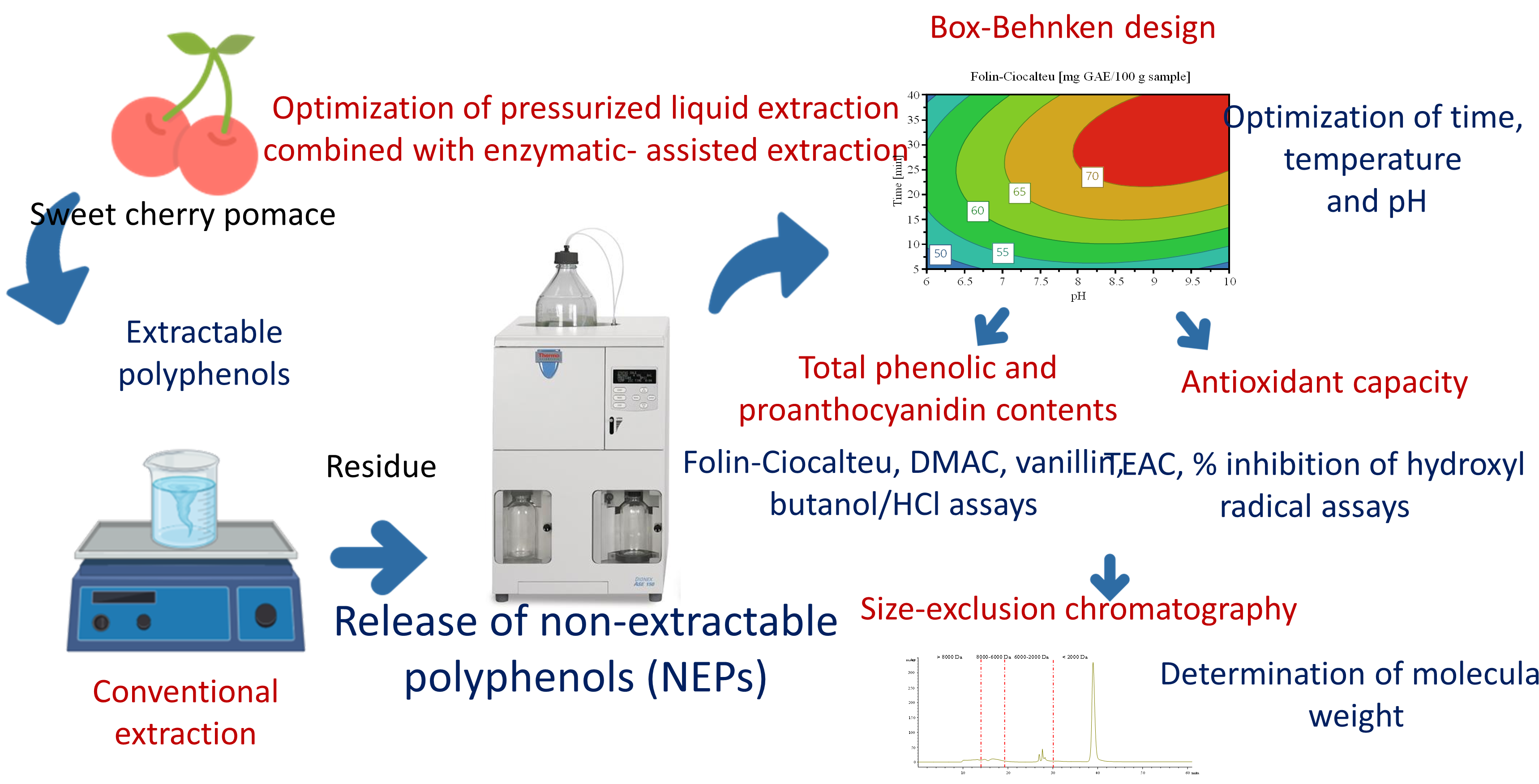
Sweet cherry pomace is a by-product that can be a source of bioactive phenolic compounds. Usually, polyphenols have been extracted using conventional extraction methodologies. However, a significant fraction, called non-extractable polyphenols (NEPs), remains retained in the conventional extraction residues. Therefore, this work is aimed, for the first time, to investigate the release of NEPs from cherry pomace combining pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) and enzyme-assisted extraction (EAE) using Promod enzyme. A response surface methodology was employed to study the influence of temperature, time, and pH on the NEPs extraction. The response variables were the total phenolic content (TPC) measured by Folin-Ciocalteu method, total proanthocyanidin (PA) content evaluated by vanillin, DMAC, and butanol/HCl assays, and total antioxidant capacity determined by Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity and inhibition of hydroxyl radical assays. The results indicated that PLE-EAE was more suitable and selective to obtain NEPs from sweet cherry pomace than PLE alone. In fact, the extracts obtained by PLE-EAE displayed higher TPC, PA content, and bioactivity than the extracts obtained by PLE under the same extraction conditions, and those obtained by conventional methods. Moreover, size-exclusion chromatography profiles showed that the combination of PLE and EAE enabled the recovery of NEPs with higher molecular weight than PLE without EAE treatment.