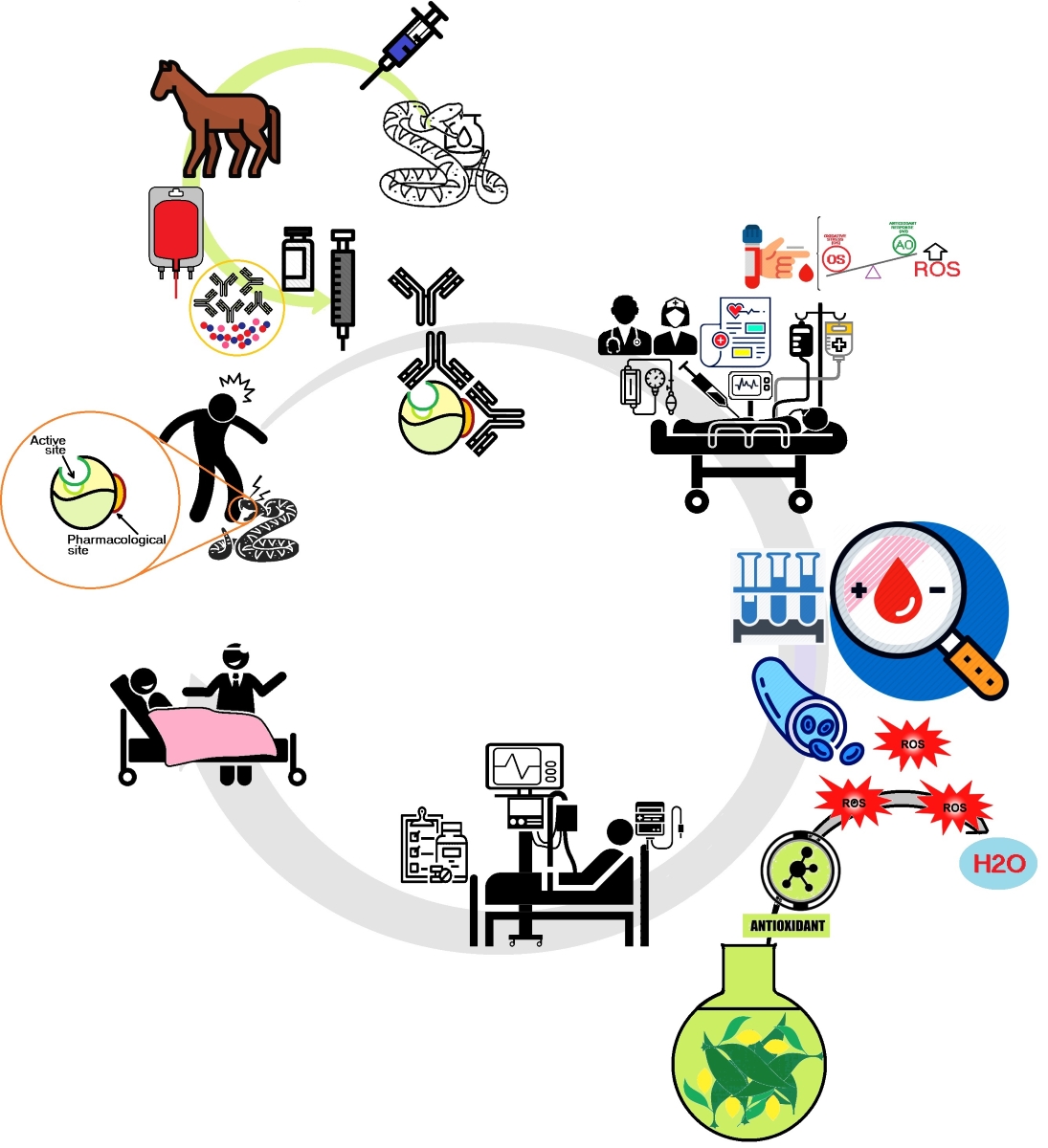
Background: Clinical cases reports with snake accidents show that venom bite induces increased oxidative stress including several markers of lipid peroxidation and other oxidative stress marker in plasma. Methods: The main findings of this work were performed with BthTx-II on paw edema of animals treated with the toxin and biochemical measurement of COX-2, PGE2, MDA and the effects of peroxiredoxin inhibitors on edema and myotoxicity were also evaluated. Results: The results show that edema and myotoxocity induced by PLA2 (BthTx-II) induces a strong mobilization of arachidonic acid and an increase in cellular oxidative stress as measured by increased malondialdehydo (MDA) concentration and protein carbonylation. Thus, these findings establish the strong link between oxidative stress, arachidonic acid mobilization and that these events may explain the presence of oxidative stress markers in snake-bitten patients. Experiments performed with animals previously treated with commercially purchased inhibitors showed enzymes such as thioredoxin (TXN), thioredoxin reductase (TXNRD) and other glutathione (GSH)-related antioxidant defenses could play an essential role controlling and defining the end of edema on the late phase of PLA2 BthTx-II-induced process. Conclusion. This study showed that thioate-dependent antioxidant enzymes play an important role in resolving the edema induced by BthTx-II.