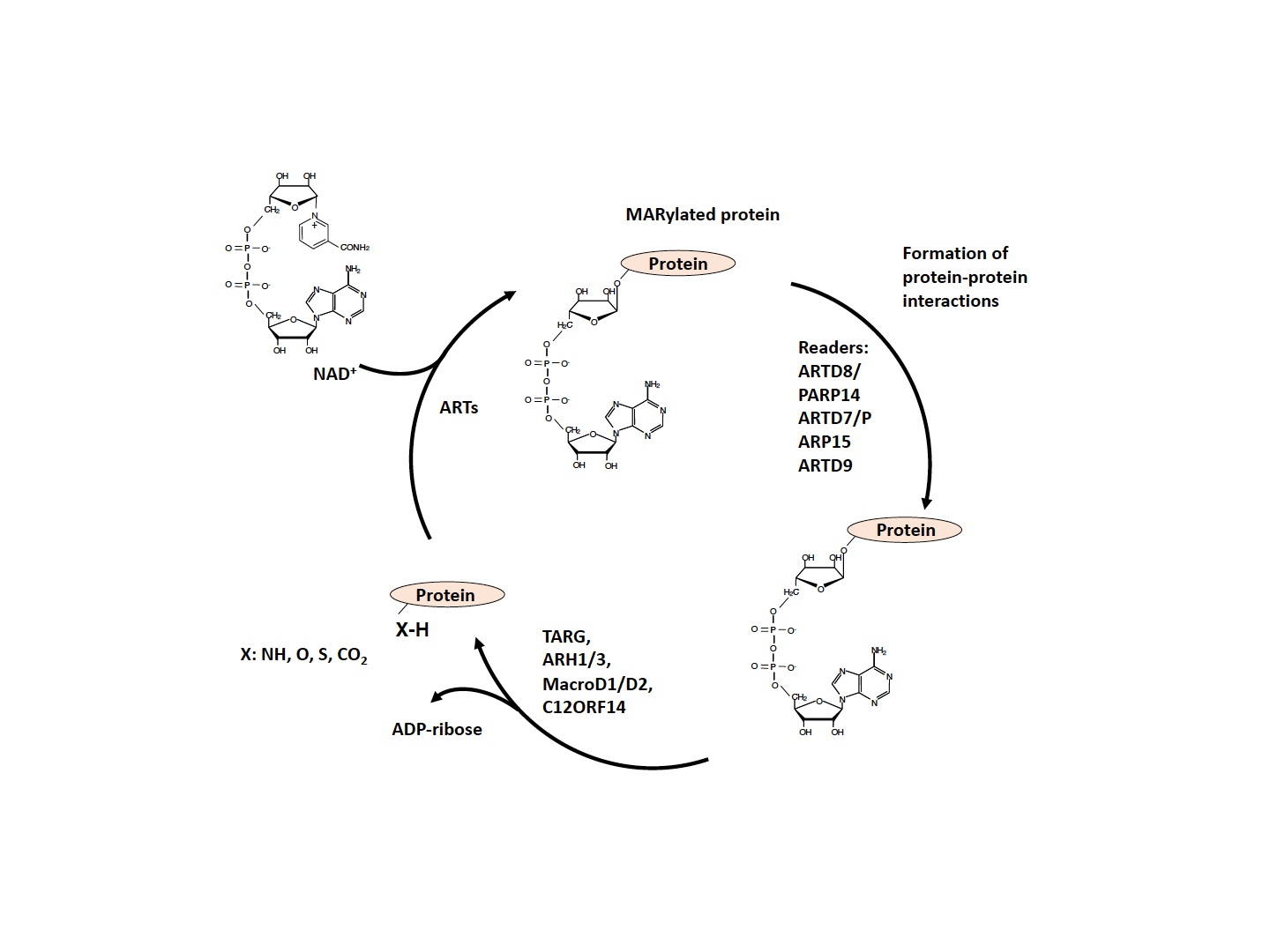
Among post-translational modifications of proteins, ADP-ribosylation has been studied for over fifty years, assigning to this PTM a large set of functions, including DNA repair, transcription and cell signaling. This review presents an update on the function of a large set of enzyme writers, the readers that are recruited by the modified targets, and the erasers that reverse the modification to the original amino acid residue, removing the covalent bonds formed. In particular, the review provides details on the involvement of the enzymes performing MAR/PAR cycling in cancers. Of note, there is potential for application of the inhibitors developed for cancer also in the therapy of non-oncological diseases such as the protection against oxidative stress, suppression of inflammatory responses, and the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. This field of studies is not concluded, since novel enzymes are being discovered at a rapid pace.