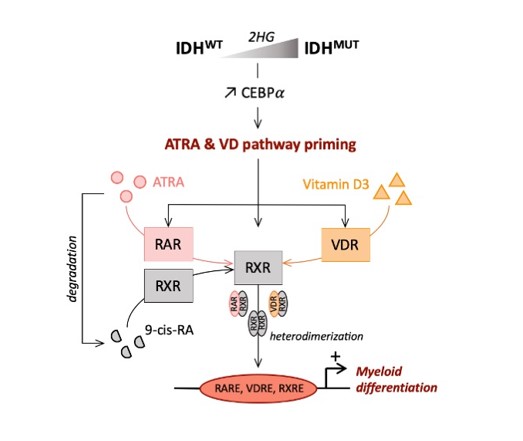
Relapses and resistance to therapeutic agents are major barriers for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. This unfavorable circumstance emphasizes the need for new strategies targeting drug-resistant cells. As IDH mutation is present in the preleukemic stem cells and systematically conserved at relapse, targeting mutant IDH cells would be essential to achieve a long-term remission in the AML subgroup with IDH mutation. Here, using a panel of human AML cell lines and primary AML patient specimens harboring IDH mutation, we showed that the presence of IDH mutation through the production of an oncometabolite (R)-2-HG induces vitamin D receptor related transcriptional programs, priming these AML cells to differentiate with pharmacological doses of ATRA or/and VD. This activation occurs in a CEBP-dependent manner. Accordingly, our findings illuminate potent and cooperative effects of IDH mutation and vitamin D pathway to differentiate in AML, revealing a novel therapeutic approach easily transferable/immediately applicable in clinics for this subgroup of AML patients.