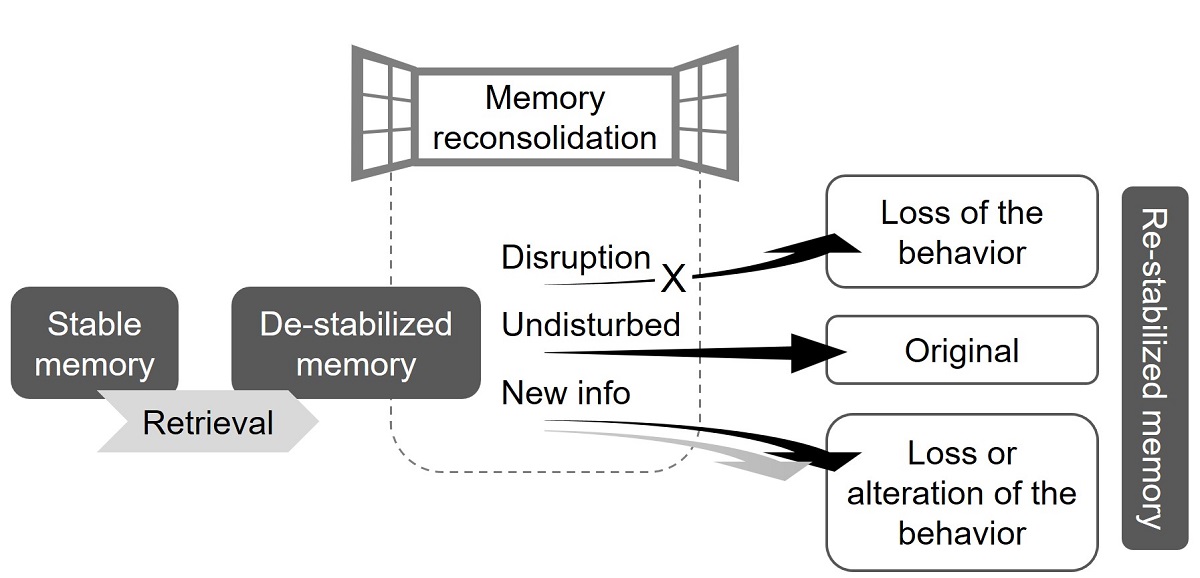
Alcohol and nicotine are widely-abused legal substances worldwide. Relapse to alcohol or tobacco seeking and consumption after abstinence is a major clinical challenge, and is often evoked by cue-induced craving. Therefore, disruption of the memory for the cue-drug association is expected to suppress relapse. Memories have been postulated to become labile shortly after their retrieval, during a “memory reconsolidation” process. Interference with the reconsolidation of drug-associated memories has been suggested as a possible strategy to reduce or even prevent cue-induced craving and relapse. Here, we surveyed the growing body of studies in animal models and in humans assessing the effectiveness of pharmacological or behavioral manipulations in reducing relapse by interfering with the reconsolidation of alcohol and nicotine/tobacco memories. Our review points to the potential of targeting the reconsolidation of these memories as a strategy to suppress relapse to alcohol drinking and tobacco smoking. However, we discuss several critical limitations and boundary conditions, which should be considered to improve the consistency and replicability in the field, and for development of an efficient reconsolidation-based relapse prevention therapy.