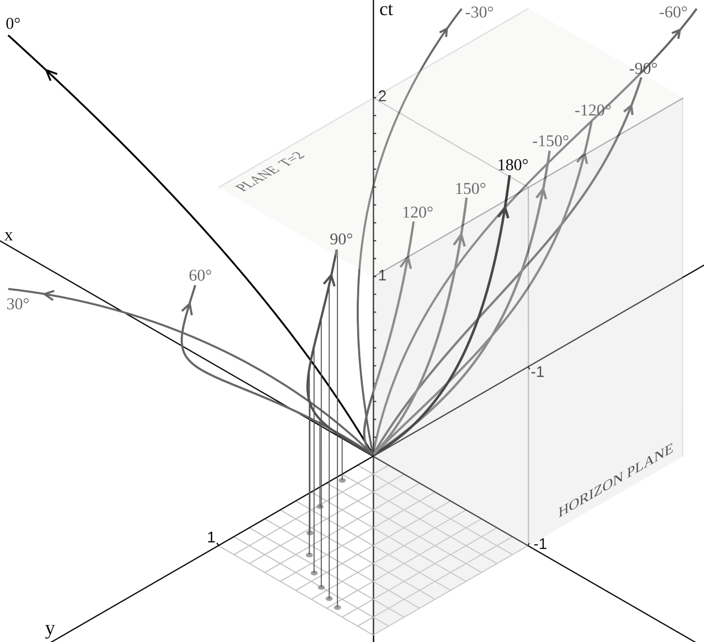
We all have in mind Einstein's famous thought experiment in the elevator where we observe the free fall of a body, and then the trajectory of a light ray. Simply here, in addition to the qualitative aspect, we carry out the exact calculation, and for the first time the worldlines equations are given. We consider a uniformly accelerated reference frame in rectilinear translation, and we show that the trajectories of the particles are semi-ellipses with the center on the event horizon. The frame of reference is non-inertial, the space-time is flat, and the computations are performed within the framework of special relativity. Some experimental consequences are discussed, especially the experiment with the accelerated Michelson-Morley interferometer is solved, and we described an experiment where a new relativistic paradox appears --- a particle of matter seems to go faster than light. The differences, compared to the classical case, are important at large scale and close to the horizon, but they are small in the lift where the interest is above all theoretical. The concepts of metric, coordinated velocity and horizon are discussed, and the analogy with the black hole is made.