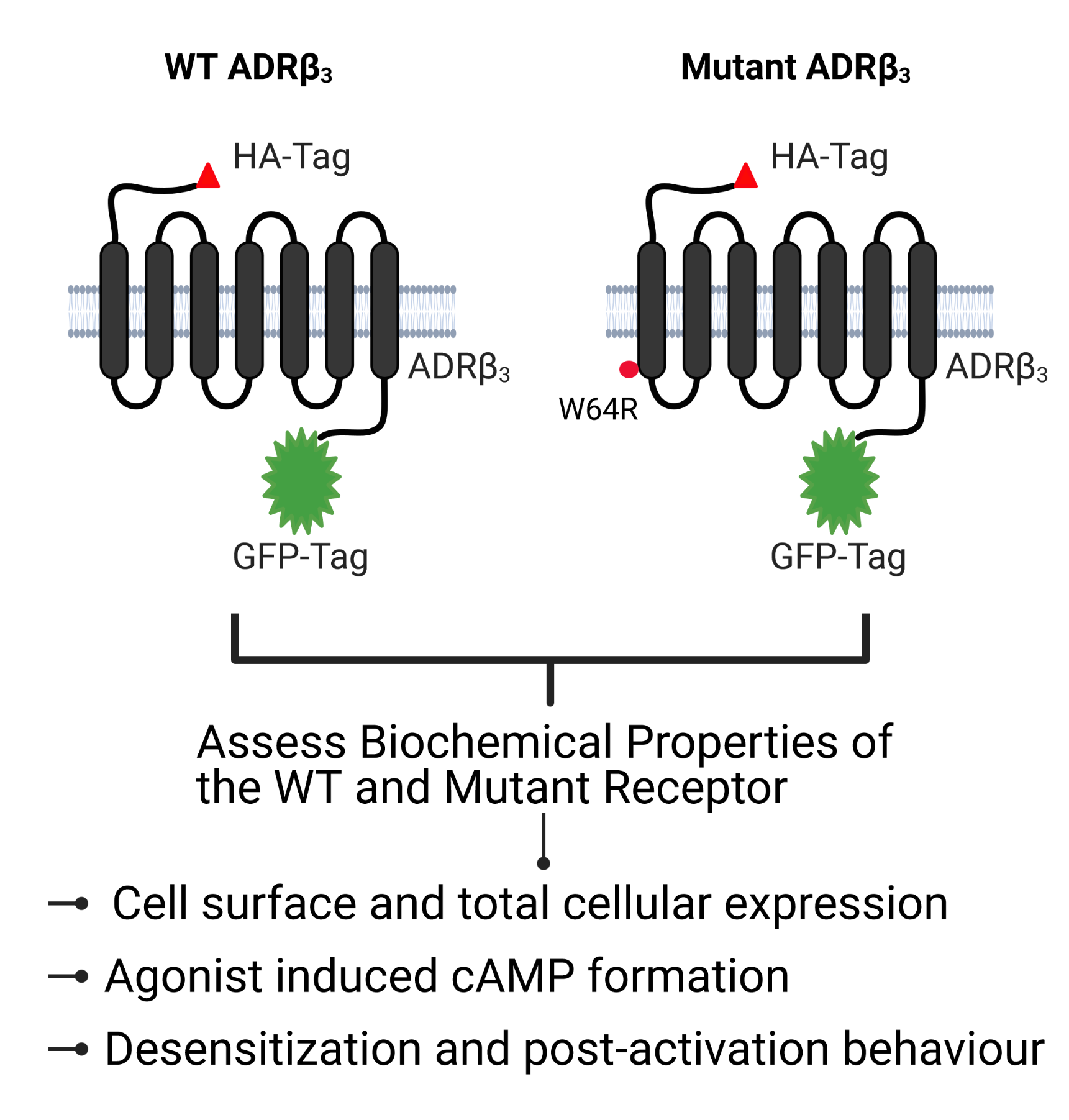
Adrenergic receptor β3 (ADRβ3) is a member of the rhodopsin-like G protein-coupled receptor family. The binding of the ligand to ADRβ3 activates adenylate cyclase and increases cAMP in the cells. ADRβ3 is highly expressed in white and brown adipocytes and controls key regulatory pathways of lipid metabolism. Trp64Arg (W64R) polymorphism in the ADRβ3 has been associated with the early development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, lower resting metabolic rate, abdominal obesity, and insulin resistance. It is unclear how the substitution of W64R affects the functioning of ADRβ3. This study was initiated to functionally characterize this obesity-linked variant of ADRβ3. We evaluated in detail the expression, subcellular distribution, and post-activation behavior of the WT and W64R ADRβ3 using a single cell quantitative fluorescence microscopy. When expressed in HEK 293 cells, ADRβ3 shows a typical distribution displayed by other GPCRs with a predominant localization at the cell surface. Unlike Adrenergic receptor β2 (ADRβ2), agonist induced desensitization of ADRβ3 does not involve loss of cell surface expression. WT and W64R variant of ADRβ3 displayed comparable biochemical properties and there was no significant impact of the substitution of Tryptophan with Arginine on the expression, cellular distribution, signaling, and post-activation behavior of ADRβ3. The obesity-linked W64R variant of ADRβ3 is indistinguishable from the WT ADRβ3 in terms of expression, cellular distribution, signaling, and post-activation behavior.