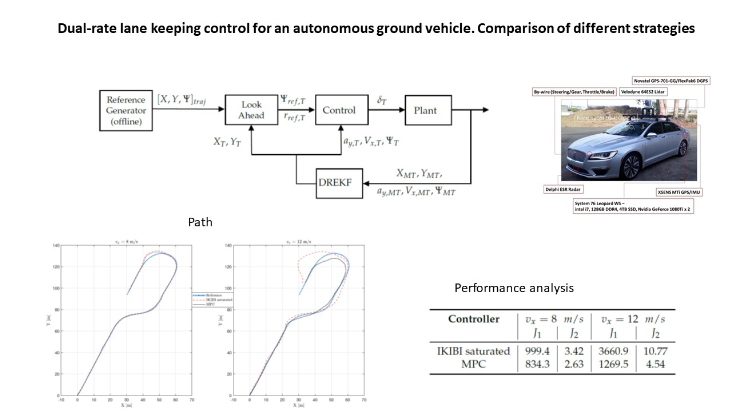
In this contribution, different lane-keeping control strategies for Autonomous Ground Vehicles (AGV) have been analyzed and compared. The AGV must be oriented and kept within a given reference path using the front wheel steering angle as the control action for a specific longitudinal velocity. While non-linear models can describe the lateral dynamics of the vehicle in an accurate manner, they might lead to difficulties when computing some real-time control laws such as Model Predictive Control (MPC). Linear Parameter Varying (LPV) models can provide a trade-off between computational complexity and model accuracy. Another way to reduce computational complexity is to explore other control strategies, for example, the one based on the Inverse Kinematic Bicycle model (IKIBI). Additionally, AGV sensors typically work at different measurement acquisition frequencies so that Kalman Filters (KF) are usually needed for sensor fusion. If these frequencies are slower than the actuation rate, a multi-rate KF may be needed. The two control strategies (MPC using a LPV model and IKIBI) have been compared in simulations over a circuit path in the presence of process and measurement Gaussian noise. The MPC controller has shown to provide a more accurate lane-keeping behavior than an IKIBI control strategy. Finally, it has been seen that Dual-Rate Extended Kalman Filters (DREKF) constitute an essential tool when only slow and noisy sensor feedback is available in an AGV lane-keeping application.