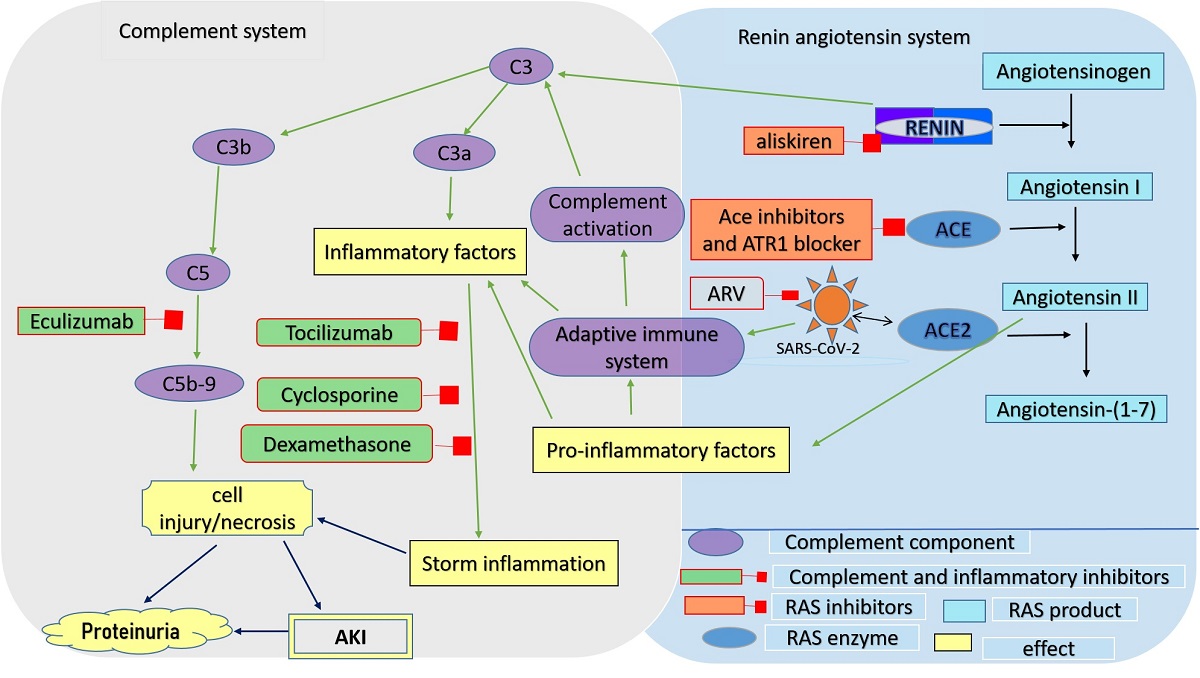
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). To contain the virus, numerous preventive measures have been taken including isolation of patients, careful infection control, social distancing, and taking vaccine. So far, new confirmed and death cases are still increasing. SARS-CoV-2 invades cells by using the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ACE2 is an essential enzyme of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) which converts angiotensin II (Ang II) to angiotensin (1-7). ACE2 is expressed in different organs, including lung, heart, and kidney. A high number of COVID-19 patients developed kidney injury has been reported. Renal impairment and acute injury are associated with mortality of COVID-19, which is 14-16 times higher than other general patients. Acute Kidney Injury has been occured in 2.9 up to 43% of intensive care unit patients. The increasing evidence show that the components of RAS can activate the complement cascade, and cytokines production. Kidney injury caused by SARS-CoV-2 is related mainly to systemic and local inflammation. Moreover, the uncontrolled immune responses mediated by SARS-CoV-2 including hypercytokinaemia, secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, antibody dependent enhancement, complement system, and phagocytic cells activation can contribute in the virus pathogenesis leading to associated renal dysfunction. However, the role and crosstalk between of RAS components and immune response in mediating kidney injury remain undefined. In this review, we focus on the recent studies to provide the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 interacting with RAS and immune responses to mediate kidney injury.