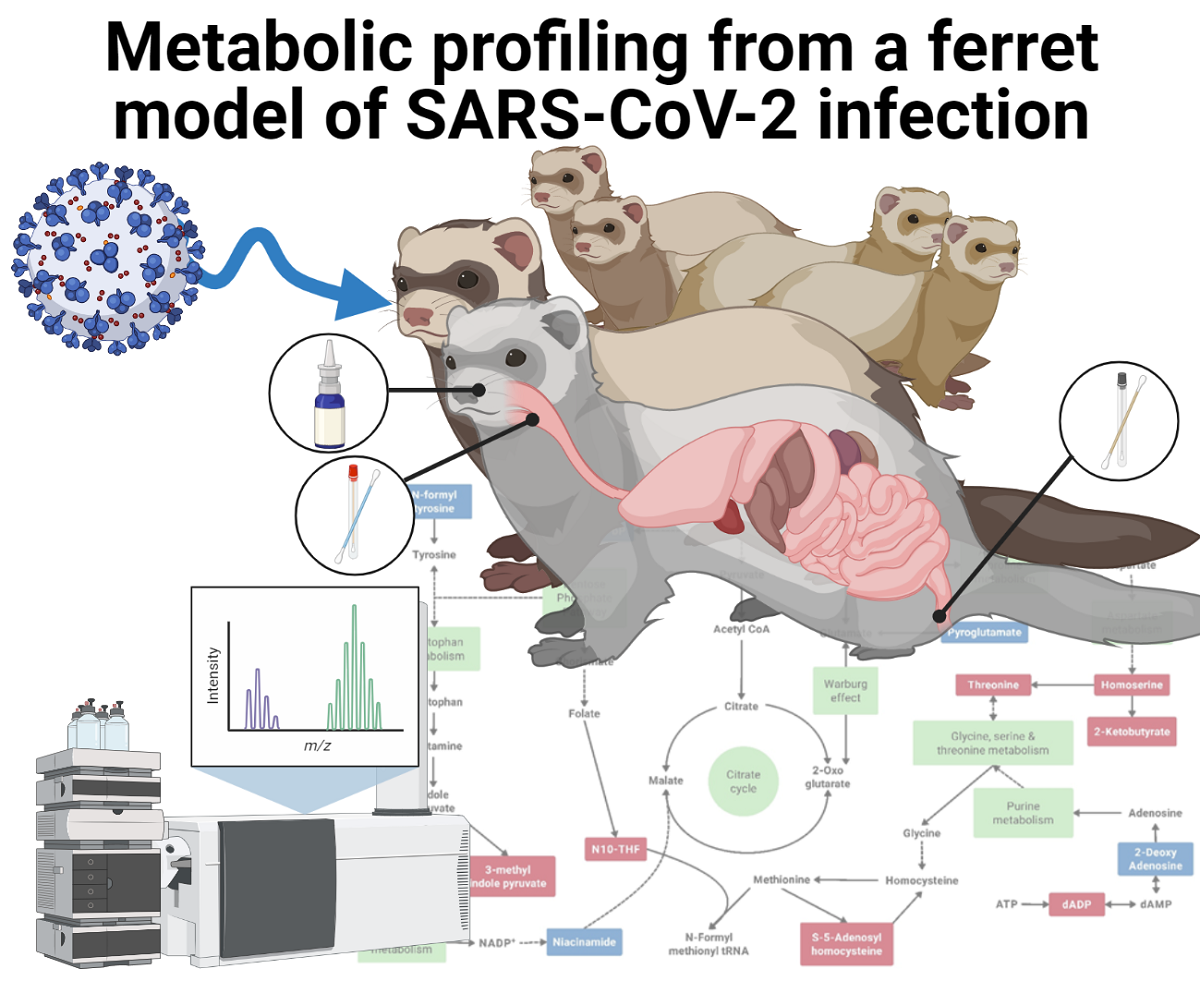
COVID-19 is a contagious respiratory disease that is causing significant global morbidity and mortality. Understanding the impact of a SARS-CoV-2 infection on the host metabolism is still in its infancy but of great importance. Herein, we investigated the metabolic response during viral shedding and post-shedding in an asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 ferret model (n=6) challenged with two SARS-CoV-2 isolates. Virological and metabolic analyses were performed on (minimally invasive) collected oral swabs, rectal swabs, and nasal washes. Fragments of SARS-CoV-2 RNA were only found in the nasal wash samples in four of the six ferrets, and in the samples collected 3 to 9 days post-infection (referred to as viral shedding). Central carbon metabolism metabolites were analyzed during viral shedding and post-shedding periods using a dynamic MRM (dMRM) database and method. Subsequent untargeted metabolomics and lipidomics of the same samples were performed using an LC-QToF-MS methodology, building upon the identified differentiated central carbon metabolism metabolites. Multivariate analysis of the acquired data identified 29 significant metabolites and three lipids that were subjected to pathway enrichment and impact analysis. The presence of viral shedding coincided with the challenge dose administered and significant changes in the citric acid cycle, purine metabolism, and pentose phosphate pathways, amongst others, in the host nasal wash samples. An elevated immune response in the host was also observed between the two isolates studied. These results support other reported metabolomic-based findings found in clinical observational studies and indicate the utility of metabolomics applied to ferrets for further COVID-19 research that advances early diagnosis of asymptomatic and mild clinical COVID-19 infections, in addition to assessing the effectiveness of new or re-purposed drug therapies.