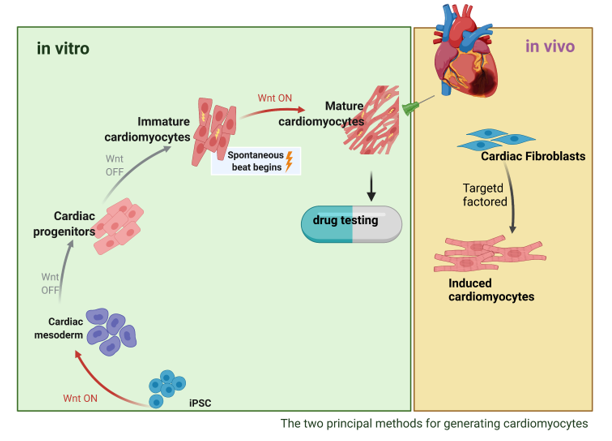
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is one of the contributing factors to more than one-third of human mortality and the leading cause of death worldwide. Cardiac myocyte death is a fundamental process in cardiac pathologies caused by various heart diseases, including myocardial infarction. Thus, strategies for replacing fibrotic tissue in the infarcted region with functional myocardium have long been a goal of cardiovascular research. This review focuses primarily on induced-pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which have emerged as perhaps the most promising source of cardiomyocytes for both therapeutic applications and drug testing. We also briefly summarize other stems- and progenitor-cell populations that have been used for regenerative myocardial therapy and attempt to generate cardiomyocytes directly from cardiac fibroblasts (i.e., transdifferentiation), which, if successful, may enable the pool of endogenous cardiac fibroblasts to be used as an in-situ source of cardiomyocytes for myocardial repair.