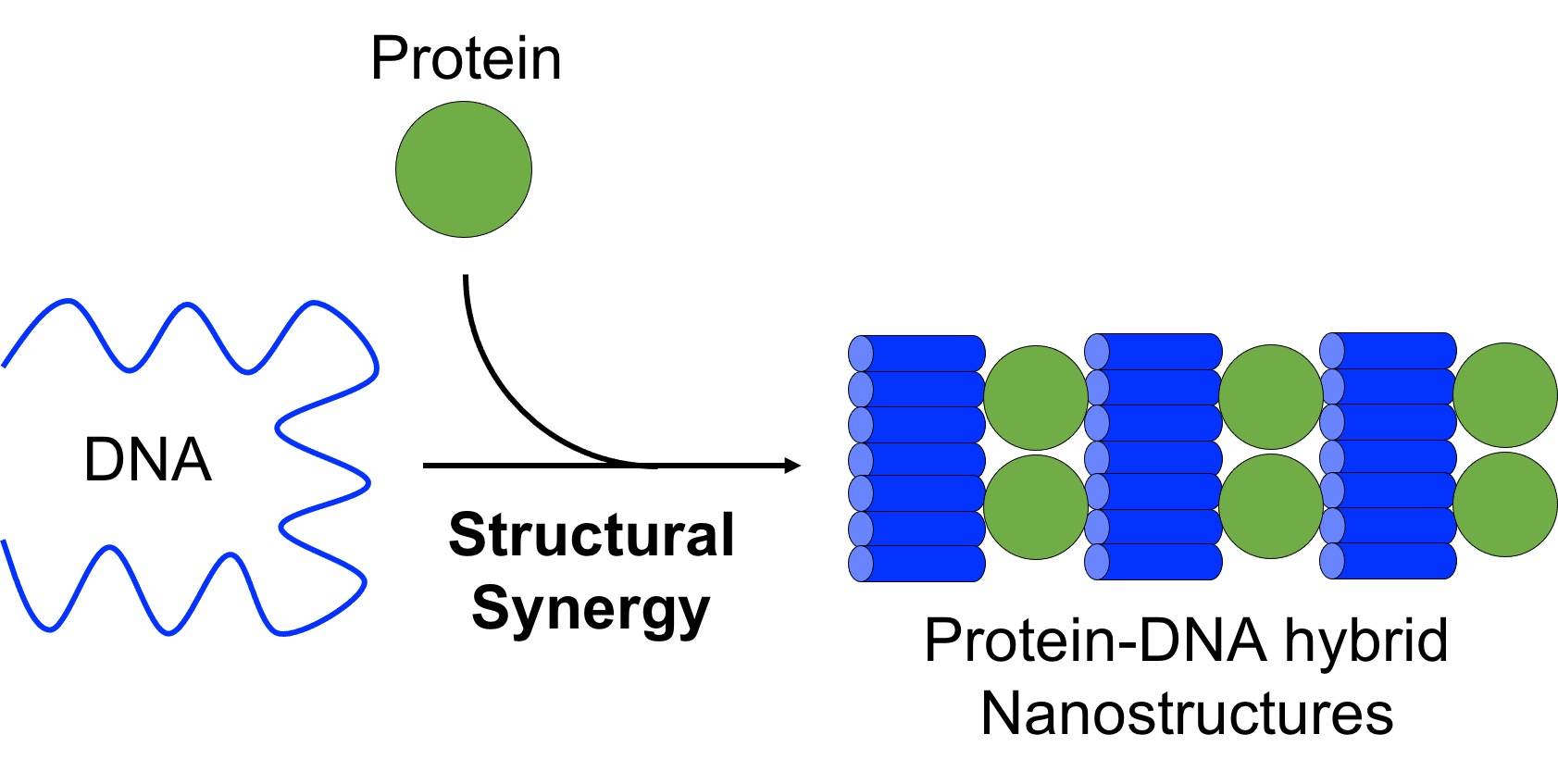
Proteins and DNA exhibit key physical chemical properties that make them advantageous for building nanostructures with outstanding features. Both DNA and protein nanotechnology have growth notably and proved to be fertile disciplines. The combination of both types of nanotechnologies is helpful to overcome the individual weaknesses and limitations of each one, paving the way for the continuing diversification of the structural nanotechnologies. Recent studies have implemented a synergistic combination of both biomolecules to assemble unique and sophisticate protein-DNA nanostructures. These hybrid nanostructures are highly programmable and display remarkable features that create new opportunities to build in the nanoscale. This review focuses on the strategies deployed to create hybrid protein-DNA nanostructures. Here, we will discuss strategies such as polymerization, spatial directing and organizing, coating, rigidizing or folding DNA into particular shapes or moving parts. The enrichment of structural DNA nanotechnology by incorporating protein nanotechnology has been clearly demonstrated and still shows a large potential to create useful and advanced materials with cell-like properties or dynamic systems. It can be expected that structural protein-DNA nanotechnology will open new avenues in the fabrication of nano-assemblies with unique functional applications and enrich the toolbox of bionanotechnology.