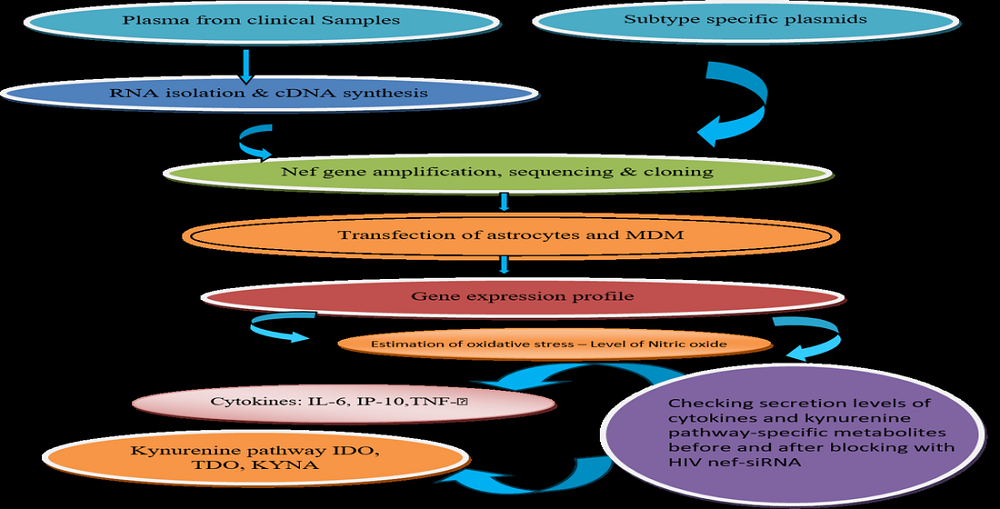
HIV-1 Nef is a multifunctional protein with well-known lethal properties. HIV infects various cells from the brain compartment and expressed nef is responsible for developing neuropathogenic potential. HIV-infected glial cells express nefvirotoxinand stimulate the cascade of various pathways to activate uninfected cells to release neurotoxic elements damaging cells themselves. A lot of genetic variabilities of this protein have been reported from patients with HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. To determine the neurotoxic potential of subtype-specific nef plasmids and nef plasmids of clinical samples with and without HAND were transfected in normal human astrocytes (NHA) and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) using nef-pCMV-HA plasmid constructs. Supernatants from subtype-specific Nef plasmids indicated the upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines. The induced expression might be due to the nef genetic variability or variations in the transfection efficiency and expression levels of nef.The mRNA expression of IL-6, IP-10, and TNF-α indicated upregulation of 5.0-fold in NHA and 3-fold in MDM with respect to empty vector control transfection. Further, the kynurenine metabolites were also assessed from culture supernatants of NHA and MDM indicating the upregulation of IDO and KYNU in NHA by 3.0-fold and 3.2-fold in MDM.The expression levels of nef and cytokines at the translational level were confirmed by western blotting and bio-plex Pro cytokine estimation assay respectively along with controls expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP).The oxidative stress was also found to be elevated as compared to control cells as determined by the estimation of nitric oxide from the culture supernatant to confirm the neurotoxic potential of HIV nef plasmids. The downregulation in the levels of cytokines, as well as kynurenine metabolites, was observed in culture supernatants after blocking the expression of nef using HIV nef siRNA. Phylogenetic analysis of Nef sequences indicated subtype C predominance except one sequence showing the partial sequence of HIV-1 subtype B sequence forming BC recombinantThe upregulation in the cytokine and pathway-specific metabolites might be linked with the neurotoxic potential of HIV-1 Nef leading to neuropathogenesis. In conclusion, the variation in the transfection efficiency, nef expression levels, and the genetic variability of Nef might be responsible for upregulating the expression levels of cytokines and kynurenine metabolites in astrocytes and MDM.