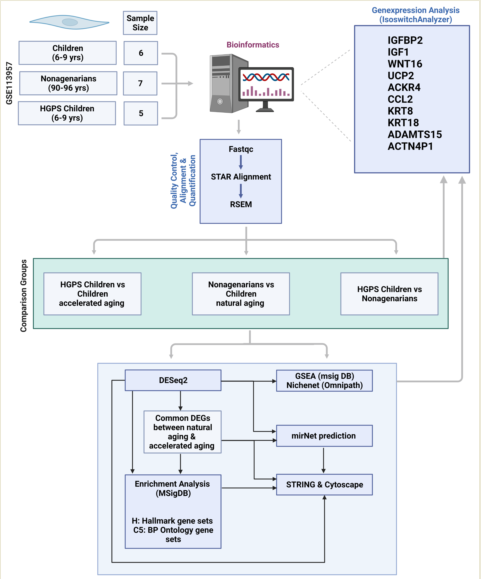
Abstract: Since ancient times aging has also been regarded as a disease, and humankind has always strived to extend the natural lifespan. Analyzing the genes involved in aging and disease allows for finding important indicators and biological markers for pathologies and possible therapeutic targets. An example of the use of omics technologies is the research regarding aging and the rare and fatal premature aging syndrome progeria (Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, HGPS). In our study, we focused on the in silico analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in progeria and aging, using a publicly available RNA Seq dataset (GEO dataset GSE113957) and a variety of bioinformatics tools. We identified several genes that appear to be involved both in natural aging and progeria (KRT8, KRT18, ACKR4, CCL2, UCP2, ADAMTS15, ACTN4P1, WNT16, IGFBP2). Further analyzing these genes and the pathways involved confirmed their possible roles in aging, suggesting the need for further in vitro and in vivo research. The graphical abstract illustrates the analysis workflow we used and will introduce in the following as an example to demonstrate the power of omics and bioinformatics.