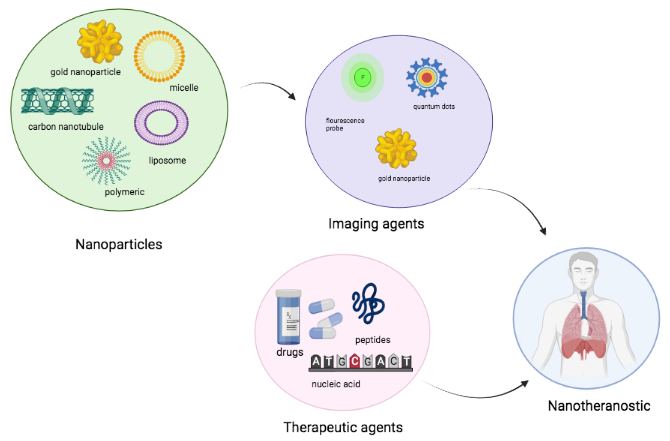
Background: Convectional methods for drug delivery often faces setbacks due to systemic distribution, short half-life and degradation of therapeutics and therefore reduce concentrations of drug available to target tissue. Nanotheranostic provide a novel method for treating and diagnosing diseases Methodology: collection and review of relevant literatureResult: while nanotheranostic offer advantage of personalized medicine and often combines diagnosis and therapy using single molecular approach, nuclear medicine relies on radioactive isotopes to diagnosed and destroys cancer cells. In both cases, nanocarriers such as lipid-based, polymer-based, drug-conjugate, inorganic nanoparticles are used to deliver drugs/probes/isotopes to target site, generating images and thereafter chemotherapy/radiotherapy begins.Conclusion: Nanotheranostic plays important role in diseases diagnostic, therapy, imaging, monitoring of disease progression / response through the use of nanocarriers. This is made possible through nanoparticles/nanocarriers that delivers drug to the target tissues/cells.