–10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampejo, T. Influenza and antiviral resistance: an overview. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020, 39, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Hurt, A.C. Neuraminidase inhibitor resistance in influenza: a clinical perspective. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018, 31, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Kang, D.; Ikematsu, H. Consecutive influenza surveillance of neuraminidase mutations and neuraminidase inhibitor resistance in Japan. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2019, 13, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorlund, K.; Awad, T.; Boivin, G.; Thabane, L. Systematic review of influenza resistance to the neuraminidase inhibitors. BMC Infec.Dis. 2011, 11, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, T.; Demicheli, V.; Di Pietrantonj, C.; Rivetti, D. Amantadine and rimantadine for influenza A in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, eCd001169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaston, J.L.; Samways, M.L.; Konstantinidi, A.; et al. Rimantadine Binds to and Inhibits the Influenza A M2 Proton Channel without Enantiomeric Specificity. Biochemistry. 2021, 60, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pielak, R.M.; Chou, J.J. Influenza M2 proton channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011, 1808, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.G.; Hayden, F.G. Antiviral Agents Against Respiratory Viruses. In: Cohen, J.; William, G. Powderly, W.G.; Opal, S.M.; eds. Infectious Diseases. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:1318–1326. [CrossRef]
- Geevarghese, B.; Simoes, E.A. Antibodies for prevention and treatment of respiratory syncytial virus infections in children. Antivir Ther. 2012, 17, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresee, J.S.; Fiore, A.E.; Fry, A.; Gubareva, L.V.; Shay, D.K.; Uyeki, T.M. Antiviral agents for the treatment and chemoprophylaxis of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Center of Disease Control and Prevention; 2011. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.g ov/view/cdc/5855/cdc_5855_DS1.pdf.
- Hayden, F.; Aoki, F. Amantadine, rimantadine, and related agents.In: Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins. 1999, 1344–1365.
- Hayden, F.; Minocha, A.; Spyker, D.; Hoffman, H. Comparative single-dose pharmacokinetics of amantadine hydrochloride and rimantadine hydrochloride in young and elderly adults. Antimicrob.Agents Chemother. 1985, 28, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintermeyer, S.M.; Nahata, M.C. Rimantadine: a clinical perspective. Ann Pharmacother. 1995, 29, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, D. Rimantadine.In: Referance Module Biomedical Science. Elsevier; 2016.
- Bright, R.A.; Medina, M.-. .J.; Xu, X.; et al. Incidence of adamantane resistance among influenza A (H3N2) viruses isolated worldwide from 1994 to 2005: a cause for concern. The Lancet. 2005, 366, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, I.G.; Hurt, A.C.; Iannello, P.; Tomasov, C.; Deed, N.; Komadina, N. Increased adamantane resistance in influenza A (H3) viruses in Australia and neighbouring countries in 2005. Antivir Res. 2007, 73, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Update: influenza activity - United States, 2009-10 season. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010, 59, 901–908.
- Dong, G.; Peng, C.; Luo, J.; et al. Adamantane-resistant influenza a viruses in the world (1902–2013): frequency and distribution of M2 gene mutations. PloS one. 2015, 10, e0119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, K.; Mitamura, K.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Goto, H.; Sugaya, N.; Kawaoka, Y. High frequency of resistant viruses harboring different mutations in amantadine-treated children with influenza. J Infect Dis. 2003, 188, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, F.; Jain, S.; Finelli, L.; et al. Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Investigation Team. Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med. 2009, 360, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deyde, V.M.; Xu, X.; Bright, R.A.; et al. Surveillance of resistance to adamantanes among influenza A (H3N2) and A (H1N1) viruses isolated worldwide. J Infec Dis. 2007, 196, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushina, N.A.; Govorkova, E.A.; Russell, C.J.; Hoffmann, E.; Webster, R.G. Contribution of H7 haemagglutinin to amantadine resistance and infectivity of influenza virus. J Gen Virol. 2007, 88, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnaccini, S.; Perez, D.R. H9 influenza viruses: an emerging challenge. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020, 10, ea038588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portsmouth, S.; Kawaguchi, K.S.; Arai, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Uehara, T. Cap-dependent Endonuclease Inhibitor S-033188 for the Treatment of Influenza: Results from a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo- and Active-Controlled Study in Otherwise Healthy Adolescents and Adults with Seasonal Influenza. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017, 4, S734–S734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Hirotsu, N.; et al. Baloxavir Marboxil for Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults and Adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2018, 379, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ison, M.G.; Portsmouth, S.; Yoshida, Y.; et al. Early treatment with baloxavir marboxil in high-risk adolescent and adult outpatients with uncomplicated influenza (CAPSTONE-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020, 20, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Baba, K.; Inoue, K.; et al. Comprehensive assessment of amino acid substitutions in the trimeric RNA polymerase complex of influenza A virus detected in clinical trials of baloxavir marboxil. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2021, 15, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checkmahomed, L.; Padey, B.; Pizzorno, A.; et al. In Vitro Combinations of Baloxavir Acid and Other Inhibitors against Seasonal Influenza A Viruses. Viruses. 2020, 12, e1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, A.; Bouvier, D.; Crépin, T.; et al. The cap-snatching endonuclease of influenza virus polymerase resides in the PA subunit. Nature. 2009, 458, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- XofluzaTM [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Pharmaceu-ticals, Inc; 2014.
- Omoto, S.; Speranzini, V.; Hashimoto, T.; et al. Characterization of influenza virus variants induced by treatment with the endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Hayden, F.G.; Kawaguchi, K.; et al. Treatment-emergent influenza variant viruses with reduced baloxavir susceptibility: impact on clinical and virologic outcomes in uncomplicated influenza. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2020, 221, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govorkova, E.A.; Takashita, E.; Daniels, R.S.; et al. Global update on the susceptibilities of human influenza viruses to neuraminidase inhibitors and the cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir, 2018-2020. Antiviral research 2022, 200, 105281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubareva, L.V.; Fry, A.M. Baloxavir and Treatment-Emergent Resistance: Public Health Insights and Next Steps. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2019, 221, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukao, K.; Noshi, T.; Yamamoto, A.; et al. Combination treatment with the cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil and a neuraminidase inhibitor in a mouse model of influenza A virus infection. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2018, 74, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, N.; Koshimichi, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Wajima, T. Evaluation of Drug-Drug Interaction Potential between Baloxavir Marboxil and Oseltamivir in Healthy Subjects. Clinical drug investigation. 2018, 38, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobar Vega, P.; Caldeira, E.; Abad, H.; Saad, P.; Lachance, E. Oseltamivir and baloxavir: Dual treatment for rapidly developing ARDS on a patient with renal disease. IDCases 2020, 21, e00819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Ison, M.G.; Mira, J.-P.; et al. Combining baloxavir marboxil with standard-of-care neuraminidase inhibitor in patients hospitalised with severe influenza (FLAGSTONE): a randomised, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled, superiority trial. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2022, 22, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




