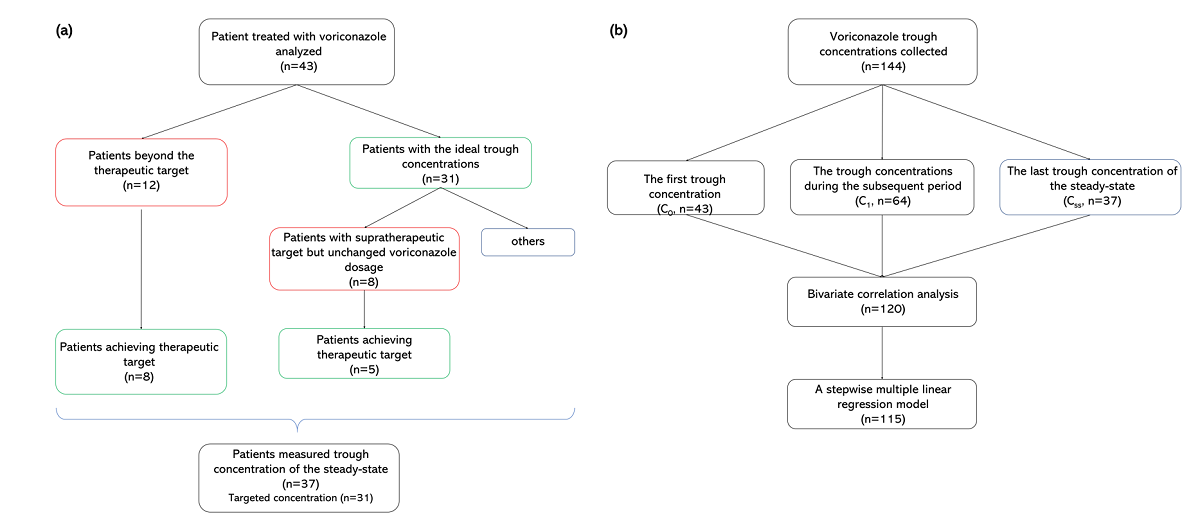
This prospective observational study aimed to describe voriconazole administrations and trough concentrations in patients with Child-pugh class C clinically, and to investigate the variability of trough concentration. A total of 144 voriconazole trough concentrations from 43 Child-pugh class C patients were analyzed. The majority of patients (62.8%) received adjustments. The repeated measured trough concentration was higher than the first and final ones generally (median, 4.33 vs. 2.99, 3.90 mg/L). Eight patients with ideal initial concentration later got supratherapeutic with no adjusted daily dose, implying accumulation. There was a significant difference in concentrations among the six groups by daily dose (P=0.006). The bivariate correlation analysis showed that sex, CYP2C19 genotyping, daily dose, prothrombin time activity, international normalized ratio, platelet, and Model for end-stage liver disease score were significant factors for concentration. Subsequently, the first four factors mentioned above entered into a stepwise multiple linear regression model (variance inflation factor < 5), implying that CYP2C19 testing makes sense for precision medicine of Child-pugh class C cirrhosis patients. The equation fits well and explains the 34.8% variety of concentrations (R^2 = 0.348). In conclusion, it needs more cautious administration clinically due to no recommendation for Child-pugh class C patients in the medication label. The adjustment of the administration regimen should be mainly based on the results of repeated therapeutic drug monitoring.