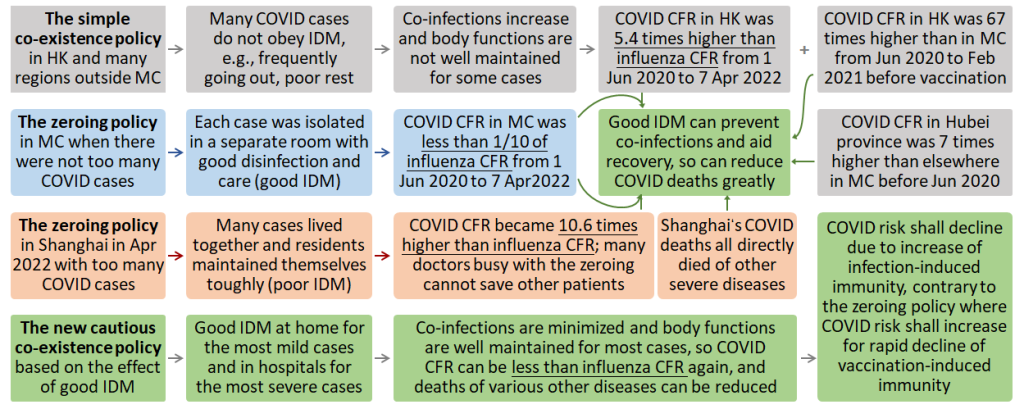
There are two contrary opinions regarding the risk if mainland China (MC) moves away from its zero-COVID policy. Some experts think the risk shall be much lower than influenza as per MC’s own COVID-19 case fatality rate (CFR), while some other experts think the risk shall be much higher than influenza as per the COVID-19 CFRs of other regions. We elucidate here that this and multiple other striking differences in the CFR between various scenarios all support and substantially resulted from the view that good IDM is highly powerful to mitigate COVID-19, where IDM (isolation-disinfection-maintenance) means isolation of COVID-19 cases from other people, disinfection of their living environments, and health maintenance (e.g., rest, nutrition, breathing). The high effect of good IDM is also supported by the theoretic functions of IDM in minimizing co-infections and maintaining body functions, and the fact that all the 505 COVID-19 deaths reported in MC in 2022 before May 5 died directly of severe underlying diseases with COVID-19. Although it is tough for people in poverty to obtain good IDM, good IDM can be feasible at home for the most mild cases and in hospitals for the most severe cases. Therefore, good IDM can be crucial to mitigating COVID-19 worldwide. It also suggests that the risk for China to end its zero-COVID policy depends on China’s control policies or measures. Based on the effect of IDM, the cautious co-existence policy was proposed for COVID-19 control. This policy could reduce the whole death toll in MC because good IDM is non-specific and can reduce deaths of various other diseases. The cautious co-existence policy (non-specific) and the vaccination policy (specific) aid each other to mitigate COVID-19, and they cannot replace each other. Those who are qualified in health for vaccination should be vaccinated against COVID-19 timely.