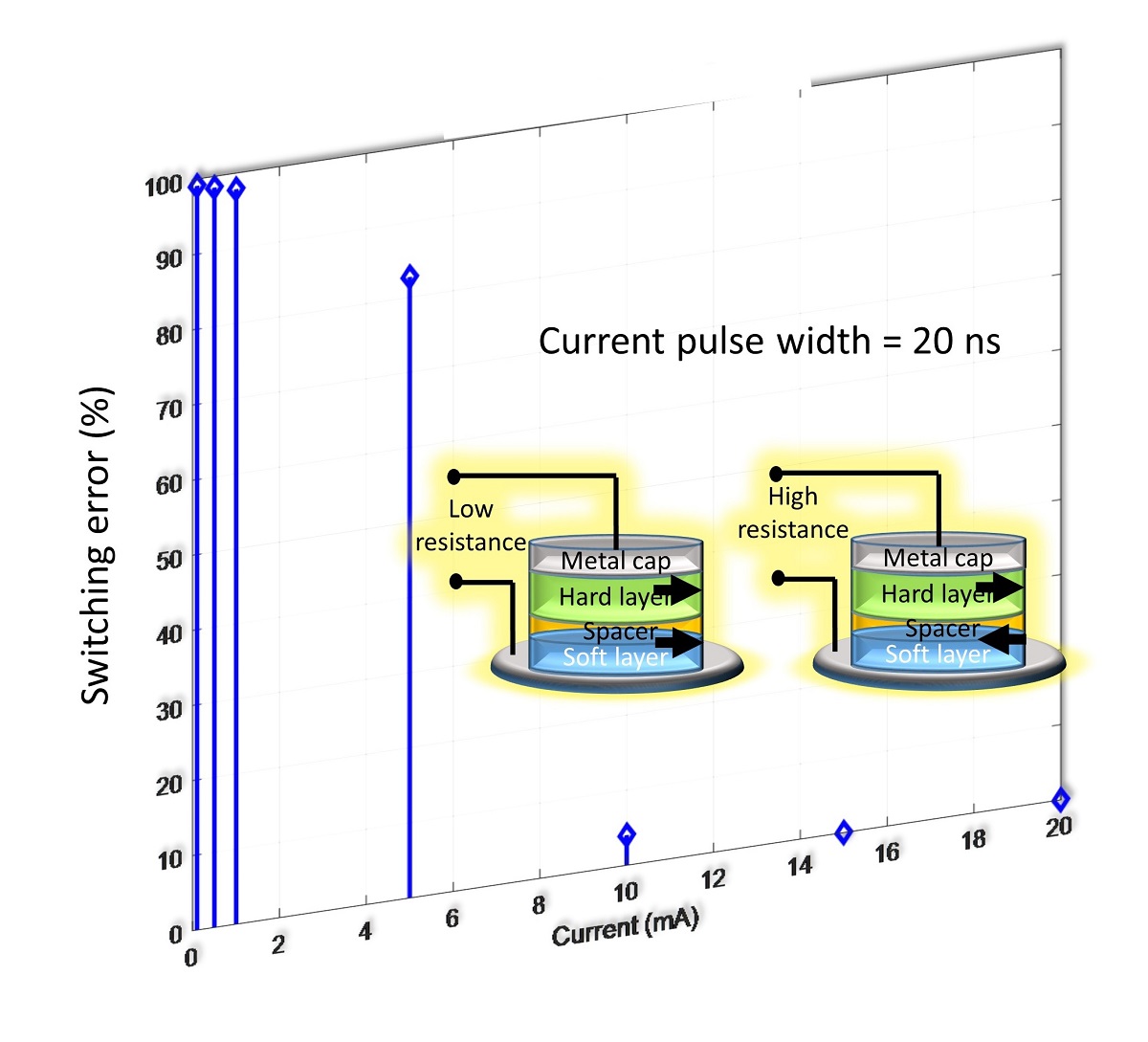
Binary switches, which are the primitive units of all digital computing and information processing hardware, are usually benchmarked on the basis of their ‘energy-delay product’ which is the product of the energy dissipated in completing the switching action and the time it takes to complete that action. The lower the energy-delay product, the better the switch (supposedly). This approach ignores the fact that lower energy dissipation and faster switching usually come at the cost of poorer reliability (i. e. higher switching error rate) and hence the energy-delay product alone cannot be a good metric for benchmarking switches. Here, we show the trade-off between energy dissipation, energy-delay product and error-probability, for both an electronic switch (a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor) and a magnetic switch (a magnetic tunnel junction switched with spin transfer torque). As expected, reducing energy dissipation and/or energy-delay-product generally results in increased switching error probability and reduced reliability.