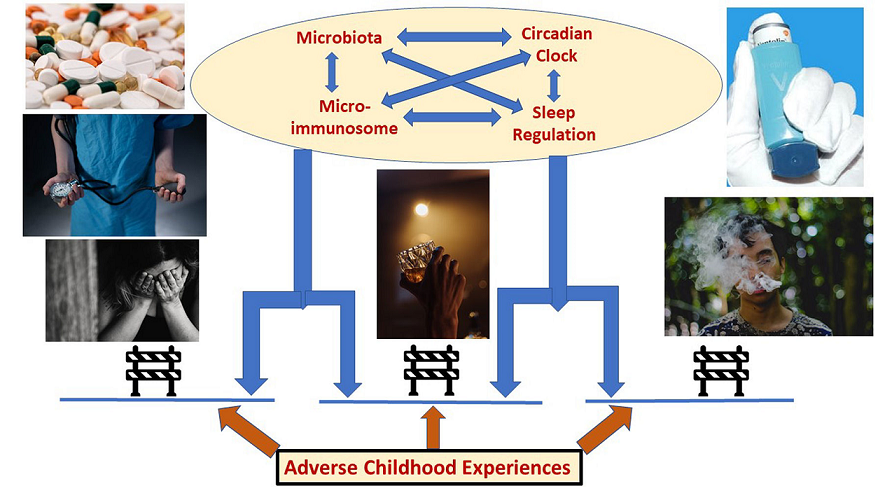
Adverse childhood experiences are known to program children for disrupted biological cycles, premature aging, microbiome dysbiosis, immune-inflammatory misregulation, and chronic disease multimorbidity. To date, the microbiome has not been a major focus of deprogramming efforts despite its emerging role in every aspect of ACE-related dysbiosis and dysfunction. This article examines: 1) the utility of incorporating microorganism-based, anti-aging approaches to combat ACE-programmed chronic diseases (also known as noncommunicable diseases and conditions, NCDs) and 2) microbiome regulation of core systems biology cycles that affect NCD comorbid risk. In this review microbiota influence over three key cyclic rhythms (circadian cycles, the sleep cycle, and the lifespan/longevity cycle) as well as tissue inflammation and oxidative stress are discussed as an opportunity to deprogram ACE-driven chronic disorders. Microbiota, particularly those in the gut, have been shown to affect host-microbe interactions regulating the circadian clock, sleep quality, as well as immune function/senescence and regulation of tissue inflammation. The microimmunosome is one of several systems biology targets of gut microbiota regulation. Furthermore, correcting misregulated inflammation and increased oxidative stress is key to protecting telomere length and lifespan/longevity and extending what has become known as the healthspan. This review article concludes that to reverse the tragedy of ACE-programmed NCDs and premature aging, managing the human holobiont microbiome should become a routine part of healthcare and preventative medicine across the life course.