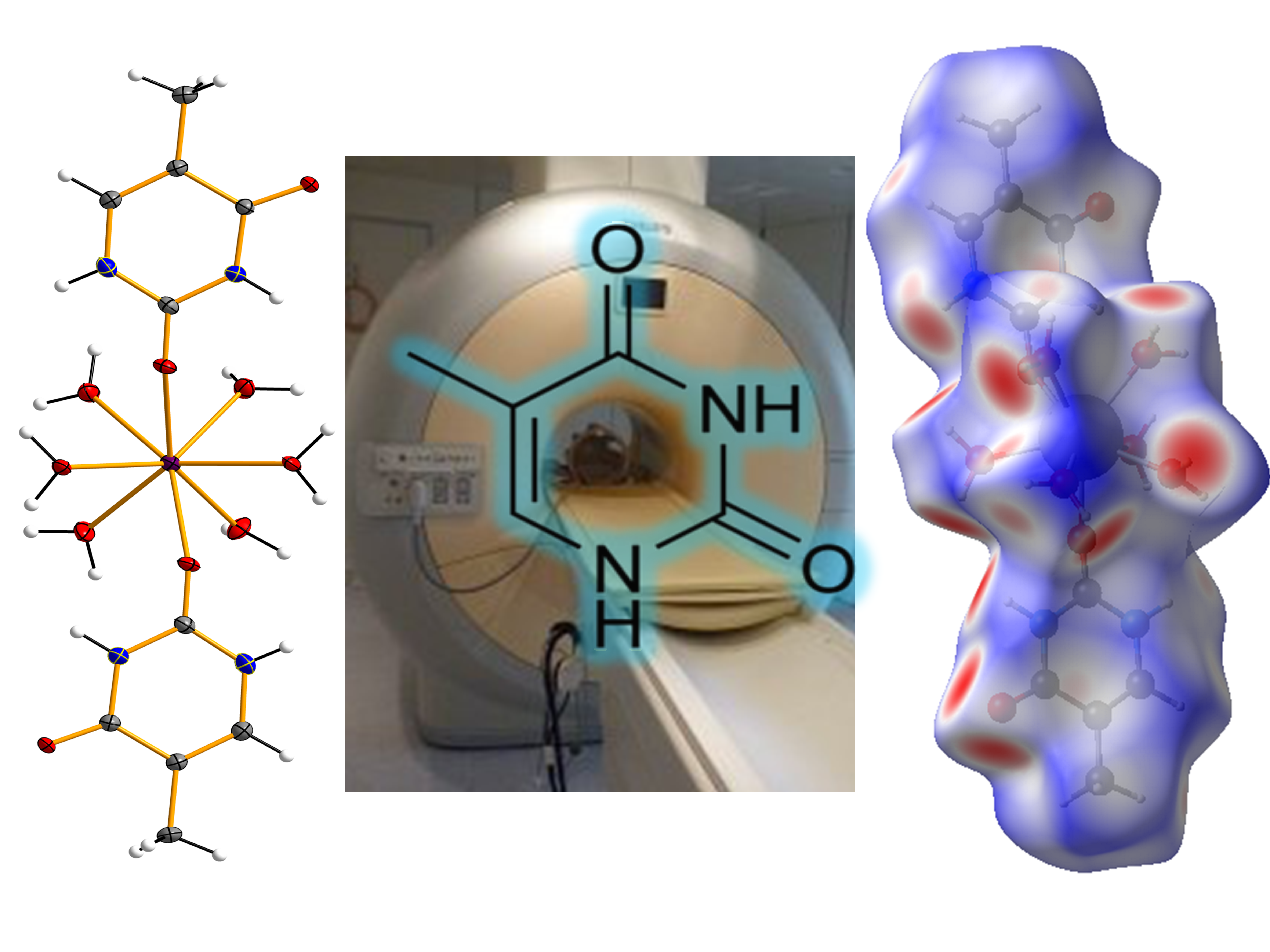
The paramagnetic gadolinium(III) ion is used as contrast agent in magnetic resonance (MR) imaging to improve the lesion detection and characterization. It generates a signal by changing the relaxivity of protons from associated water molecules and creates a clearer physical distinction between the molecule and the surrounding tissues. New gadolinium-based contrast agents displaying larger relaxivity values and specifically targeted might provide higher resolution and better functional images. We have synthesized the gadolinium(III) complex of formula [Gd(thy)2(H2O)6](ClO4)3·2H2O (1) [thy = 5-methyl-1H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione or thymine], which is the first reported compound based on gadolinium and thymine nucleobase. 1 has been characterized through vis-IR, SEM-EDAX and single-crystal X-ray diffraction techniques, and its magnetic and relaxometric properties have been investigated by means of SQUID magnetometer and MR imaging phantom studies, respectively. On the basis of its high relaxivity values, this gadolinium(III) complex can be considered a suitable candidate for contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.