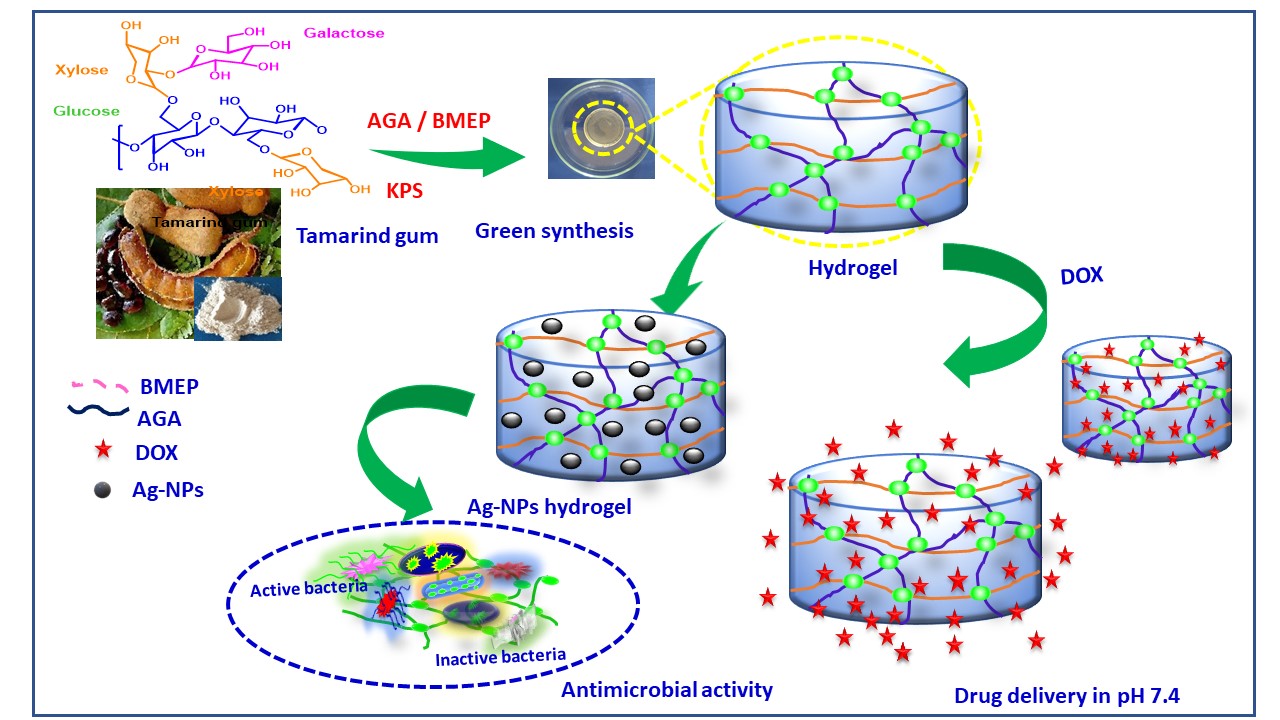
Novel pH responsive semi-interpenetrating polymer hydrogels based on tamarind gum-co-poly(acrylamidoglycolic acid) (TMGA) polymers have been synthesized using simple free radical polymerization in the presence of bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate as a crosslinker and potassium persulfate as a initiator. In addition, these hydrogels have been used as templates for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (13.4±3.6 nm in diameter, TMGA-Ag) by using leaf extract of Teminalia bellirica as reducing agent. Swelling kinetics and equilibrium swelling behavior of the TMGA hydrogels have been investigated in various pH environment the maxium % equilibrium swelling behavior observed i.e., 2882±1.2. The synthesized hydrogels and silver nanocomposites have been characterized by the UV, FTIR, XRD, SEM and TEM. TMGA and TMGA-Ag hydrogels have been investigated to study the characteristics of drug delivery and antimicrobial study. Doxorubicin hydrochloride, a chemotherapeutic agent successfully encapsulated with maximum encapulstaion efficiency i.e., 69.20±1.2 and performed in vitro release studies in pH physiological and gastric environment at 37 ℃. The drug release behavior is examined with kinetic models such as zero order, first order, Higuchi, Hixson Crowell, Korsmeyer-Peppas. These release data was the best fitted with the Korsemeyer-Peppas transport mechanism with n=0.91. Treatment effect on HCT116 Cell, human colon cancer cells were assessed with cell viability and cell cycle analysis. Antimicrobial activity of TMGA-Ag hydrogels is studied against to Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia. Finally, the results demonstrate that TMGA and TMGA-Ag are promising candidates for anti-cancer drug delivery and inactivation of pathogenic bacteria, respectively.