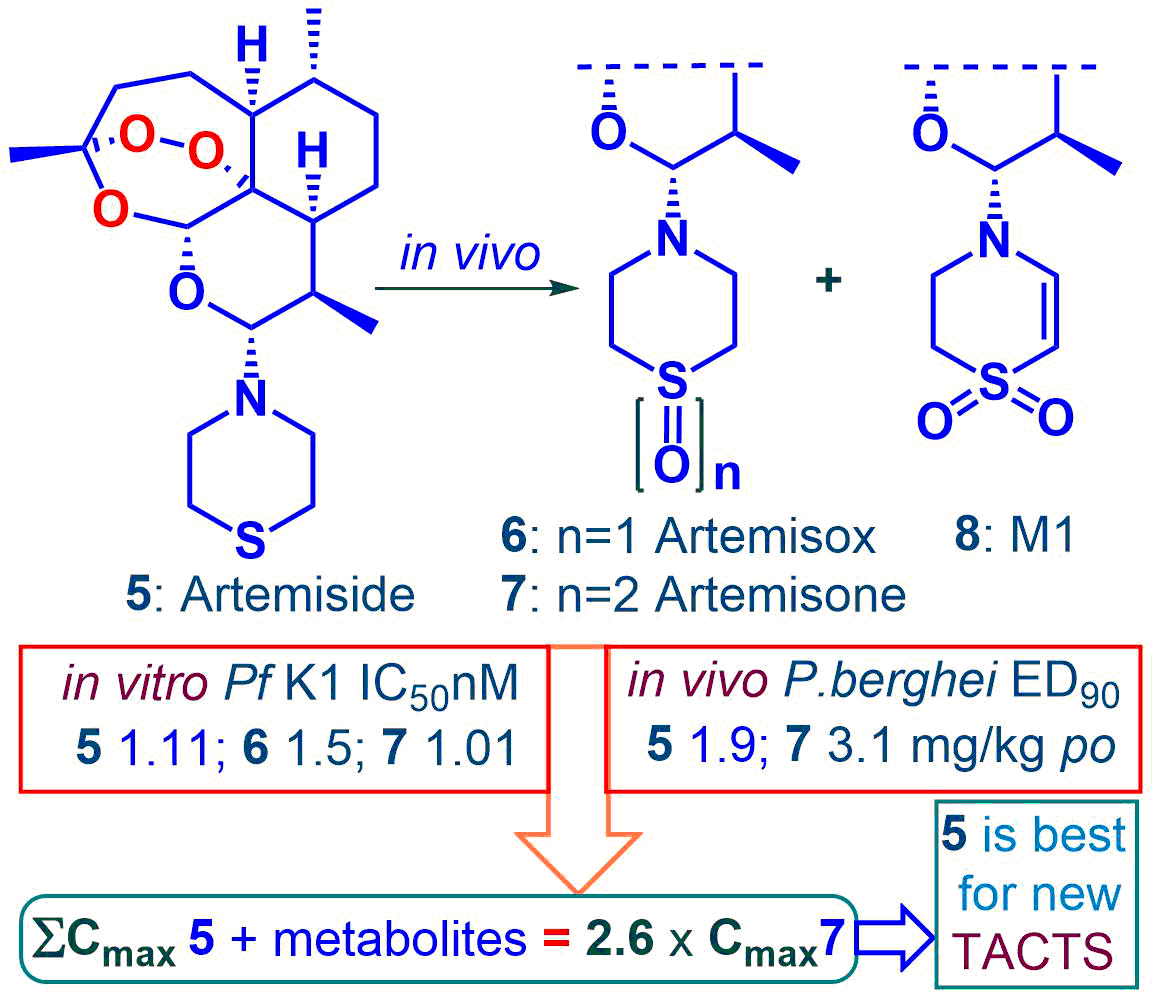
Because of the need to replace the current clinical artemisinins in artemisinin combination therapies, we are evaluating fitness of amino-artemisinins for this purpose. These include the thiomorpholine derivative artemiside obtained in one scalable synthetic step from dihydroartemisinin (DHA) and the derived sulfone artemisone. We have recently shown that artemiside undergoes facile metabolism via the sulfoxide artemisox into artemisone and thence into the unsaturated metabolite M1; DHA is not a metabolite. Artemisox and M1 are now found to be approximately equipotent with artemiside and artemisone in vitro against asexual P. falciparum (Pf) blood stage parasites (IC50 1.5 – 2.6 nM). Against Pf NF54 blood stage gametocytes, artemisox is potently active (IC50 18.9 nM early-stage, 2.7 nM late-stage). Comparative drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic (DMPK) properties were assessed via po and iv administration of artemiside, artemisox and artemisone in a murine model. Following oral administration, the composite Cmax value of artemiside plus its metabolites artemisox and artemisone formed in vivo is some 2.6-fold higher than that attained following administration of artemisone alone. Given that efficacy of short half-life rapidly-acting antimalarial drugs such as the artemisinins is associated with Cmax, it is apparent that artemiside will be more active than artemisone in vivo, due to additive effects of the metabolites. As is evident from earlier data, artemiside indeed possesses appreciably greater efficacy in vivo against murine malaria. Overall, the higher exposure levels of active drug following administration of artemiside coupled with its synthetic accessibility indicate it is much the preferred drug for incorporation into rational new artemisinin combination therapies.