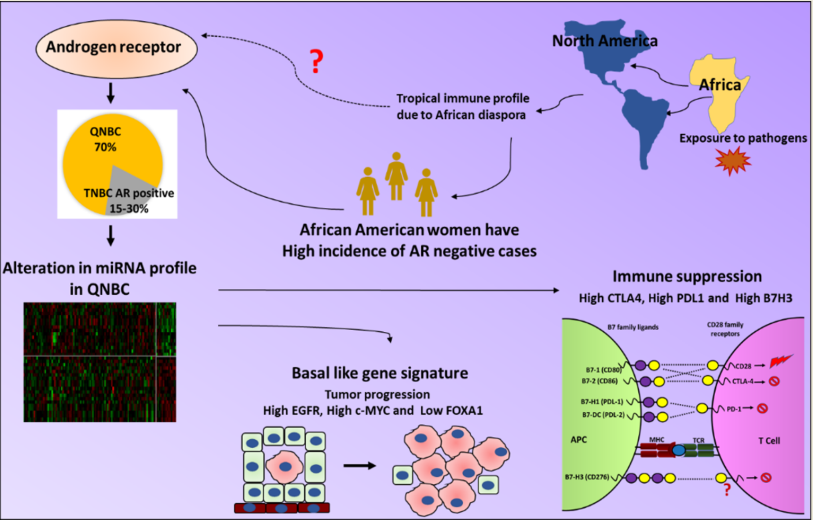
Background: We previously found that QNBC tumors are more frequent in African Americans compared to TNBC tumors. To characterize this subtype further, we sought to determine the miRNA-mRNA profile in QNBC patients based on race. Methods: Both miRNA and mRNA expression data were analyzed from TCGA and validated using datasets from the METABRIC, TCGA proteomic, and survival analysis by KMPLOT. Results: miRNA-mRNAs which include FOXA1 and MYC (mir-17/20a targets); GATA3 and CCNG2 (mir-135b targets); CDKN2A, CDK6, and B7-H3 (mir-29c targets); and RUNX3, KLF5, IL1-β, and CTNNB1 (mir-375 targets) were correlated with basal-like and immune subtypes in QNBC patients and associated with a worse survival. Conclusion: Thus, QNBC tumors have an altered gene signature implicated in racial disparity and poor survival.