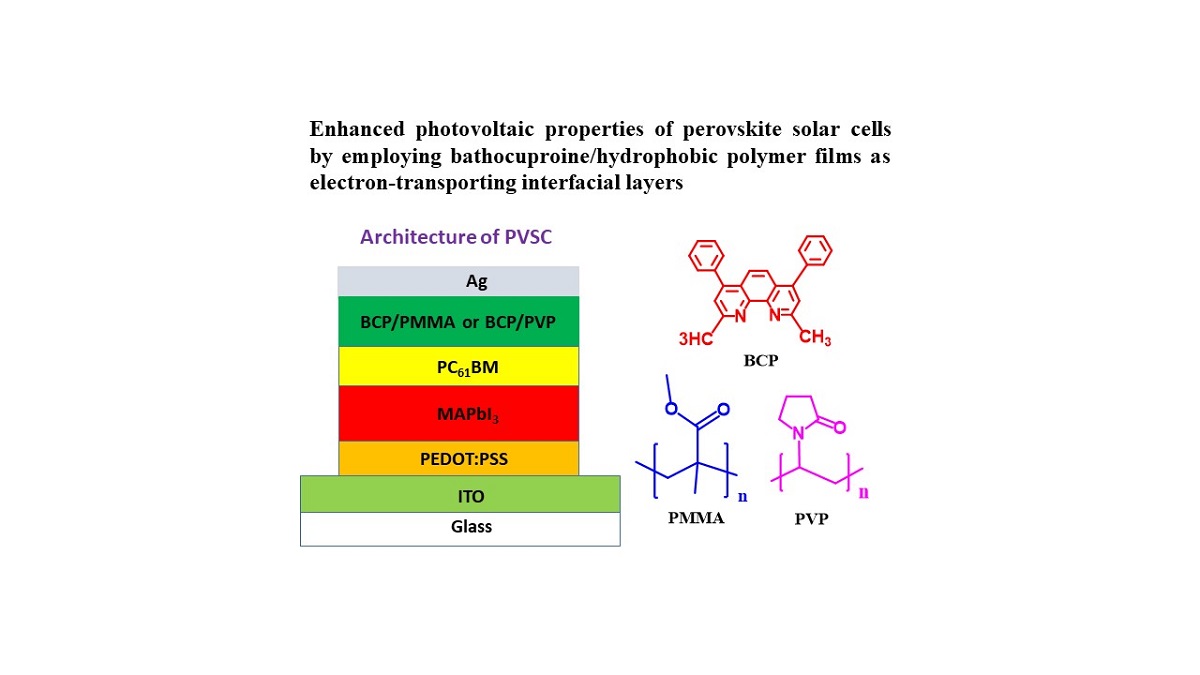
In this study, we improved the photovoltaic (PV) properties and storage stabilities of inverted perovskite solar cells (PVSCs) based on methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3) by employing bathocuproine (BCP)/poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) and BCP/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as hole-blocking and electron-transporting interfacial layers. The architecture of the PVSCs was indium tin oxide/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrenesulfonate/MAPbI3/[6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester/BCP:PMMA or BCP:PVP/Ag. The presence of PMMA and PVP affected the morphological stability of the BCP and MAPbI3 layers. The storage-stability of the BCP/PMMA-based PVSCs was enhanced significantly relative to that of the corresponding unmodified BCP-based PVSC. Moreover, the PV performance of the BCP/PVP-based PVSCs was enhanced when compared with that of the unmodified BCP-based PVSC. Thus, incorporating hydrophobic polymers into BCP-based hole-blocking/electron-transporting interfacial layers can improve the PV performance and storage stability of PVSCs.