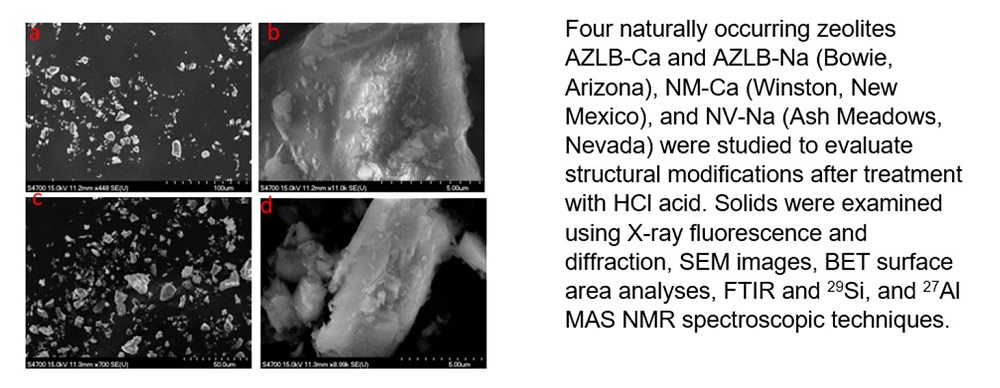
Four naturally occurring zeolites AZLB-Ca and AZLB-Na (Bowie, Arizona), NM-Ca (Winston, New Mexico), and NV-Na (Ash Meadows, Nevada) were studied to evaluate structural modifications after treatment with HCl acid. AZLB-Ca and AZLB-Na are chabazite-like species and become amorphous when boiled in concentrated HCl acid as confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction. In contrast, NM-Ca and NV-Na which are clinoptilolite-like species withstood boiling in concentrated HCl acid. This treatment removes calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, aluminum, and iron atoms or ions from the framework while leaving the silicon framework intact as confirmed via X-ray fluorescence and diffraction. SEM images on calcined and HCl treated NV-Na were obtained. BET surface area analysis confirmed an increase in surface area for the two zeolites after treatment, NM-Ca (20.0(1) to 111(4) m2/g) and NV-Na (19.0(4) to 158(7) m2/g). 29Si and 27Al MAS NMR were performed on the natural and treated NV-Na zeolite and the data for the natural NV-Na zeolite suggested a Si:Al ratio of 4.33 similar to that determined by X-Ray fluorescence of 4.55. Removal of lead ions from solution decreased from the native (NM-Ca, 0.27(14), NV-Na, 1.50(17) meq/g) compared to the modified zeolites (30 min HCl treated NM-Ca 0.06(9) and NV-Na, 0.41(23) meq/g) and also decreased upon K+ ion pretreatment in the HCl modified zeolites.