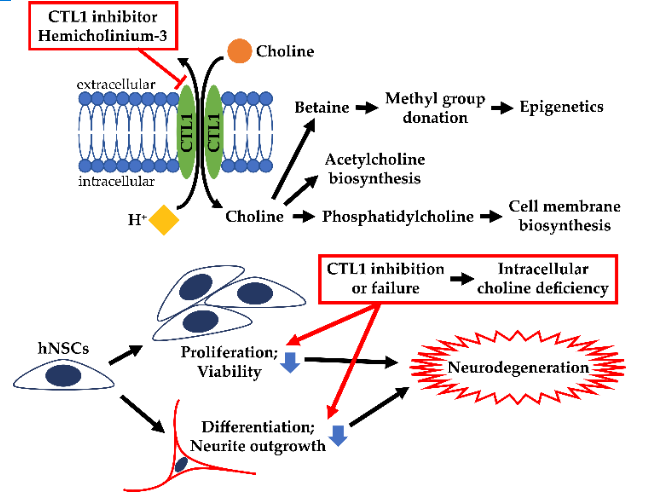
Choline and choline metabolites are essential for all cellular functions. They have also been reported to be crucial for neural development. In this work, we studied the functional characteristics of the choline uptake system in human neural stem cells (hNSCs). Additionally, we investigated the effect of extracellular choline uptake inhibition on the cellular activities in hNSCs. We found that the mRNAs and proteins of choline transporter-like protein 1 (CTL1) and CTL2 were expressed at high levels. Immunostaining showed that CTL1 and CTL2 were localized in the cell membrane and partly in the mitochondria, respectively. The uptake of extracellular choline was saturable and performed by a single uptake mechanism, which was Na+-independent and pH-dependent. We conclude that CTL1 is responsible for extracellular choline uptake, and CTL2 may uptake choline in the mitochondria and be involved in DNA methylation via choline oxidation. Extracellular choline uptake inhibition caused intracellular choline deficiency in hNSCs, which suppressed cell proliferation, cell viability, and neurite outgrowth. Our findings contribute to the understanding of the role of choline in neural development as well as the pathogenesis of various neurological diseases caused by choline deficiency or choline uptake impairment.