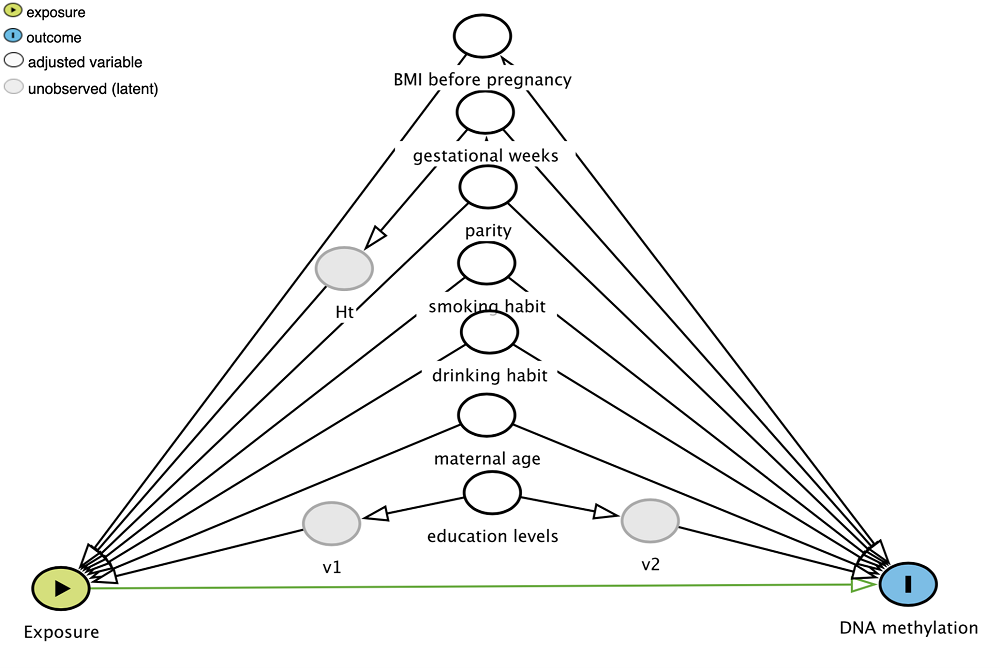
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism for gene expression modulation and can be used as a predictor of future disease risks. A prospective birth cohort study was performed to clarify the effects of neurotoxicants on child development, namely, the Tohoku Study of Child Development, in Japan. This study aimed to evaluate the association of prenatal exposure to five toxic metals—arsenic, cadmium, mercury, lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs, N = 166)—with global DNA methylation in umbilical cord blood DNA. DNA methylation markers, 5-methyl-2’-deoxycytidine (mC) and 5-hydroxymethyl-2’-deoxycytidine (hmC), were determined using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The mC content in cord blood DNA was positively correlated with Pb and Sb levels (r = 0.442 and 0.288, respectively) but not with cord blood PCBs. We also observed significant positive correlations among Pb levels, maternal age, and hmC content (r = 0.159 and 0.243, respectively). The multiple regression analysis among the potential predictors demonstrated consistent positive associations between Pb and Sb levels and mC and hmC content. Our results suggest that global DNA methylation is a promising biomarker for prenatal exposure to Pb and Sb.