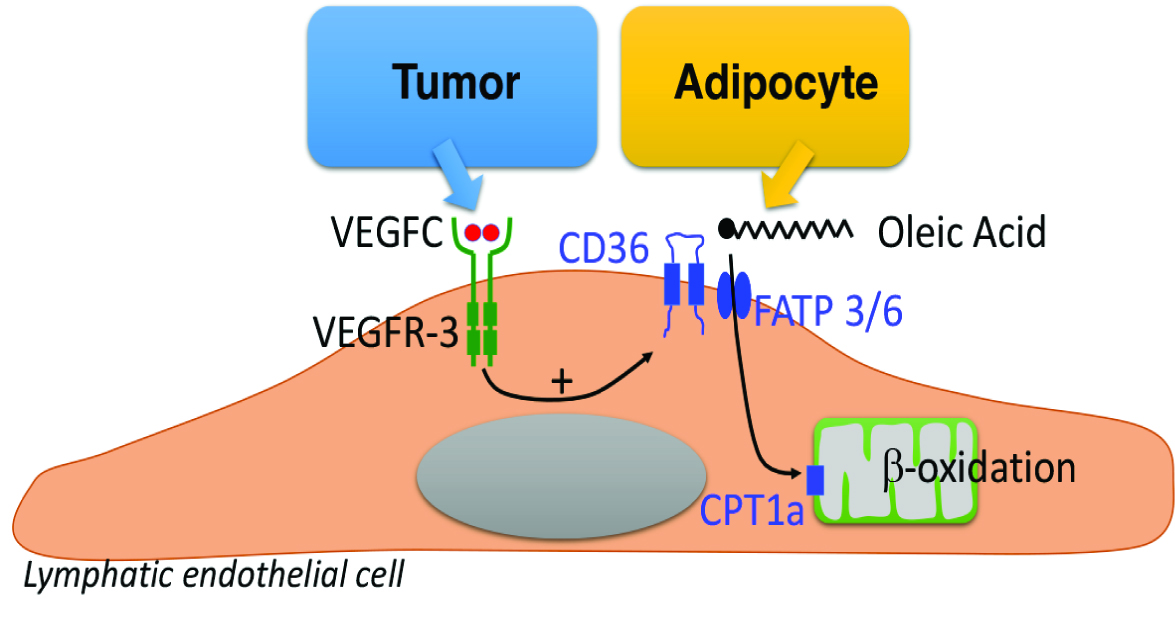
In cancer, the lymphatic system is hijacked by tumor cells to escape from primary tumor and to metastasize to the sentinel lymph nodes. Tumor lymphangiogenesis is stimulated by the vascular endothelial growth factors-C (VEGFC) after binding to its receptor VEGFR-3. However, how VEGFC cooperates with other molecules to promote lymphatic neovessels growth is not fully determined. Here, we found that tumor lymphangiogenesis developed in tumoral lesions and in their surrounding adipose tissue (AT). Interestingly, lymphatic vessel density correlated with an increase of circulating free fatty acids (FFA) in the lymph from tumor-bearing mice. We found that adipocyte-released FFA are uploaded by lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC) to stimulate their sprouting. Lipidomic analysis identified the monounsaturated oleic acid (OA) as the major circulating FFA in the lymph in tumoral context. OA transporters FATP-3, -6 and CD36 were only upregulated on LEC in the presence of VEGFC showing a collaborative effect of these molecules. OA released from adipocytes is taken up by LECs to stimulate the fatty acid β-oxidation, leading to increase adipose tissue lymphangiogenesis. Our results provide new insights on the dialogue between tumors and adipocytes via the lymphatic system and identify a key role for adipocyte-derived FFA in the promotion of lymphangiogenesis, revealing novel therapeutic opportunities for inhibitors of lymphangiogenesis in cancer.