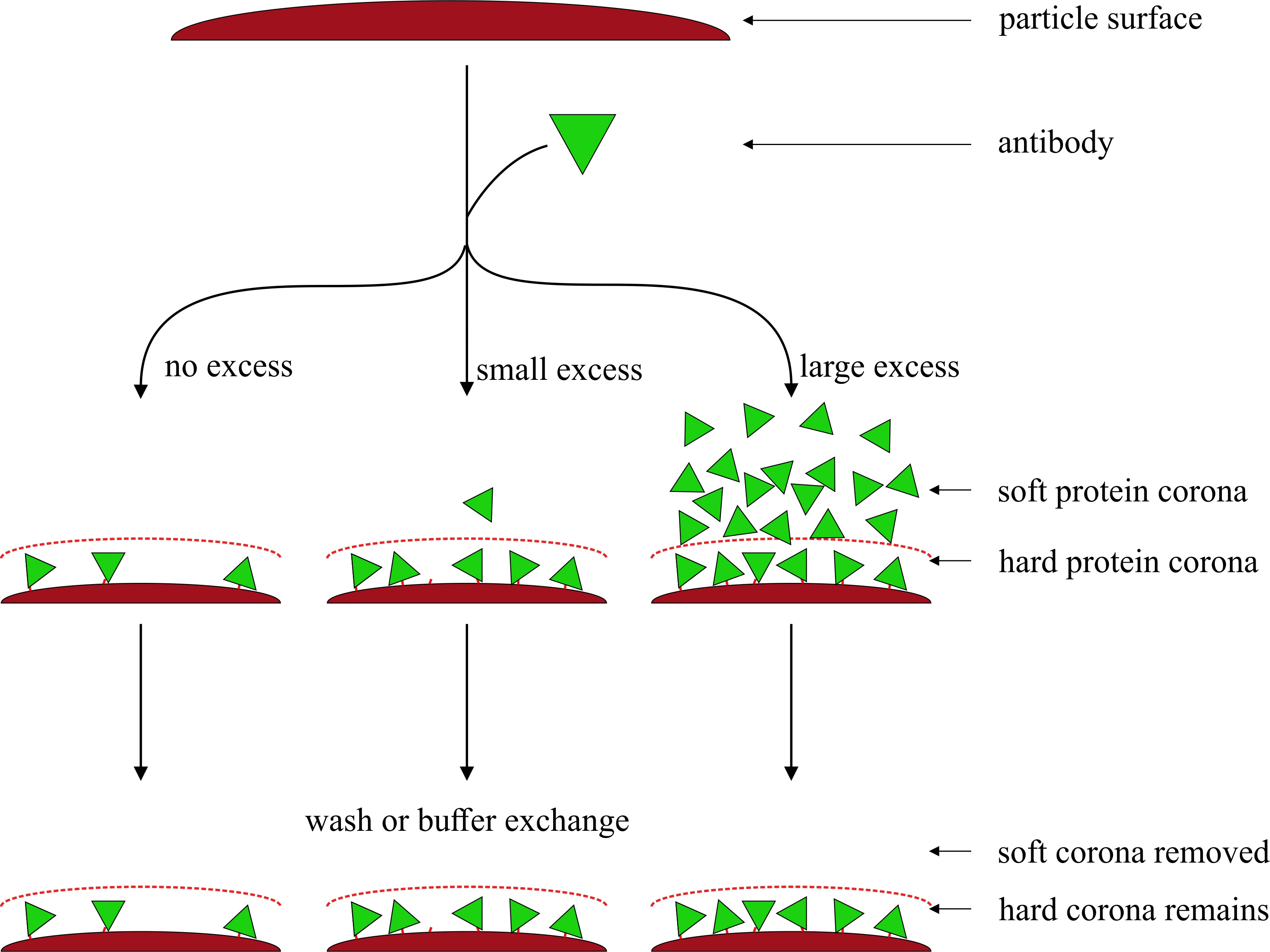
Protein immobilization for the functionalization of particles is used in various applications, including biosensors, lateral-flow immunoassays (LFIA), bead-based assays, and others. Common methods for the quantification of bound protein are measuring protein in the supernatant before and after coating and calculating the difference. This popular approach has the potential for a significant overestimation of the amount of immobilized protein since layers not directly bound to the surface (soft protein corona) are usually lost during washing and handling. Only the layer directly bound to the surface (hard corona) can be used in subsequent assays. A simplified amino acid analysis method based on acidic hydrolysis and RP-HPLC-FLD of tyrosine and phenylalanine (aromatic amino acid analysis, AAAA) is proposed to directly quantify protein bound to the surface of gold nano- and latex microparticles. The results are compared with indirect methods such as colorimetric protein assays, such as Bradford, bicinchoninic acid (BCA), as well as AAAA of the supernatant. For both particle types, these indirect quantification techniques show a protein overestimation of up to 1700% compared to the direct AAAA measurements. In addition, protein coating on latex particles was performed both passively through adsorption and covalently through EDC/sulfo-NHS chemistry. Our results showed no difference between the immobilization methodologies. This finding suggests that usual protein determination methods are no unambiguous proof of a covalent conjugation on particles or beads.