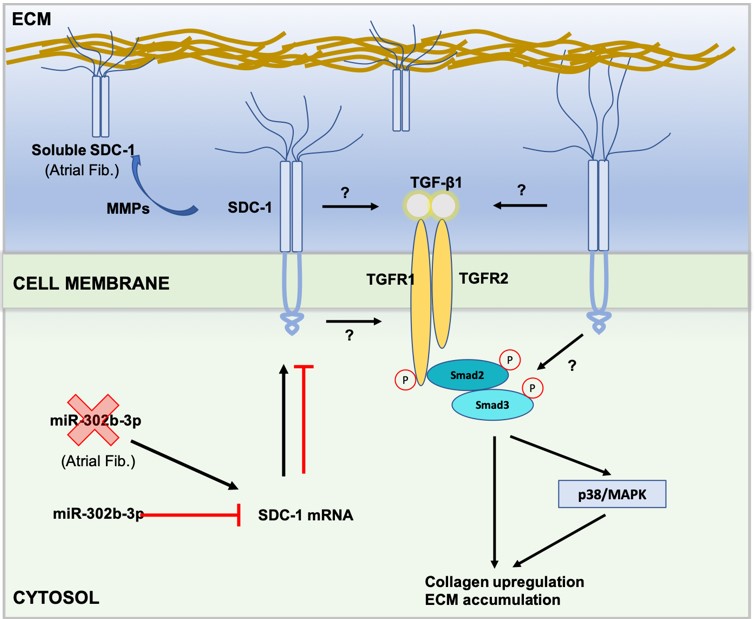
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a form of sustained cardiac arrhythmia and microRNAs (miRs) play crucial roles in pathophysiology of AF. To identify novel miR-mRNA pairs, we performed RNAseq from atrial biopsies of AF and non-AF patients. Differentially expressed miRs (11-down and 9-up) and mRNAs (95-up and 82-down) were identified and hierarchically clustered in a heat-map. Subsequently, GO, KEGG, and GSEA analyses were run to identify deregulated pathways. Then, miR targets were predicted in miRDB database, and a regulatory network of negatively correlated miR-mRNA pairs was constructed using Cytoscape. To select potential candidate genes from GSEA analysis, top-50 enriched genes in GSEA were overlaid with predicted targets of differentially deregulated miRs. Besides, protein-protein-interaction (PPI) network of enriched genes in GSEA was constructed, and subsequently GO and canonical pathway analyses were run for genes in PPI network. Our analyses showed that TNF-α, p53, EMT, and SYDECAN1 signaling were among the highly affected pathways in AF samples. SDC-1 (syndecan-1) was the top-enriched gene in p53, EMT, and SYDECAN1 signaling. Consistently, SDC-1 mRNA and protein levels were significantly higher in atrial samples of AF patients. Among negatively correlated miRs, miR-302b-3p was experimentally validated to suppress SDC-1 transcript levels. Overall, our results suggested that miR-302b-3p/SDC-1 axis may involve in pathogenesis of AF.