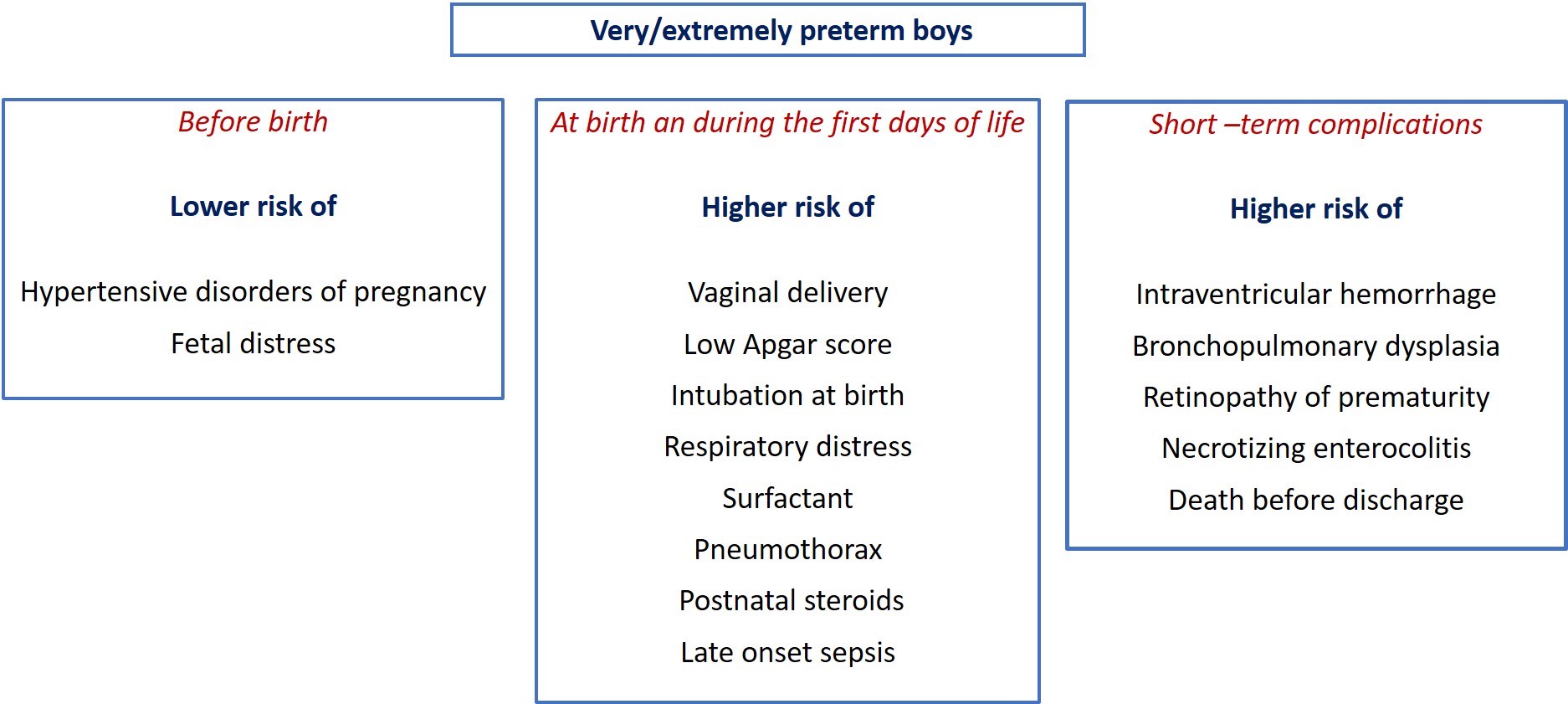
A widely accepted concept is that boys are more susceptible than girls to oxidative stress related complications of prematurity, including bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), and periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). We aimed to quantify the effect size of this male disadvantage by performing a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies exploring the association between sex and complications of prematurity. Risk ratios (RRs) and 95% CIs were calculated by a random-effects model. Of 1365 potentially relevant studies, 41 met the inclusion criteria (625680 infants). Male sex was associated with decreased risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, fetal distress, and C-section, but increased risk of low Apgar score, intubation at birth, respiratory distress, surfactant use, pneumothorax, postnatal steroids, late onset sepsis, any NEC, NEC>stage 1 (RR 1.12, CI 1.06-1.18), any IVH, severe IVH (RR 1.28, CI 1.22-1.34), severe IVH or PVL, any BPD, moderate/severe BPD (RR 1.23, CI 1.18-1.27), severe ROP (RR 1.14, CI 1.07-1.22), and mortality (RR 1.23, CI 1.16-1.30). In conclusion, preterm boys have higher clinical instability and greater need for invasive interventions than preterm girls. This leads to a male disadvantage in mortality and short-term complications of prematurity.