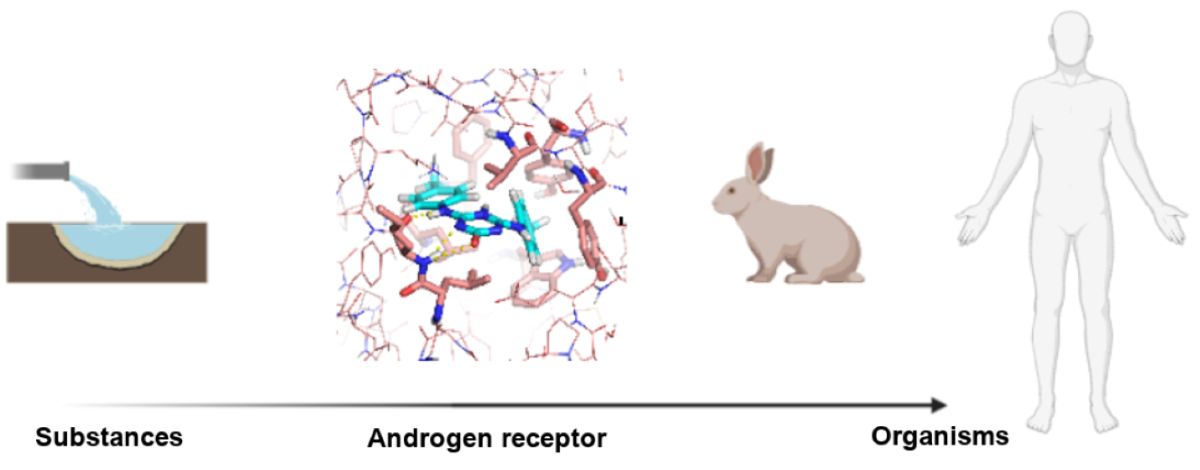
Substances that can modify the androgen receptor pathway in humans and animals are entering the environment and food chain with the proven ability to disrupt hormonal systems and leading to toxicity and adverse effects on reproduction, brain development, and prostate cancer, among others. State-of-the-art databases with experimental data of human, chimp, and rat effects by chemicals have been used to build machine learning classifiers and regressors and evaluate these on independent sets. Different featurizations, algorithms, and protein structures lead to different results, with deep neural networks on user-defined physicochemically-relevant features developed for this work outperform graph convolutional, random forest, and large featurizations. The results can help provide clues on risk of substances and better experimental design for toxicity assays. Source code and data are available at https://github.com/AlfonsoTGarcia-Sosa/ML