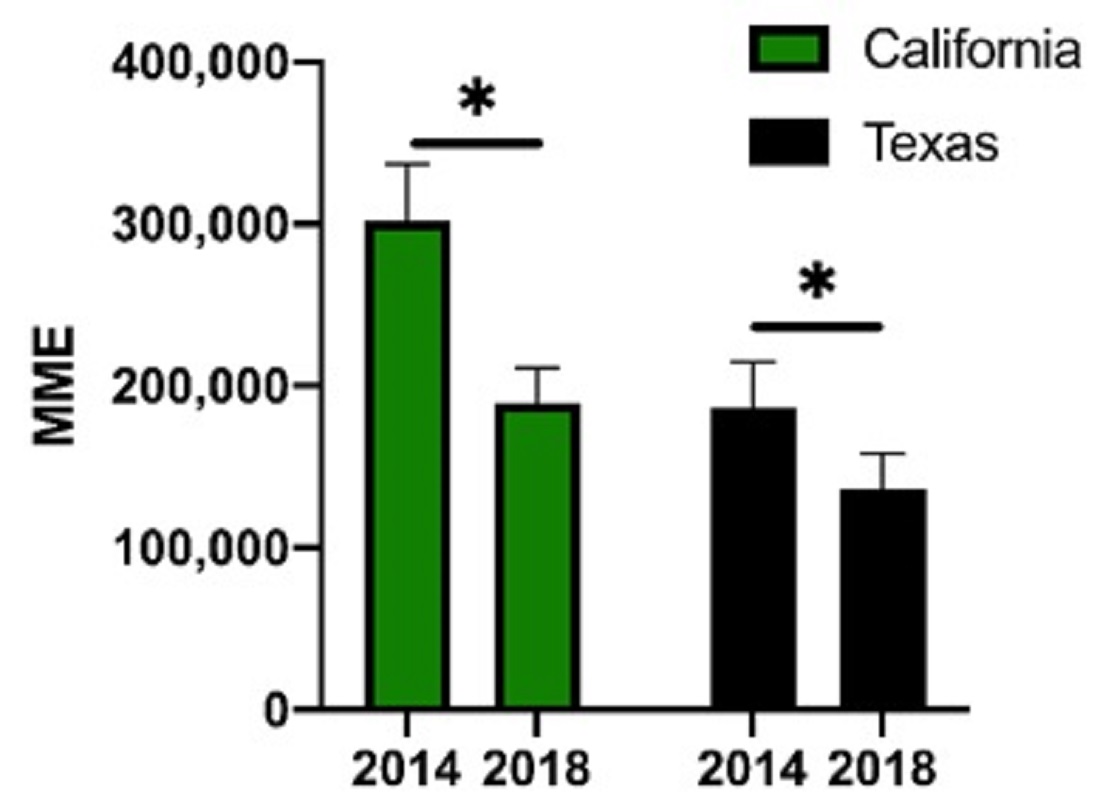
The US opioid overdose epidemic has risen to an all-time high. Prescription opioids often serve as a gateway to illicit opioids which have appreciable overdose potential. Recent investigations have highlighted the efficacy and safety of marijuana-based products for pain management. Providing alternative pain treatment options may help mitigate the opioid epidemic. The distribution of codeine, fentanyl, hydrocodone, morphine, and oxycodone per 100K people and by 3-digit zip codes and overdose rates from 2014 to 2018 in California, which legalized recreational marijuana in 2016, were compared to Texas, where marijuana is functionally prohibited. Drug weights were obtained from the Automation of Reports and Consolidated Orders System and converted to oral morphine milligram equivalents. Overdose data was retrieved from the Centers for Disease Control’s WONDER database. California (-43.7%) and Texas (-27.3%) showed significant reductions in cumulative opioid distribution from 2014 to 2018. Opioid distribution per 100K people decreased -38.9% in California relative to -26.4% in Texas. Opioid and heroin overdoses increased between 1999 and 2019 by +11.6% in California but +272.7% in Texas. This evidence supports marijuana legalization as a mitigating factor to the opioid epidemic and opioid misuse.