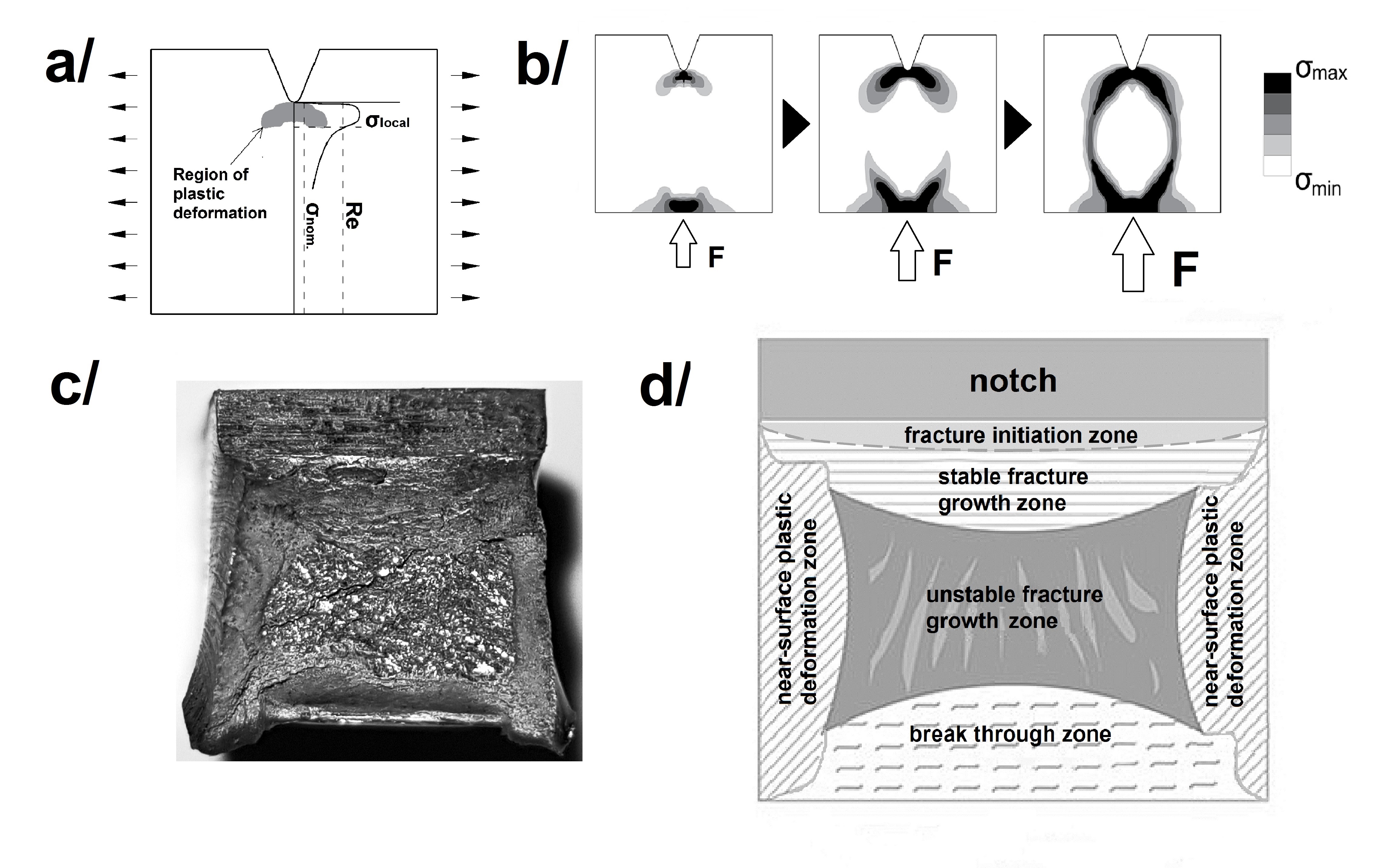
The change in the value of the breaking energy is discussed here for selected steel grades used in building structures after subjecting the samples made of them to episodes of heating in the steady-state heating regime and then cooling in a simulated fire conditions. These changes were recorded based on the instrumented Charpy impact tests, in relation to the material initial state. The S355J2+N, 1H18N9T steels and also X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 duplex steel were selected for detailed analysis. The fire conditions were modelled experimentally by heating the samples and then keeping them for a specified time at a constant temperature of: 600°C (first series) and 800°C (second series), respectively. Two alternative cooling variants were investigated in the experiment: slow cooling of the samples in the furnace, simulating the natural fire progress, without any external extinguishing action, and cooling them in water mist simulating an extinguishing action by a fire brigade. The temperature of the tested samples was set at the level -20oC and alternatively at the level + 20oC. The conducted analysis is aimed at assessing the risk of sudden, catastrophic fracture of load-bearing structure made of steel degraded as a result of a fire previously occurred with different development scenarios.