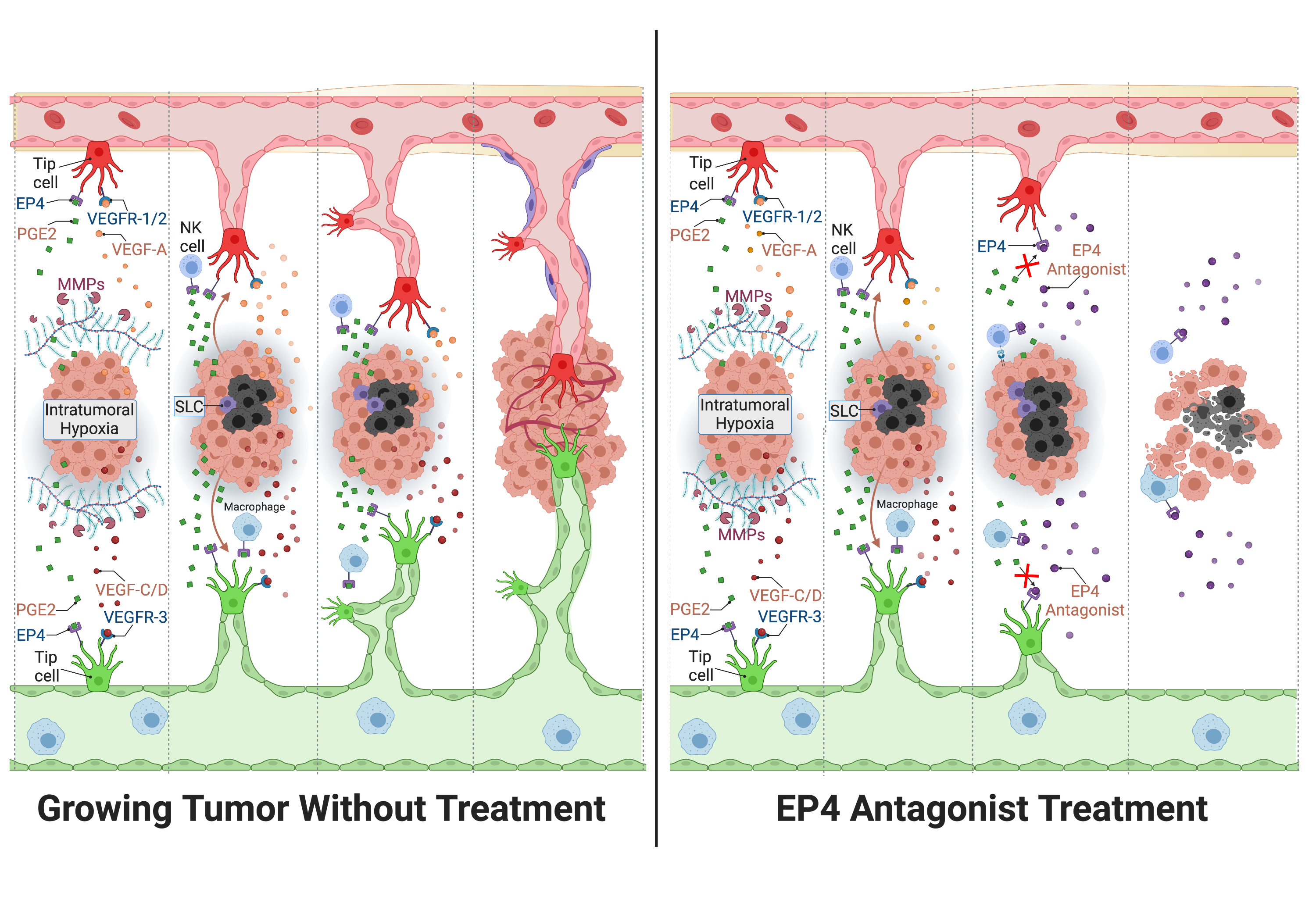
Formation of new blood (angiogenesis) and lymphatic (lymphangiogenesis) vessels are major events associated with most epithelial malignancies, including breast cancer. Angiogenesis is essential for cancer cell survival. Lymphangiogenesis is critical in maintaining tumoral interstitial fluid balance and importing tumor-facilitatory immune cells. Both vascular routes also serve as conduits for cancer metastasis. Intratumoral hypoxia promotes both events by stimulating multiple angiogenic/lymphangiogenic growth factors. Studies on tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis and its exploitation for therapy have received less attention from the research community than those on angiogenesis. Inflammation is a key mediator of both processes, hijacked by many cancers by aberrant expression of the inflammation-associated enzyme cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-2. In this review, we focus on breast cancer and show that COX-2 is a major promoter of both events, primarily resulting from the activation of Prostaglandin (PG) E receptor EP4 on tumor cells, tumor-infiltrating immune cells, and endothelial cells; and induction of oncogenic microRNAs. COX-2/EP4 pathway also promotes additional events in breast cancer progression, such as cancer cell migration, invasion, and stimulation of stem–like cells. Based on a combination of studies using multiple breast cancer models, we show that EP4 antagonists hold a major promise in breast cancer therapy in combination with other modalities including immune check-point inhibitors