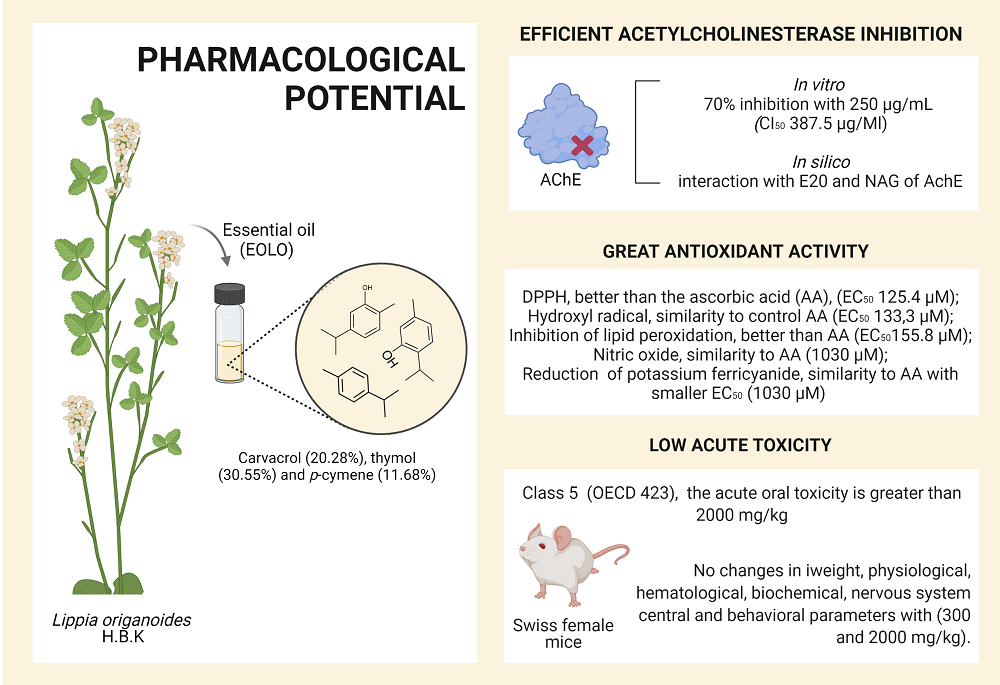
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by a progressive decline of cognitive functions. The class of drugs used for the treatment are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Essential oils have contributed to folk medicine and discovery of new drugs for a long time. The purpose of the study was to investigate the in vitro and in silico the anti-acetylcholinesterase activity, as well as acute toxicity of the essential oil of Lippia origanoides. EOLO was obtained by hydrostelting and analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The inhibition assay of acetylcholinesterase enzyme activity was evaluated in vitro, as well as in silico by docking. The effects of EOLO on hematological, biochemical and behavioral parameters were analyzed in mices. We expose that EOLO shows good anti-acetylcholinesterase activity and low toxicity, possibly resulting from the action of the majority compounds thymol, carvacrol and p-cymene. The anti-acetylcholinesterase potential in vitro demonstrating a 70% inhibition. The docking results elucidated the participation of the major phenolics in AChE inhibition by interacting with the catalytic cavity of AchE. The acute oral toxicity test classified as low toxicity. These results contribute to expand the knowledge about essential oil of Lippia origanoides. Therefore, appears to be promising for herbal medicine production with anti-acetylcholinesterase and antioxidant activity.