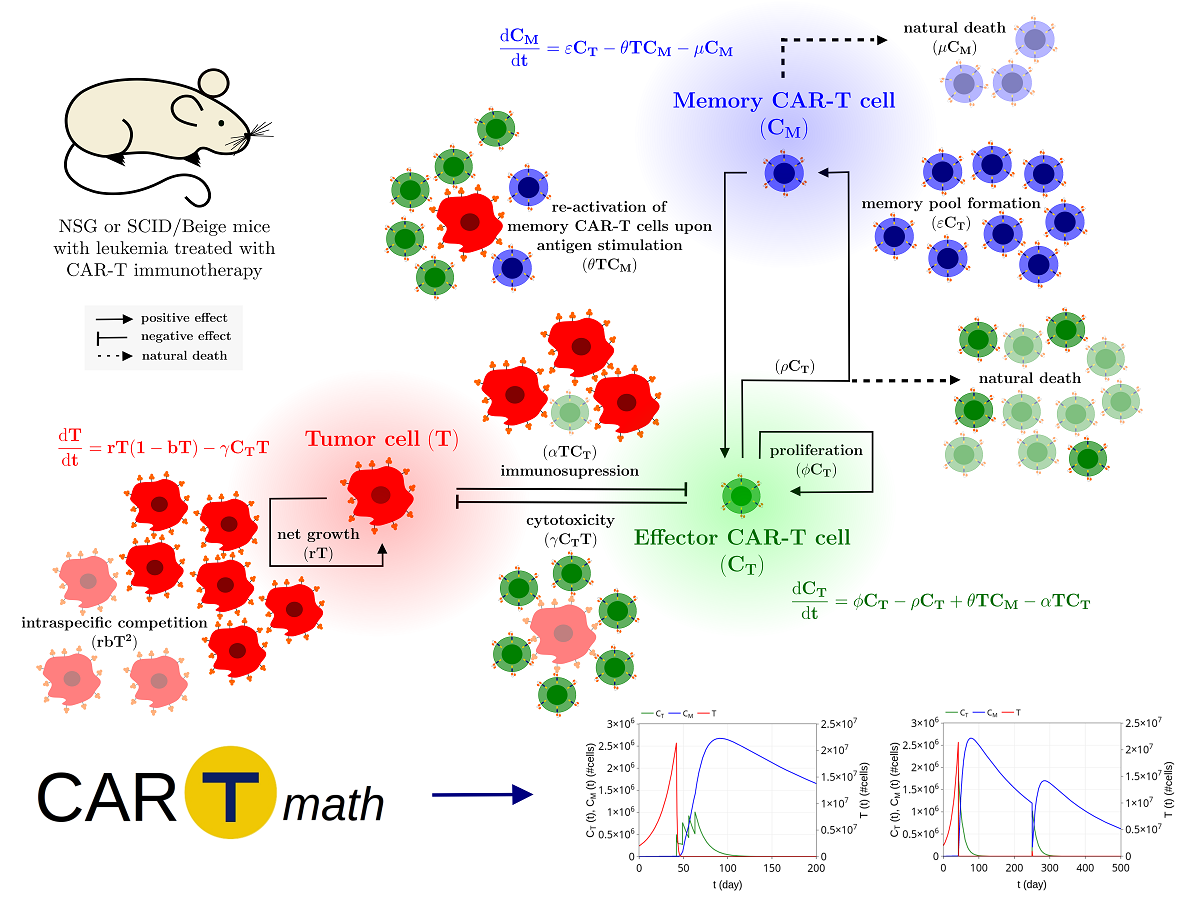
Immunotherapy has gained great momentum with chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy, in which patient’s T lymphocytes are genetically manipulated to recognize tumor-specific antigens increasing tumor elimination efficiency. In the last years, CAR-T cell immunotherapy for hematological malignancies achieved a great response rate on patients and is a very promising therapy for several other malignancies. Each new CAR design requires a preclinical proof-of-concept experiment using immunodeficient mouse models. The absence of a functional immune system in these mice makes them simple and suitable to be mathematically modeled. In this work, we developed a three population mathematical model to describe tumor response to CAR-T cell immunotherapy in immunodeficient mouse models, encompassing interactions between a non-solid tumor and CAR-T cells (effector and long-term memory). We account for several phenomena, such as tumor-induced immunosuppression, memory pool formation, and conversion of memory into effector CAR-T cells in the presence of new tumor cells. Individual donor and tumor specificities were considered as uncertainties in the model parameters. Our model is able to reproduce several CAR-T cell immunotherapy scenarios, with different CAR receptors and tumor targets reported in the literature. We found that therapy effectiveness mostly depends on some specific parameters such as the differentiation of effector to memory CAR-T cells, CAR-T cytotoxic capacity, tumor growth rate, and tumor-induced immunosuppression. In summary, our model can contribute to reduce and optimize the number of in vivo experiments with in silico tests to select specific scenarios that could be tested in experimental research. Such in silico laboratory was made available in a Shiny R-based platform called CARTmath. It is an open-source, easy to run simulator, available at github.com/tmglncc/CARTmath or directly on the webpage cartmath.lncc.br, containing this manuscript results as examples and documentation. The developed model, together with the CARTmath platform, provides potential use for assessing different CAR-T cell immunotherapy protocols and associated efficacy, becoming an accessory towards in silico trials.