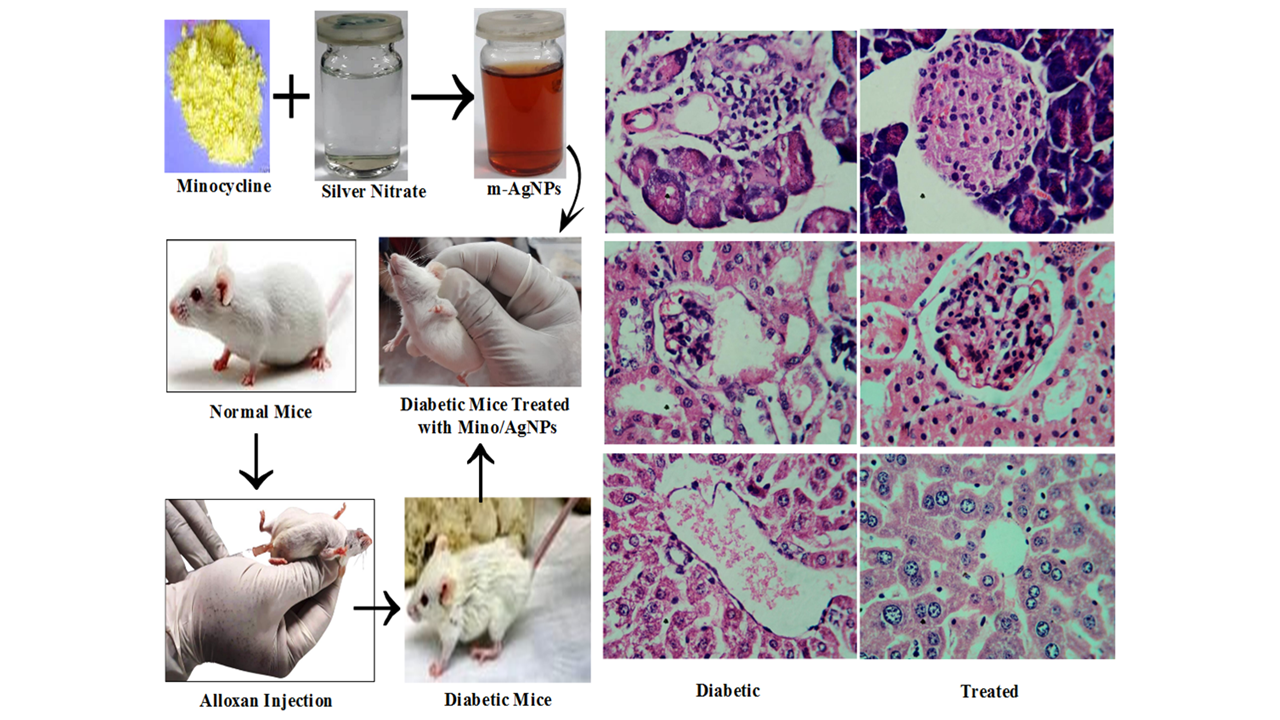
Diabetes is a life-threatening disease and chronic diabetes affects the parts of the body including the liver, kidney and pancreas. The root cause of diabetes is mainly associated with oxidative stress produced by reactive oxygen species. The minocycline is a polyphenolic drug with excellent antioxidant activities. The objective of the present study was to investigate the antidiabetic potential of minocycline modified silver nanoparticles (Mino/AgNPs) against alloxan-induced diabetic mice. The Mino/AgNPs were synthesized using minocycline as reducing and stabilizing agents. UV-vis, FTIR, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were applied for the characterization of Mino/AgNPs. The 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging assay was conducted to determine the antioxidant potential of newly synthesized Mino/AgNPs. The results revealed that the Mino/AgNPs showed higher radical scavenging activity (IC50 = 19.7 µg/mL) as compared to the minocycline (IC50 = 26.0 µg/mL) and ascorbic acid (IC50 = 25.2 µg/mL). Further, the Mino/AgNPs were successfully employed to examine their antidiabetic potential against Alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Hematological results showed that the mice treated with Mino/AgNPs demonstrated a significant decrease in fasting blood glucose level and lipid profile as compared to the diabetic group. The histopathological examination confirmed that the diabetic mice treated with Mino/AgNPs showed significant recovery and revival of histo-morphology of kidney, central vein of liver and islet cells of the pancreas compared to the diabetic mice. Hence Mino/AgNPs have good antidiabetic potential and could be an appropriate nanomedicine to prevent the development of diabetes.