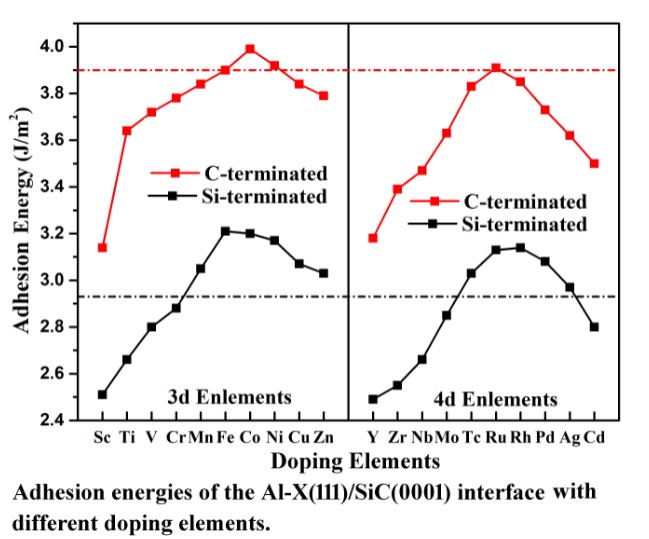
In this work, effects of 20 transition element additives on the interfacial adhesion energy and electronic structure of Al (111)/6H-SiC (0001) interfaces have been studied by first principles method. For clean Al (111)/6H–SiC (0001) interfaces, both Si-terminated and C-terminated interfaces have covalent bond characteristics. The C-terminated interface has stronger binding energy, which is mainly due to the stronger covalent bond formed by the larger charge transfer between C and Al. The results show that the introduction of many transition elements, such as 3d transitional group Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn and 4d transitional group Tc, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, can improve the interfacial adhesion energy of the Si-terminated Al (111)/6H-SiC (0001) interface. However, for the C-terminated Al (111)/6H-SiC (0001) interface, only the addition of Co element can improve the interfacial adhesion energy. Bader charge analysis shows that the increase of interfacial binding energy is mainly attributed to more charge transfer.