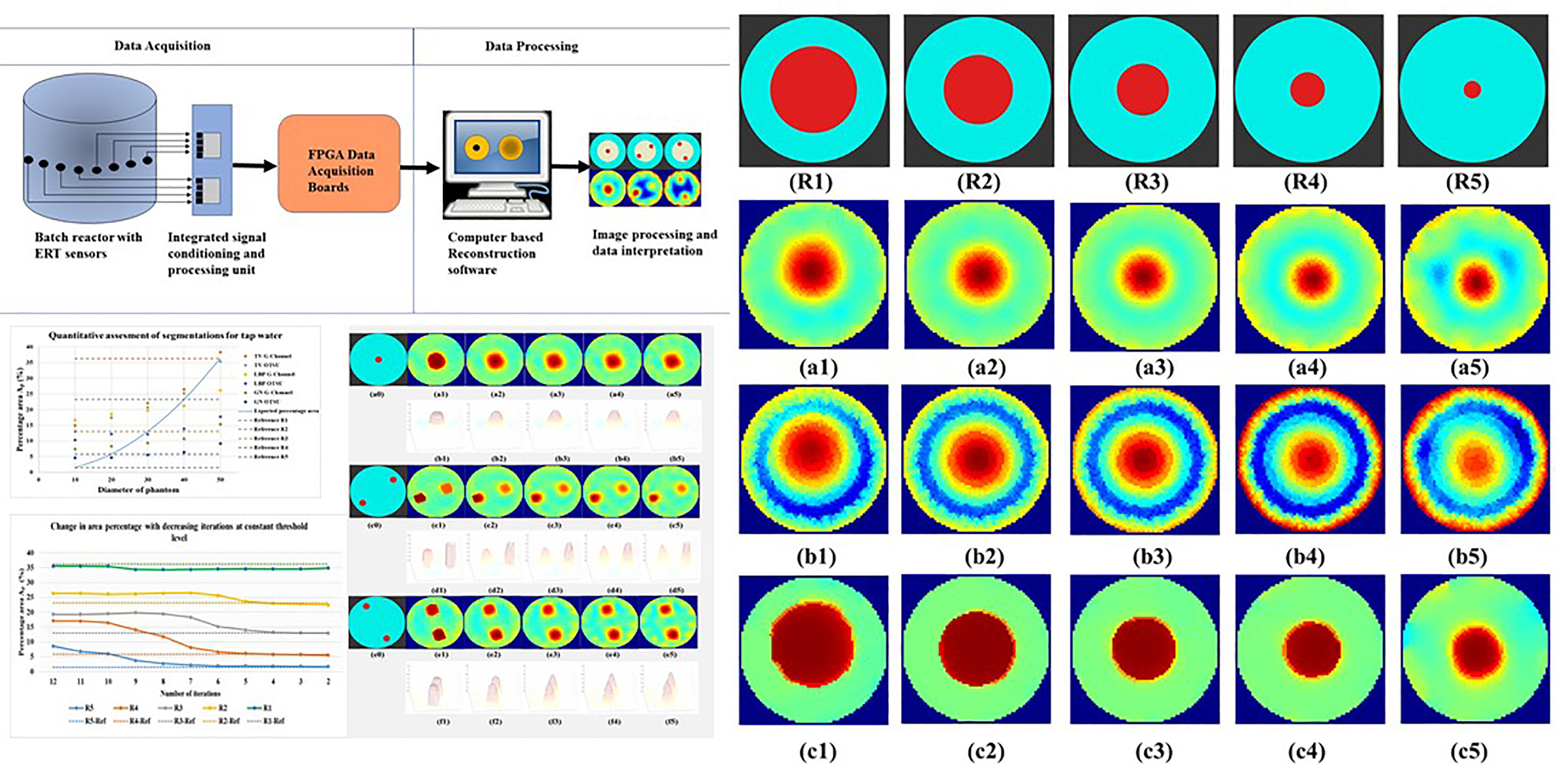
Crystallization is a significant procedure in the manufacturing of many pharmaceutical and solid food products. In-situ Electrical Resistance Tomography (ERT) is a novel Process Analytical Tool (PAT) to provide a cheap and quick way to test, visualize, and evaluate the progress of crystallization processes. In this work, the spatial accuracy of the non-conductive phantoms in low conductivity solutions was evaluated. Gauss-Newton, Linear Back Projection, and iterative Total Variation reconstruction algorithms were used to compare the phantom reconstructions for tap water, industrial-grade saturated sucrose solution, and demineralized water. Cylindrical phantom measuring 10 mm in diameter and a cross-section area of 1.5 % of the total beaker area was detected at the center of the beaker. Two phantoms with a 10 mm diameter were visualized separately in non-central locations. The quantitative evaluations were done for the phantoms with radii ranging from 10 mm to 50 mm in demineralized water. Multiple factors such as ERT device and sensor development, FEM mesh density and simulations, image reconstruction algorithms, number of iterations, segmentation methods, and morphological image processing methods were discussed and analyzed to achieve spatial accuracy. The development of ERT imaging modality for the purpose of monitoring crystallization in low conductivity solutions was performed satisfactorily.